* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Single Phase Motors
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Dynamometer wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Presentation of
ELECTRIC MACHINES
Title: Single Phase Motors
By: Rahul Khanna{130800111008}EC3rd Sem
Guided By: Prof. Ravi Patel
AC Motor:::
• An AC motor is an electric motor driven by an alternating current (AC).
Types of AC Motor::: [depending on the type of rotor used]
o The first type is the induction motor or asynchronous motor:
This type relies on a small difference in speed between the rotating
magnetic field and the rotor to induce rotor current.
oThe second type is the synchronous motor:
This type does not rely on induction and as a result can rotate
exactly at the supply frequency or a sub-multiple of the supply
frequency.
Slip:::
Types of Single Phase Motors Are:::
[construction & method of starting]
These motors are designed to operate from single phase supply, are manufactured in large no. of
types for the use in home, offices, factories etc. small motors come in Kilo Watt power ratings. By
the advancement made in designs of fractional kilo watt motors, the applications of these motors
differs.
• Induction Motors
• Repulsion Motors
• A.C. Series Motors
• Un-exited Synchronous Motors
Double Revolving Field Theory:::
o However, if the rotor is given an initial rotation in either direction, the torque due to the rotating
field acting in the direction of initial rotation coil will be more than that due to the other rotating
field and the motor will develop a net positive torque in the same direction as the initial rotation.
o Thus the motor will keep running in the direction of initial rotation.
o According to this theory, any alternating quantity can be resolved into two rotating components
which rotate in opposite directions and each having magnitude as half of the maximum
magnitude of the alternating quantity.
o In case of single phase induction motors, the stator winding produces an alternating magnetic
field having maximum magnitude of Φ1m.
o According to double revolving field theory, consider the two components of the stator flux, each
having magnitude half of maximum magnitude of stator flux i.e. (Φ1m/2). Both these components
are rotating in opposite directions at the synchronous speed Ns which is dependent on frequency
and stator poles.
o Let Φf is forward component rotating in anticlockwise direction while Φb is the backward
component rotating in clockwise direction. The resultant of these two components at any instant
gives the instantaneous value of the stator flux at the instant. So resultant of these two is the
original stator flux.
fig shows the stator flux and its two components Φf and Φb. At start both the components are
shown opposite to each other in the Fig.1(a). Thus the resultant ΦR = 0. This is nothing but the
instantaneous value of the stator flux at start. After 90o , as shown in the Fig. 1(b), the two
components are rotated in such a way that both are pointing in the same direction. Hence the
resultant ΦR is the algebraic sum of the magnitudes of the two components. So ΦR = (Φ1m/2) +
(Φ1m/2) =Φ1m. This is nothing but the instantaneous value of the stator flux at θ = 90o as shown in the
Fig 1(c). Thus continuous rotation of the two components gives the original alternating stator flux.
Both the components are rotating and hence get cut by the motor conductors. Due to cutting of flux,
e.m.f. gets induced in rotor which circulates rotor current. The rotor current produces rotor flux. This
flux interacts with forward component Φf to produce a torque in one particular direction say
anticlockwise direction. While rotor flux interacts with backward component Φb to produce a torque
in the clockwise direction. So if anticlockwise torque is positive then clockwise torque is negative.
At start these two torque are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. Each torque tries to
rotate the rotor in its own direction. Thus net torque experienced by the rotor is zero at start. And
hence the single phase induction motors are not self starting.
Torque speed characteristics:::
• The two oppositely directed torques and the resultant torque can be shown
effectively with the help of torque-speed characteristics.
Starting methods:::
o single-phase capacitor-start motors
o capacitor-run motors
osplit-phase motors
o shaded-pole motors
o small polyphase induction motors.
Capacitor start induction motor:::
Capacitor run motors:::
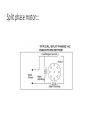
Split phase motor:::
Shaded pole motors:::
Blocked Rotor test for Induction Motor:::
• Blocked rotor test is conducted on an induction motor. It is also known as short circuit test or
locked rotor test or stalled torque test.
• From this test short circuit current at normal voltage, power factor on short circuit, total leakage
reactance, starting torque of the motor can be found.
• The test is conducted at low voltage because if the applied voltage was normal voltage then the
current flowing through the stator windings were high enough to over heat the winding and
damage them.
• The blocked rotor torque test is not performed on a wound rotor motors because the starting
torque can be varied as desired. However, blocked rotor current test is conducted on squirrel cage
rotor motors.
0-10A
0-300V
{some one can hold this
shaft to block the rotation}
Method:::
• In the blocked rotor test, the rotor is locked
• A low voltage is applied on the stator terminals so that full load current flows in the
stator winding.
• The current, voltage and power input are measured at this point.
• When the rotor is stationary the slip ,S=1.
• The test is conducted at 1/4th the rated frequency as recommended by IEEE.
• This is because the rotor's effective resistance at low frequency may differ at high
frequency.
• The test can be repeated for different values of voltage to ensure the values obtained are
consistent.
• As the current flowing through the stator may exceed the rated current, the test should
be conducted quickly.
• By using the parameters found by this test, the motor circle diagram can be constructed.
No Load Test of Induction Motor:::
• By the name no load test it means that there is no load- that is load is zero. But it is exact
opposite. No load means infinite load test. It is because in no load there is NO load , and no load
means it is open circuit . Open circuit means infinite resistance.
• But that was the case in transformers, where you can open circuit the low voltage of transformer
and obtain readings. But how will you do that in Induction motor? How can you make infinite
resistance at load side?
• If slip=0, then Rl' will be infinite. And you can make slip zero by making synchronous
speed Ns equal to actual speed N.
• So slip will be zero. Load resistance will be infinite.
0-10A
0-300V
No load at output of motor
Method:::
• Connect the circuit.
• Supply the rated voltage to induction motor, keep it running.
• The current drawn by motor is quit low
• Take care of the voltmeter should be of voltage ratings of induction
motor & the ratings of ammeter should be low because the current
drawn by motor is very small.
• Take the readings of voltmeter, ammeter and wattmeter.