* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint Presentation - healthcaresciencemcghin
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
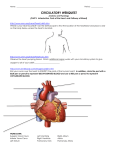
1.What consists of the heart, blood vessels, & blood Circulatory system 2. What is the muscular hollow organ often called the “pump” of the body Heart 3.How big is the heart? Approximately the size of a closed fist. 4. What cavity is the heart located in? Mediastinal cavity , between the lungs, behind the sternum & above the diaphragm 5. What are the 3 layers of tissue that form the heart? Endocardium, myocardium, pericardium 6.The muscular layer of the heart is the ? myocardium 7. The smooth layer of cells that lines the inside of the heart & is continuous with the inside of blood vessels? endocardium 8. A double-layered membrane, or sac, that covers the outside of the heart. pericardium 9. A muscular wall that separates the heart into a right & left side, prevents blood from moving between the right & left sides of the heart is the______? septum 10. The upper part of the septum is called the_____? Interatrial septum 11. The lower part of the septum is called the____? Interventricular septum 12. The heart is divided into 4 parts or chambers. The upper chambers are called the___________? Atria 13. The lower chambers are called the____________? ventricles 14. Which part of the heart receives blood as it returns from body cells_______. Right atrium 15. Which part of the heart receives blood from the right atrium & pumps the blood into the pulmonary artery, which carries the blood to the lungs. Right ventricle 16. Which part of the heart receives oxygenated blood from the lungs? The left atrium 17. Which part of the heart receives blood from the left atrium & pumps the blood into the aorta for transport to the body cells_____? The left ventricle 18. What keeps the blood flowing in the right direction? One-way valves 19. This heart valve is located between the right atrium & the right ventricle? Tricuspid valve 20. This valve is located between the right ventricle & the pulmonary artery & carries blood to the lungs. Pulmonary valve 21. This valve is located between the left atrium & left ventricle. Mitral valve 22. This valve is located between the left ventricle & the aorta____? Aortic valve 23. The largest artery in the body is the______? aorta 24. The only artery in the body which carries unoxygenated blood_____? Pulmonary artery 25. The cardiac cycle consists of a brief period of rest called______? diastole 26. The cardiac cycle in which the ventricles contract__________? systole 27. The blood in the ______side of the heart is low in___________ and high in _____________? Right, oxygen, carbon dioxide 28. What blood vessels bring the blood from the lungs to the left side of the heart_______? Pulmonary veins 29. These are a group of nerve cells located in the right atrium which send out an electrical impulse that spreads out over the muscles in the atria______? Sinoatrial (SA) node, or the “pacemaker” 30. After the electrical impulse passes through the atria it reaches the___________, a group of nerve cells located between the atria & ventricles. atrioventricular (AV) node 31. To where does the AV node send the electrical impulse________? Bundle of His (which are nerve fibers in the septum 32. The bundle of His divides into a_________and ________which carry the impulse down through the ventricles. Right bundle branch and left bundle branch 33. The bundle branches further subdivide into the ___________, a network of nerve fibers throughout the ventricles. Purkinje fibers 34. The electrical conduction pattern occurs approximately every______seconds. 0.8 seconds 35. The movement of the electrical impulse can be record on an________ & used to detect abnormal activity or disease. ECG or EKG 36. Are abnormal heart rhythms and can be mild to lifethreatening_____? Arrhythmias 37. An early contraction of the atria is called__________? Premature atrial contraction (PAC) 38. A condition in which the ventricles contract at random without coordination & decreases or eliminates blood output is called________? Ventricle fibrillation 39. What can be used to diagnose arrhythmias_______&__________? Cardiac monitors & electrocardiograms 40. What is the device that shocks the heart with an electrical current to stop the uncoordinated contraction & allow the SA node to regain control?_____________ defibrillator 41. A small battery-powered device with electrodes to regulate the heart’s rhythm. pacemaker 42.Which kind of pacemakers deliver electrical impulses at a predetermined rate? fixed 43. Which type of pacemaker is the most common & deliver electrical impulses only when the heart’s own conduction system is not responding correctly. Demand pacemakers 44. Most manufactures still recommend that people with pacemakers avoid close contact with___________ &______________? Microwave ovens & digital cellular telephones 45. What are the 3 main types of blood vessels? Arteries, capillaries, & veins 46. These blood vessels carry blood away from the heart_________. arteries 47. The largest artery in the body is the______? aorta 48. The smallest branches of arteries are called_______? arterioles 49. Arterioles join with which blood vessels_____? capillaries 50. Which blood vessels are more elastic because they receive the blood as it is pumped from the heart. arteries 51. Which blood vessels connect arterioles with venules____? capillaries 52. How many layers of cells do capillaries have? Only one layer of cells 53. The smallest branches of veins, which connect with venules capillaries________? 54.What are the 2 largest veins?Superior vena cava & inferior vena cava 55. The blood vessels which brings the blood from the upper part of the body to the right atrium is the_____? Superior vena cava 56. The blood vessels which brings the blood from the lower part of the body to the right atrium is the______? Inferior vena cava 57. Which blood vessels are thinner & have less muscle tissue than do arteries? veins 58. Most veins contain_______which keep the blood from flowing in a backward direction. valves 59. The ________that flows through the circulatory system is often called a tissue because it contains many kinds of cells. blood 60. How many quarts of blood are there in an average adult? 4-6 quarts of blood 61. What are 6 functions of blood as it circulates through the body? 1.Transports oxygen from the lungs to the body cells. 2. Transports carbon dioxide from the body cells to the lungs. 3. Transports nutrients from the digestive tract to the body cells. 4. Transports metabolic waste from the body cells to the organs of excretion. 5. Transports heat produced by various body parts. 6. Transports hormones produced by endocrine glands to the body organs. 62. Blood is made of the fluid called________& formed or solid elements called________ _______? Plasma, blood cells 63.What substances make up Plasma? 90% water, blood proteins, such as fibrinogen & prothrombin, nutrients such as carbohydrates & proteins, mineral salts or electrolytes, potassium, calcium, & sodium, gases such as carbon dioxide & oxygen, metabolic waste products, hormones, enzymes. 64. Why are fibrinogen & prothrombin necessary? Necessary for clotting 65. What are the 3 main kinds of blood cells? Erythrocytes, leukocytes, thrombocytes 66. Where are erythrocytes (RBC) produced? Red bone marrow 67. How long do erythrocytes (RBC) live? 120 days 68. How many erythrocytes are in one cubic millimeter (approximately 1 drop of blood? 4.5million to 5.5 million 69. What complex protein is found in the erythrocyte? hemoglobin 70. Hemoglobin carries both_______&___________. Oxygen & carbon dioxide 71. What gives blood its characteristic red color? Hemoglobin carrying oxygen 72. What color is the blood which contains less oxygen? Dark red with a bluish cast 73. Where are leukocytes (WBCs) produced? Bone marrow & lymph tissue 74. How long do leukocytes live? 3-9 days 75. What is the normal leukocyte count per cubic millimeter of blood? 5,000 to 10,000 per cubic millimeter 76. What is the main function of leukocytes? Fight infection 77. What does the term phagocytosis mean? The process of engulfing, & ingesting & destroying of pathogens 78. What are the 5 types of leukocytes? neutropils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes, lymphocytes 79. What is the function of the neutrophils? Phagocytize bacteria 80. What is the function of the Eosinophils? Remove toxins & defend the body from allergic reactions 81. What is the function of the Basophils? Participate in the body’s inflammatory response; produce histamine, a vasodilator, & heparin, an anticoagulant 82.What is an anticoagulant? A blood thinner. 83. What is the function of monocytes? Phagocytize bacteria & foreign materials 84. What is the function of lymphocytes? Provide immunity for the body by developing antibodies; protect against the formation of cancer cells. 85. What does the term anemia mean? An inadequate number or red blood cells, hemoglobin, or both. 86. Give 4 signs & symptoms of Anemia Pallor(paleness), fatigue, dyspnea (difficult breathing), & rapid heart rate 87.What causes Iron deficiency anemia? Caused by inadequate amount of iron to form hemoglobin in erythrocytes. 88. What is Aplastic anemia? disease caused by injury to or destruction of bone marrow, resulting in poor or no formation of red blood cells. 89. What is the cause of pernicious anemia? A lack of intrinsic factor ( a substance normally present in the stomach), that results in inadequate absorption of B12. 90. How is Pernicious Anemia corrected? Administering B12 injections 91. What is Sickle cell anemia? Abnormal crescent-shaped erythrocytes that carry less oxygen, break easily, & block blood vessels. 92. What populations of people does Sickle cell anemia exclusively affect? African Americans 93. An___________is a ballooning out of, or saclike formation on, an artery wall. aneurysm 94. ____________is a hardening or thickening of the arterial walls, resulting in a loss of elasticity and contractility. arteriosclerosis 95. ____________occurs when fatty plaques (frequently cholesterol) are deposited on the walls of the arteries narrowing the arterial opening & reducing blood flow. atherosclerosis 96. Plaques which break loose & circulate through the bloodstream are called_________. emboli 97. Procedure used to remove or compress the cholesterol deposits, or the insertion of a stent to allow blood blow through the artery is known as___________. Angioplasty 98. What is procedure is done when the arteries are completely blocked? Coronary artery bypass graft 99. A condition that occurs when the heart muscles do not beat adequately to supply the blood needs of the body___________. Congestive heart failure (GHF) 100. An inherited disease that occurs almost exclusively in males but can be carried by females_____________. Hemophilia 101. The medical term for high blood pressure? Hypertension 102. What blood pressure reading is regarded as hypertension? 140/90 103. What is the term used for the drugs used to treat hypertension? Antihypertensive drugs 104. What drugs are used to remove retained fluids from the body? diuretics 105. A malignant disease of the bone marrow or lymph tissue resulting in a high number of immature white blood cells. Leukemia 106. Occurs when a blockage in the coronary arteries cuts off the supply of blood to the heart___________? Myocardial infarction, or heart attack 107. When heart tissue dies it is known as an _________? infarct 108.What are some signs & symptoms of a myocardial infarct? Severe crushing pain radiates to the left arm, neck, & jaw; pressure in the chest; perspiration & cold, clammy skin; dyspnea; & change in blood pressure 109. If the heart stops, what should be started immediately? Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) 110. What is the medical term for “clot-busting” drugs? thromboytics 111. What is the purpose of anticoagulant drugs? They help thin the blood. 112. What are arrhythmias? Abnormal heart rhythms 113. What is the medical term for an inflammation of a vein? Phlebitis 114. What is the medical term when there is a thrombus, or clot in a vein? thrombophlebitis 115. What is the medical term for dilated swollen veins that have lost elasticity and cause stasis, or decreased blood flow? varicose veins 116.What is this procedure? Opens clogged arteries by positioning a guided catheter which is inflated & cracks the plaque. Conventional balloon angioplasty 117.Which procedure is this? A device is a balloon on one side and an opening on the other.The plaque is squeezed and shaved off. coronary atherectomy 118. Which procedure is this?A special catheter is inflated and a stent is left in place to keep the vessel open. Coronary stent