* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atoms
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
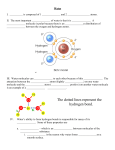
Chapter 2 Organic ◦ Study the carbon compounds ◦ Applied to the living process Inorganic ◦ The chemistry of all substances but not the carbon compounds ◦ Applied to non-living process Atoms Smallest particle of an element Basic building blocks of all matter. They contain protons, neutrons, and electrons. Nucleus: is the center of the atom, contains protons and neutrons. Proton: Positively charged Neutron: Neutral charge (no charge) Electron: Negatively charged. They are in constant motion in the space surrounding the nucleus. Element A pure substance, made of only one kind of atom. EX: C, H, O, N *Carbon, *Hydrogen, *Oxygen and *Nitrogen. These four elements make up 99% of living things. They are the most abundant • Most abundant compound in human body is water (H2O). Compound ◦ Made up of chemically combined elements EX: NaCl (sodium chloride) & H2O (water) Molecule ◦ Type of a compound ◦ Elements are held together by a COVALENT BOND ◦ EX: Water = H2O Isotopes ◦ Atoms of same element that differ in the number of neutrons ◦ EX: Carbon 12, Carbon 13, Carbon 14 – all have 6 protons, but C12 has 6 n, C13 has 7 n, C14 has 8 n Take out a separate sheet of paper. Fold both the left and right edges in towards the middle of the page so you have 2 flaps. Divide these flaps into 9 equals sections with a ruler and a pencil. Use scissors to cut this flaps. On the front of the flap, write the following atomic symbols and vocabulary words: ◦ C, H, O, P, K, I, N, S, Ca, Fe, Mg, Na, Cl ◦ Element, compound, isotope, molecule, atom On the inner flap, write the corresponding atomic name of the element or definition of the vocabulary word. When finished quiz yourself 2 times, using your Study Book. Then quiz your shoulder partner. How & Why Atoms Combine • Atoms combine with other atoms when conditions are right • When atoms combine, they become more stable • For most elements, an atom becomes stable when its outer shell has 8 e- (H is stable at 2 e-) Molecular formula: The symbols and numbers of each type of atom/element found in that molecule. Organic Molecules: Contain Carbon (C) Examples: CO2 C6H12O6 Chemical Equation: Equations of molecules involved in a chemical reaction (REACTANTS) along with what they form (PRODUCTS) from the reaction. Examples of Chemical Reactions: 1)Photosynthesis (REACTANTS) 6CO2 + 12 H2O light chlorophyll (PRODUCTS) C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O 2) Respiration Energy is released from carbohydrates in the mitochondria (found inside cells) (REACTANTS) C6H12O6 + 6O2 (PRODUCTS) 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP (energy) Aerobic respiration: Uses oxygen and carbohydrates to produce energy. Carbon dioxide and water are given off as waste products. Anaerobic respiration: Uses carbohydrates to produce energy without oxygen. The waste products of this type of reaction vary. The following are examples of anaerobic respiration. Glucose Glucose lactic acid + Energy ethyl alcohol + carbon dioxide About 60-90 percent of an organism is water Water is used in most reactions in the body. Water is called the universal solvent. Polarity Water is a molecule with positive and negative charges at either end, which allows it to bond with adjacent water molecules. The positively charged hydrogen attracts to the negatively charged oxygen end by a hydrogen bond. Cohesion: attraction between molecules of the same substance. Adhesion: attraction between molecules of different substances. Surface tension is the cohesion of water molecules at the surface of a body of water. All the water molecules are “holding” each other together or creating surface tension. Capillary action however, is related to the adhesive properties of water. A giant molecule of living matter formed by the joining of smaller molecules. Carbohydrates, fats, proteins and nucleic acids are examples of macromolecules. Monomers : a subunit that serves as the building block of polymer (links) Polymers: a large molecule consisting of many identical or similar monomers linked together. (chain) Carbohydrates (58% diet) Starches - contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms and break down into sugars which are readily available energy sources. They are molecules found in cell walls which gives them support. Lipids (30% diet) Fats and oils - contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms and break down into the fatty acids and are for stored energy sources. They are what cell membranes are made of. Glycerol Proteins (12 % diet) Meats - contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms and break down into amino acids which are important for regulating chemical reactions that occur in living things. These are building materials of all cell parts. Some proteins control the rate of reactions and regulate cell processes. Some are used to form bones and muscles. Others transport substances into or out of cells or help to fight disease. Nucleic Acids Are macromolecules containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon and phosphorus. They are made from individual nucleotides. Nucleotides contain three parts: a sugar a phosphate group a nitrogenous base DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid: It is the genetic material that organisms inherit from their parents It is copied and passed along from one generation of cells to the next. It stores information for the synthesis of proteins. RNA – ribonucleic acid: A copy of DNA that transmits messages to the cell for protein synthesis. Enzymes: are proteins that make the reaction happen faster because they reduce the activation energy. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates, and the enzymes convert them into different molecules.