* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download drugs and meds answers pharm products and antacids
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
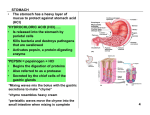
Pharmaceutical Products 1) Drugs and medicines generally are taken to improve human health. What are three different ways in which they affect the person who takes them? Alters: physiological state, sensory perception, mood or emotion 2) Explain the term: Placebo effect Contain no active ingredient, patient believes they are receiving drug so convince themselves they have affects 3) Outline the steps that a drug must go through from the time it is discovered before it can be approved for human consumption Drug discovery; animal testing where LD50 and ED50 established; clinical trials on humans for safety, efficacy, and side effects, clinical trials are double blind where neither patient or researcher knows who has drug vs. placebo, half of patients receive drug, half receive placebo; release to market 4) Explain the term: Lethal Dose (LD50) dose that is lethal to 50% of population 5) Explain the term: Effective Dose (ED50) dose where 50% of population see desired effects 6) What are four main methods by which drugs are introduced into the body Injection, inhalation, rectal, oral are the main ones 7) What are three different methods for injections intravenous, subcutaneous, intramuscular 8) Define the term “therapeutic window”. What does a narrow therapeutic window of a drug indicate? What does a broad therapeutic window indicate? Doses between LD50 and LD50 , narrow window indicates the ranges of safe and effective doses is small, easy to overdose and must be closely controlled/monitored; broad window has a wider range between LD50 and LD50 , 9) Explain the term: Side Effect An effect of a drug that is not the intended one. Examples are aspirin is a pain reliever but also thins blood, morphine is a pain reliever but also stops diarrhea 10) Describe and explain the principle of risk to benefit ratio as it pertains to drug administration. A low risk drug is desired, but depending on the condition being treated a higher risk may be acceptable 11) Describe and explain the principle of tolerance as it pertains to drug administration. The body adapts to the drug. It takes more and more drug to achieve the initial effect 12) State two reasons why tolerance may lead to death. Increased exposure to toxic side effects and higher doses could lead to overdose Antacids 1) Are antacids strong or weak acids or strong or weakbases? Weak base 2) What does an antacid do? Neutralizes excess stomach acid 3) What are some causes of acid indigestion/heartburn? Excess stomach acid rises in the esophagus and burns the lining 4) Write the balanced equation for the reaction of magnesium hydroxide with stomach acid. Mg(OH)2 + 2 HCl MgCl2 + 2 H2O 5) Which of the following compounds neutralizes more HCl? Mg(OH)2 or NaHCO3 ? Explain. Mg(OH)2 because it one mole will neutralize two moles of HCl and one mole NaHCO3 neutralizes only one 6) Antacids often combine with alginates. Why? Forms a layer that float on top of the stomach acid to prevent it from rising into the esophagus 7) Antacids often combine with dimethicone. Why? Anti-floaming agent that prevents flatulence/burping 8) What are the possible side effects from high doses of antacids? Constipation, basic stomach 9) Tums is a common antacid product sold over the counter in grocery stores and pharmacies. Tums contains 500 mg of Calcium Carbonate as its active ingredient. Gaviscon contains 105 mg Magnesium hydroxide and 160 mg of aluminum hydroxide. Calculate the number of moles of hydrochloric acid that each tablet would neutralize. CaCO3 + 2HCl CaCl2 + H2O + CO2 Tums: 0.500 g CaCO3 x 1mole CaCO3/100.09 g x 2 mole HCl/1 mole CaCO3 = 0.0099 mole HCl Gaviscon: Mg(OH)2 + 2 HCl MgCl2 + 2 H2O 0.105 g Mg(OH)2 x 1mole Mg(OH)2 /58.33 g x 2 mole HCl/1 mole Mg(OH)2 = 0.0036 mole HCl Al(OH)3 + 3 HCl AlCl3 + 3 H2O 0.160 g Al(OH)3 x 1mole Al(OH)3 /78.01 g x 3 mole HCl/1 mole Al(OH)3 = 0.0062 mole HCl Total moles = 0.0096