* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 62 The Cold War Begins
Cuba–Soviet Union relations wikipedia , lookup
Domino theory wikipedia , lookup
Operation Anadyr wikipedia , lookup
Berlin Blockade wikipedia , lookup
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Eastern Bloc media and propaganda wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Iron Curtain wikipedia , lookup
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1962–1979) wikipedia , lookup
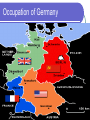
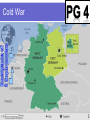
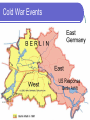
THE COLD WAR READING pg 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. C A C D C Global II The Cold War and European Recovery Ch 33, Sec 1 The Cold War Begins Pg 712 - 719 Objectives 16.1 What did the wartime conferences decide? 16.2 How did the U.S. respond to the expansion of Soviet influence? 16.3 Why did Berlin become a focal point of the Cold War? Lesson Launch Please discuss the following: What is this picture trying to demonstrate about Stalin & his ambitions? Why might the “West” feel a threat from the “East”? Wartime Conferences 1. Atlantic Charter (Feb. 1941) Goal: Self-determination for all countries ~ post WWII Agreed upon by Churchill & Roosevelt [Guiding principle of US foreign policy Post WWII Era] 2. Tehran, Iran (Nov. 1943) Plans for invasion of France Division of Poland & Germany post WWII Wartime Conferences 3. Yalta Conference (Feb. 1945) 1. 2. 3. Big Three – Winston Churchill, FDR, Stalin USSR would join the United Nations. Divide Germany into 4 “zones” Help the freed peoples of Europe to: (a) (b) (c) (d) maintain law and order carry out emergency relief measures set up governments hold free elections Occupation of Germany West Germany East Germany Controlled by G.B. USA & France Rebuild economy Create stable gov’t Denazification Removal of all traces of Nazism in Germany Controlled by Soviet Russia (USSR) No sympathy Punish Germans for WWII Dismantle Industry Sent to Soviet Union to help rebuild USSR! Origins of the Cold War U.S.A 1946 Diplomatic Protests “Iron Curtain Speech” 1947 Military Aid to Greece and Turkey (Truman Doctrine) 1947 European Recovery Act (Marshall Plan) 1948 Berlin Airlift 1949 North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NAT0) U.S.S.R Keep Troops in Iran Pressure on Turkey Aid to Greek Communists Economic Aid to Eastern Europe – Molotov Plan Blockade of Berlin Eastern Europe military Alliance: later called Warsaw Pact - 1955 The Cold War Winston Churchill’s “Iron Curtain Speech” Iron Curtain Speech Study Questions 1. Magna Carta, the Bill of Rights[English], the Habeus Corpus, trial by jury, and English Common Law, most famous American Declaration of Independence 2. Marshal Stalin [Joseph Stalin] 3. to Trieste in the Adriatic an iron curtain has descended across the Continent [Europe] 4. the fruits of war and expansion of their power and doctrines Iron Curtain Speech Study Questions 5. Strength weakness, especially military weakness 6. The Sinews of Peace “Iron Curtain” 7. The United Nations Cold War Def: A state of tension & hostility among nations w/o armed conflict Soviet Union 1. 2. Spread of communism necessary for Soviet security Communism must triumph over capitalism throughout the world USA 1. 2. Expansion of Soviet power a threat to the safety of the free world Containment: Policy where the U.S. tries to prevent the Soviet Union from expanding beyond its boarders Both Countries build up military (“Arms Race”) in fear & reaction to the other compete economically & Militarily Review Time!! What did the Yalta Conference decide? What are some differences between East & West Germany? Soviet Satellites/Bloc Behind The “IRON CURTAIN” Def: Communist-dominated nations of Eastern Europe – Extensions of Soviet Communist Power! (a) (b) (c) Dictatorships Communist economies Denied civil liberties Soviet Russian Control (a) (b) “Advised” by USSR Tied to Russian trade agreements (a) (c) (d) COMECON – Communist Economic Assistance from USSR Russian military forces present Warsaw Pact Military alliance of Soviet Bloc US Policy toward Communism “Containment” Try to keep USSR to current boundaries & Influence Truman Doctrine Aid all people fighting a foreign oppressor Examples: Berlin Blockade & Berlin Airlift Korean War Vietnam War Cuban Missile Crisis SALT I & II NATO Military Presence Guantanamo Bay (Cuba) Marshall Plan Economic aid to strengthen any economy – help economic recovery! Reasons: 1. 2. Feared economic collapse…lead to communism Future trade partners Examples: $13 Billion to Europe $400 Million to Greece US Policy toward Communism Truman Doctrine Marshall Plan Containment Summary US policy during the Cold War Era. The goal was to prevent the spread of communism & the U.S.S.R.’s influence. The Truman Doctrine (support countries fighting a foreign aggressor) and Marshall Plan (financial aid to strengthen economies) were central parts of Containment. The Korean & Vietnam Wars were Cold War conflicts due to the US policy of Containment. Cold War Alliances 1.Answers vary – US, CAN, UK 2.Answers vary – USSR, POL, CZECH 3.Answers vary – SWITZ, AUST, YUGO NEUTRAL NATIONS 1959 World map of alignments: NATO member states Other allies of the USA Colonized countries Warsaw Pact member states Other allies of the USSR Non-aligned nations Cold War Events Conflict over Berlin/Germany Problem: 1. 2. 3. Soviet Solution Last Wall, known as the “Wall” US Response Blockade of Berlin in 1948 1. Berlin Airlift 1961 Built the Berlin Wall – Under Nikita Khrushchev (Soviet Ruler after Stalin) Anti- Column Control Lighting vehicle Track Track System Trench Watch Towers Other Barriers Signal Fence Back -land Wall 1 - East Berlin 2. 2 – Border area 1. West Berlin Soviet fear of German reunification Berlin is a “capitalist” star in a sea of Communism Many “East Germans” defecting through Berlin. Closure On what three things the wartime conferences decide? How did the U.S. respond to Soviet Expansion? Why was Berlin a focal point of the Cold War? Homework Divided Berlin Pg 716