* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IFA - Sheldon ISD
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
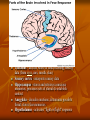
IFA Reflect on a time when you have been stressed. What were your emotions and how did you handle them. Student Assignment Your assignment is a term paper worth 400 points. It will be the major part of your grade this term. You are to study the dating and marriage practices of a foreign country and compare them to those practiced in Texas. Write a double spaced, typed research paper, 12-15 pages long. APA style is mandatory Use a minimum of eight resources, two of which must be personal interviews of people who have lived in the country on which you are reporting. Refer to special reference books which have been put on reserve at the library. Stress and Coping What is stress? A subjective feeling in response to stressors that are perceived as frustrating or threatening. The stressor is the activity, emotion, or responsibility which is placing a demand upon you and causing stress How do you cope with stress? Using coping strategies and defense mechanism The way in which we deal with stress will make our lives pleasant and comfortable or leave us stressed and incapable of performing our obligations to the best of our abilities Emotions What are emotions? Feelings that involve physical and psychological responses “fight or flight”-physical response to emotions related to challenge or threat Prepare body for aggression (fight) Prepare body to escape perceived danger (flight) Learning to control emotions-a major task Children learn to repress unacceptable emotions Types of Emotions Anxiety Fear Anger Aggression Anxiety Vague unpleasant feeling that produces physical sensations Result: tension and increased heart rate Often can not identify reason for emotional distress Fear Distressing negative sensation induced by a perceived threat Result of a specific, identifiable cause Physiological reactions similar to anxiety Thalamus - decides where to send incoming sensory data (from eyes, ears, mouth, skin) Sensory cortex - interprets sensory data Hippocampus - stores and retrieves conscious memories; processes sets of stimuli to establish context Amygdala - decodes emotions; determines possible threat; stores fear memories Hypothalamus - activates "fight or flight" response Anger a strong feeling of displeasure and belligerence aroused by a wrong Inborn and instinctive Emotional reaction to a loss Aggression a hostile or destructive mental attitude or behaviour Combination of frustration, hate, rage Student Activity Watch the video about the effects of stress on the body and answer the questions. IFA Reproduce the graph for “Fight or Flight” response THINK-OGRAM Your check is in the mail Stay on track SOLUTIONS Eggs over Easy Be on Time Forgive and Forget Microscope Perceptions of Control “In control” “powerlessness” “hopelessness” Spiritual Distress “In control” Perception that one has choices and is able to create a change in physiological state or current life circumstances “Powerlessness” Perception that one’s actions cannot effect change in outcome long-term feeling of powerlessness lead to feeling of physical and mental fatigue which can ultimately lead to depression “Hopelessness” Perception that one’s need have no potential to be met Long-term feeling of hoplessness often leads to depression Spiritual Distress Questions: The meaning of one’s life Meaning of suffering and pain The value of living Prolonged distress leads to depression A short-term spiritual distress is a type of personal introspection that promotes personal growth and development Coping with Stress Coping Refers to how the mind reacts to stress Coping mechanisms Vary from person to person Event that stresses one person, might not stress another Conscious behavior usually based on success of previous coping experiences Defense Mechanisms Compensation Denial Displacement Intellectualization Minimization Projection Rationalization Reaction formation Regression Repression Compensation Covering up weakness by emphasizing a more desirable trait or by overachievement in a more comfortable area Purpose: Allows person to overcome weakness and achieve success Ex: high school student too small to play football become star tennis player Denial An attempt to ignore unacceptable realities by refusing to acknowledge them Purpose: temporarily isolates person from full impact of a traumatic situation Ex: a mother, though told her daughter has terminal cancer, continues to plan for her daughter’s college entrance Displacement Transferring emotional reactions from one subject or person to another person Purpose: Allows feelings to be expressed through to a less meaningful Ex: a boyfriend and girlfriend are arguing, and he gets so angry that he slams his fist into the wall Intellectualization Emotional response that would normally accompany a painful (or uncomfortable) incident is avoided by use of academic or intellectual explanations that remove personal feelings from the incident Purpose: protects person from emotional reality of loss Ex: pain over best friend’s sudden is reduced by saying, “He wouldn’t have wanted to live disabled” Minimization Not acknowledging the significance of one’s behavior Purpose: Allows a person to decrease and trivialize responsibility for behavior Ex: A teenager says, “Dont believe everything my kid brother tell you. I wasn’t so drunk I couldn’t drive.” Student Activity Identify the correct Defense mechanism associated with the explanation Projection Projects shortcomings or feeling on others Purpose: Allows person to deny existence of shortcoming Ex: A disgruntled college freshman when called to meet with her advisor believes that she’s called in because the advisor doesn’t like her Rationalization Justification of certain behaviors by faulty logic and attribution of socially acceptable motive that dod not in fact inspire the behaviors Purpose: helps person cope with inability to acknowledge inappropriate behavior Ex: A student cheats on a n exam but blames the teacher for not making the material more understandable Reaction formation Individual acts exactly opposite to the way he/she feels Purpose: form of repression that allows feelings to be acted on in a more acceptable way Ex: teenager has bitterness towards girls who beat her out of her cheerleading position, but acts very sweet and friendly when they see each other Regression Resorting to an earlier stage of life that is generally less demanding and responsible Purpose: allows person to return to point in development when nurturing and dependency were acceptable Ex: a adult throws a temper tantrum when he cant have his own way Repression An unconscious mechanism by which threatening thoughts, feelings, and desires are kept from becoming conscious Purpose: protects person from traumatic experience until he/she has resources to cope Ex: child who was verbally abused by her alcoholic mother cannot remember certain events during her childhood Types of behavior Maladaptive behvaior- result of ineffective coping Psychotic behavior-most severe manifestation of ineffective coping Caused by psychosis State cause by lack of contact with reality Mind consciously use many defense mechanisms to deny, destroy, and avoid reality when it can consciously cope and solve problems