* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unemployment and Inflation
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Participatory economics wikipedia , lookup
Interest rate wikipedia , lookup
Full employment wikipedia , lookup
Nominal rigidity wikipedia , lookup
Phillips curve wikipedia , lookup
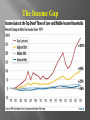
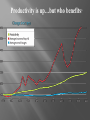
Ch. 13 UNEMPLOYMENT INFLATION A closer look…. When people are unemployed, they experience uncertainty… on a larger scale, unemployment causes uncertainty in the American economy as a whole causing it to malfunction Unemployment rate: the % of the civilian work force out of a job but actively looking for work important point: maintaining a low unemp. rate is one of the major goals in stabilizing the economy Those who have stopped looking for work Those who work in family businesses without pay Cyclical: Associated with ups/downs of the business cycle Characteristics Up during recessions Down during recoveries or booms Structural: Unemp. caused by changes in the economy such as tech advances or discoveries of natural resources Characteristics occurs when workers are replaced by machines Occurs when workers’ skills no longer match those needed to do a job Seasonal Caused by changes in the seasons or weather Characteristics Affects construction workers in the north Affects farm workers Frictional Temporary unemp. between jobs *firings *layoffs *retraining Characteristics Always exists to some degree Zero unemployment is NOT achievable or desireable A rate of 4%-6% is generally considered acceptable Many who have a job are underemployed…they work in jobs below their skills/training Defined: prolonged rise in the general level of prices High inflation is a major economic problem, especially when inflation rates change greatly from year to year. Purchasing Power Your money buys less Income If wage increases match the inflation rate, a worker's real income stays the same. If income is fixed income, or income that does not increase even when prices go up, the economic effects of inflation can be devastating use price indexes…an average price of a standard group of items and how that avg. price changes over time Economists CPI based on a “market basket” of typical consumer products (see chart on p. 339) 1982-84 prices are the base year Inflation of 1-3% is acceptable PPI is similar to CPI, but tracks prices producers charge their customers (EG, how much a steel producer charges GM for sheet metal) Food and energy prices are volatile … can and do spike up sharply now and again. To accurately study long-term trends in the inflation rate, economists exclude food and energy from the “core inflation rate” The worst kind of inflation…inflation out of control Can be 100-500% monthly…money loses most of its value Only occurs rarely, but when it does, it can lead to total economic collapse: e.g. Post WWI Germany 2 main reasons why inflation occurs: Prices rise as a result of excessive business and consumer demand. what causes excessive demand??? 3 causes: If money supply grows too fast, consumers spend add’l money on a limited supply of goods/svcs. If taxes are reduced, consumers have extra money to spend If gov’t increases its spending The bottom line: Whatever the causes, excessive demand PULLS prices higher (“demand – pull” inflation) Prices go up because producers’ costs increase: For example: 1. higher costs for raw materials 2. Wage demands of labor unions In general, as costs to produce increase, producers pass along costs to consumers…result is higher prices The Poverty Threshold …is an income level below which income is insufficient to support a family or household. The Poverty Rate …is the % of people in a particular group who live in households below the official poverty line. The Census Bureau collects data about how many families and households live in poverty. Lack of Education The median income of high-school dropouts in 1997 was $16,818, which was just above the poverty line for a family of four. Location On average, people who live in the inner city earn less than people living outside the inner city. Shifts in Family Structure Increased divorce rates result in more single-parent families and more children living in poverty. Economic Shifts Workers without college-level skills have suffered from the ongoing decline of manufacturing, and the rise of service and high technology jobs. Racial and Gender Discrimination Some inequality exists in wages between whites and minorities, and men and women. Income Gap A 1999 study showed that the richest 2.7 million Americans receive as much income after taxes as the poorest 100 million Americans… Differences in skills, effort, and inheritances are key factors in understanding the income gap. The Income Gap Productivity is up…but who benefits?