* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Proofs - Midthun Math
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Algebraic variety wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Algebraic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
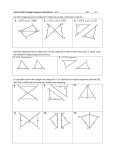
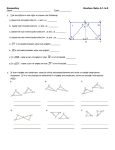
Proofs Geometry - Chapter 2 Proof • Step – by – step from given to answer • Each step has a reason – Reasons are theorems, postulates or definitions • Two types: – Algebraic – Solving mathematical equations – Geometric – Proving or finding measures Algebraic Proof Tools (Reasons) Algebraic Proof Tools (Reasons) Example • Algebraic Example: Solve: -5 = 3n + 1 Solve for x: Geometric Proofs Geometry 2.6 • Typically used to establish relationships or prove congruence – Then used to solve or work with Algebraic aspects • Definitions – Statements that describe a mathematical object or relationship • Postulates – Relationships that have always proven accurate (accepted without proof) • Theorems – Statements that have been proven Geometric Proofs - Example Geometry 2.6 Triangles • Attributes: What do we know about triangles? Triangles • Types - Classifications – By Angles: • Acute • Obtuse • Right – By Congruent Parts: • Scalene • Isosceles • Equilateral Triangles – Angle Relationships Geometry 4.3 • Triangle Sum Theorem – Sum of the angle measures of a triangle is 180o • Example: p. 232 • Exterior Angle Theorem – Measure of the exterior angle of a triangle = sum of the opposite interior angles • Example: p. 233 • Third Angle Theorem – If 2 angles of one triangle are congruent to 2 angles of another – their third angles are congruent • Example: p. 234 Congruence - Congruent Figures Geometry 4.4 • Same Size – Same Shape – All angles are congruent (same measure) – All lengths are congruent (same length) • Any shape, 2 or 3 dimensional • Labeling: – Congruent parts in the same order in both figures Triangle Congruence (4.5-4.7) • Several ways to prove congruence – SSS – Three sides congruent: p. 250 – SAS – Two sides & included angle: p. 251 – ASA – Two angles & included side: p. 261 – AAS – Two angles and an adjoining side: p. 262 – HL (Right Triangles only) – Hypotenuse/Leg: p. 263 – CPCTC • Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles are Congruent • P. 268 Parallelograms • Attributes - Quadrilateral – – – – – Both pairs of opposite sides are Parallel Both pairs of opposite sides are congruent One pair opposite sides are congruent AND parallel Diagonals of quadrilateral bisect each other Both pairs of opposite angles are congruent • Special Cases – Rectangle – Rhombus – Square Parallelograms • Using Attributes in Proofs • To prove a parallelogram • To prove triangles