* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Visual Testing
Self-assembled monolayer wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Energy applications of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Low-energy electron diffraction wikipedia , lookup
Tunable metamaterial wikipedia , lookup
Surface tension wikipedia , lookup
Ultrahydrophobicity wikipedia , lookup
Sessile drop technique wikipedia , lookup
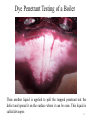
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Non-Destructive testing is the use of noninvasive techniques to determine the integrity of a material, component or structure or quantitatively measure some characteristics of an object. It is the testing of materials, for surface or internal flaws or metallurgical condition, without interfering in any way with the integrity of the material or its suitability for service. i.e. Inspect or measure without doing harm. 1 Importance of NDT 1. NDT increases the safety and reliability of the product during operation. 2. It decreases the cost of the product by reducing scrap and conserving materials, labor and energy. 3. It enhances the reputation of the manufacturer as a producer of quality goods. All of the above factors boost the sales of the product which bring more economical benefits for the manufacturer. 4. NDT is also used widely for routine or periodic determination of quality of the plants and structures during service. 5. This not only increases the safety of operation but also eliminates any forced shut down of the plants. 2 Methods of NDT Visual 3 Six Most Common NDT Methods 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Visual Testing (VT) Dye Penetrant Testing (DPT) Magnetic Particle Testing (MPT) Ultrasonic Testing (UT) Eddy Current Testing (ECT) Radiography Testing (RT) 4 Visual Testing Visual testing is the most basic and common inspection method involves in using of human eyes to look for defects. But now it is done by the use special tools such as video scopes, magnifying glasses, mirrors, or borescopes to gain access and more closely inspect the subject area. Visual Testing Equipments: •Mirrors (especially small, angled mirrors), •Magnifying glasses, •Microscopes (optical and electron), •Borescopes and fiber optic borescopes, •Closed circuit television (CCTV) systems, •Videoscope. 5 • Cheapest and simplest technique in detecting surface flaws • Good light is essential and usually some form of magnification is used. • A disadvantage is that even with magnification of up to 5 times some surface flaws may not be noticed. Visual Testing Equipments Fig: Videoscope Fig: Advanced Videoscope Fig. Microscope Fig: Borescopes Fig: Magnifying glass 7 Dye Penetrant Testing This method is commonly used for detect the surface cracks or defects. Dye penetrant Testing (DPT) is one of the most widely used nondestructive Testing (NDT) methods. DPT can be used to inspect almost any material provided that its surface is not extremely rough. 8 Dye Penetrant Testing Process Three liquids are used in this method. 1. Cleaner 2. Penetrant 3. Developer 9 Dye Penetrant Testing of a Boiler At first the surface of the material that is to be tested is cleaned by a liquid. The liquid is called cleaner. 10 Dye Penetrant Testing of a Boiler Then a liquid with high surface wetting characteristics is applied to the surface of the part and allowed time to seep into surface breaking defects. This liquid is called penetrant. After five or ten minutes the excess penetrant is removed from the surface. 11 Dye Penetrant Testing of a Boiler Then another liquid is applied to pull the trapped penetrant out the defect and spread it on the surface where it can be seen. This liquid is called deveoper. 12 Findings After Dye Penetrant Testing there are two surface cracks are Detected. Two surface cracks 13 Advantages of Dye Penetrant Testing This method has high sensitivity to small surface discontinuities. Large areas and large volumes of parts/materials can be inspected rapidly and at low cost. Indications are produced directly on the surface of the part and constitute a visual representation of the flaw. Aerosol spray can make penetrant materials very portable. Penetrant materials and associated equipments are relatively inexpensive. 14 Limitations of Dye Penetrant Testing Only surface breaking defects can be detected. Precleaning is critical since contaminants can mask defects. The inspector must have direct access to the surface being inspected. Surface finish and roughness can affect inspection sensitivity. Post cleaning of acceptable parts or materials is required. Chemical handling and proper disposal is required. 15