* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Range Variance and Standard Deviation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
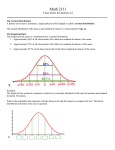
Section 2.4: Measures of Variation Today we will study • How to find the range of a data set. • How to find the variance and standard deviation of a population and a sample. • How to interpret the standard deviation. Range DEFINITION The range of a data set is the difference between the maximum and minimum data entries in the set. Range = (Maximum data value) - (Minimum data value) Remark Range is easy to compute, but we ignore most of the information about the data set by only considering two values, the largest/smallest. Variance and Standard Deviation DEFINITION The sample variance of a sample data set of n values: Sample variance = s2 = Σ(x − x̄)2 n−1 DEFINITION The sample standard deviation of a sample data set is a measure of variation of values about the mean. It is a type of average deviation of values from the mean. r Σ(x − x̄)2 Sample standard deviation = s = n−1 Remarks • The standard deviation is a measure of variation of all values from the mean. • The values of the standard deviation is usually positive. It is zero only when all of the data values are the same number (can not be negative). A larger value indicate greater amounts of variation. • The value of the standard deviation can increase dramatically with the inclusion of several outliers. • The units of standard deviation are the same as the units of the original data values. GUIDELINES Finding the Sample Variance and Sample Standard Deviation x̄ = 1. Find the mean of the sample data set. Σx n x − x̄ 2. Find the deviation of each entry. (x − x̄)2 3. Square each deviation. Σ(x − x̄)2 4. Add to get the sum of the squares. Σ(x − x̄)2 n−1 r Σ(x − x̄)2 s = n−1 s2 = 5. Divide by n − 1 to get the sample variance. 6. Find the square root to get the sample standard deviation. In general, we do not have access to population data. Note that the calculations of the Population Variance and Population Standard Deviation are slightly different than those above. DEFINITION The population variance and population standard deviation of a population data set of N values are: Population variance = σ 2 = Σ(x − µ)2 N r Population standard deviation = σ = σ is the lowercase Greek letter sigma. The symbols and formulas. Population Sample Variance σ2 s2 Standard deviation σ s Mean µ x̄ Number of entries N n Deviation x−µ x − x̄ Sum of squares Σ(x − µ)2 Σ(x − x̄)2 Σ(x − µ)2 N 68-95-99.7 Rule Bell-Shaped Distribution 99.7% of data 95% of data 68% of data b µ − 3σ µ − 2σ µ−σ b µ µ+σ µ + 2σ µ + 3σ Empirical Rule (or 68-95-99.7 Rule) For data with a (symmetric) bell-shaped distribution, the standard deviation has the following characteristics. 1. About 68% of the data lie within one standard deviation of the mean. 2. About 95% of the data lie within two standard deviations of the mean. 3. About 99.7% of the data lie within three standard deviations of the mean. STATISTICS(REG) - M109 x