* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Visualization of Two-Dimensional Second
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
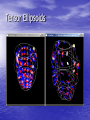
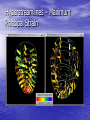
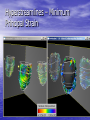
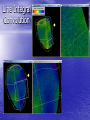
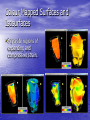
New Techniques for Visualizing and Evaluating Left Ventricular Performance Burkhard Wünsche1 & Alistair Young2 1Division for Biomedical Imaging & Visualization Department of Computer Science 2Department of Anatomy with Radiology University of Auckland New Zealand Introduction • Heart diseases remain the biggest killer in the western world. • An improved understanding of cardiac mechanics might advance the diagnosis and treatment of heart diseases. • This presentation explains how myocardial deformation can be measured and visualized. Overview • Myocardial strain • A left-ventricular finite element model • Computing ventricular performance measures • Visualizing myocardial strain • Conclusion Myocardial Strain • Regional altered myocardial mechanics • have been originally determined by measuring wall thickening. A full description of the myocardial deformation is given by the strain tensor which is mathematical represented by a 3x3 matrix. Finite Element Modelling The geometry of an element is defined by specifying coordinates, coordinate derivatives and interpolation functions. x(ξ) v B (ξ) k i i k i k Material Coordinates World Coordinates Finite Element Model of the Left Ventricle • Developed by Alistair A. Young et. al., 1994/95 University of Pennsylvania. Measuring Myocardial Strain • Use tagged MRI data set • Compute displacement field from points on tag • lines Compute strain tensor from displacement gradient tensor Computing Volume Measures • Substitution rule for multi-dimensional integration [Heuser 1981] - Ω is the domain of the finite element - f is the identity function - x(ξ) is the mapping from material to world coordinates. • Efficiently evaluated using Gaussian Quadrature. Myocardial Volume • Select all elements and sum up their volume • Volume reduction higher than expected due to underestimation of wall thickening caused by the limited tag line resolution in radial direction. Ventricular Volume • Construct new elements modelling the ventricular cavity. Computing Area Measures The Visualization of Myocardial Strain Principal Strains Any 3-dimensional symmetric tensor T has 3 eigenvalues i and 3 mutually perpendicular eigenvectors vi such that Tv i i v i i 1,...,3 The eigenvalues of a strain tensor E are called the principal strains and the corresponding eigenvectors are called the principal directions. Tensor Ellipsoids Hyperstreamlines – Maximum Principal Strain Hyperstreamlines – Minimum Principal Strain Hyperstreamlines – Minimum Principal Strain Line Integral Convolution Colour Mapped Surfaces and Isosurfaces • Separate regions of expanding and compressive strain. Conclusion • Visualizing the strain field improves the understanding • • • • of the complex deformation of the heart muscle. Using techniques new to the biomedical field offers additional insight. Tensor ellipsoids and hyperstreamlines make it possible to visualize complex deformation in a single image. Line integral convolution uncovered the presence of degenerate points at which the principal strain suddenly changes direction. Visual information can be supplemented by computing ventricular performance measures. Future Work • Further investigations necessary to find the • • relationship between degenerate points in the strain field, the myocardial fiber structure and the ventricular anatomy. Explore applications for diagnosis and surgical planning. Visualize other data sets, in particular models of ischemic myocardium. Acknowledgements • Dr. Richard White of the Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio, USA, for providing the tagged MRI data of a heart diagnosed with dilated cardiomyopathy.