* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DJS Exploration - Francis Howell High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
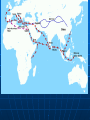
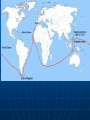
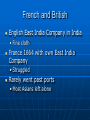
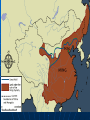
Age of Exploration and Isolation Factors that Encouraged Exploration Interaction with Muslims • Crusades Marco Polo reached China Seek Greater wealth • Spice trade as well as other luxury goods • Introduced during the Crusades Nutmeg, ginger, cinnamon and pepper • Muslims and Italians controlled trade Paid high prices for goods, so sought to bypass Other factors Spread of Christianity • Sacred duty (God, Gold and Glory) • Convert non-Christians • Bartolomeu Dias- early Portuguese explorer said to bring light to people who were in darkness Technology • Caravel- ship with triangular sails, could go against the wind • Improved navigational techniques Astrolobe- track where they were by the stars compass Portugal Leads First to establish trade outposts in Africa • First to go around Africa Strong government support for exploration • Prince Henry the Navigator Saw the wealth to be had in Africa Wanted to reach source of the treasure 1419 founded a navigation school • Mapmakers, instrument makers, shipbuilders, scientists and sea captains • Traded with Africa • slaves Portuguese in Asia 1487 Bartolomeu Dias reached tip of Africa • Made it around during a storm, returned home because of problems 1498 Vasco de Gama reached Calicut in India • Found spices and silks • Direct sea route to India Spanish Also wanted goods 1492 Columbus sailed the ocean blue • October Columbus reached the Caribbean and believed he had found new route to India Open route for colonization of Americas • Cause problems between Spain and Portugal • Line of Demarcation created by Pope Alexander VI Brazil Treaty of Tordesillas 1494 honored the line Trading Empires Europeans scramble to put up trading empires in Asia Portugal in Indian Ocean • Took control of spice trade (defeated Muslim fleet) • Took control of Strait of Hormuz which kept Muslim traders out • Captured Goa, Malacca in the Malay peninsula Gained control of the Moluccas (Spice Islands) Cheaper goods, more people could afford them Others 1521 Spanish led by Ferdinand Magellan arrived in the Philippines and claimed it • Settled in 1565 Rest of Europe descends upon Asia Other nations 1600 English and Dutch challenged Portugal • Dutch became leading sea power after Spain lost control of it Largest fleet in the world English and Dutch won control and then battled one another • East India Company Dutch East India Company was richer and more powerful European Trade Outposts 1619 Dutch outpost on Java • Took Malacca and Spice Islands Amsterdam became leading commercial center By 1700 ruled most of Indonesia Controlled Cape of Good Hope French and British English East India Company in India • Fine cloth France 1664 with own East India Company • Struggled Rarely went past ports • Most Asians left alone Ming Dynasty China dominant power • Vassal states paid tribute- Korea to Southeast Asia • Expected Europe to be submissive • Hongwu drove the Mongols out in 1368 Ruled from Nanjing Reformed, promoting power and prosperity Return to Confucianism Became a tyrant later Ming Power struggle- son Yonglo came to power • Moved court to Beijing • Curious about the world Seven voyages of exploration • Led by Muslim Admiral Zheng He Zheng He Traveled far distances Large fleet • Went to Southeast Asia and India, Arabia and eastern Africa • Impress the world with their power and splendor • Crews of over 27,000 in the floating city • Gave gifts – gold, silk, oils • 16 countries sent tribute 1433 the trips ended and China became isolated. Isolation Foreign trade kept to a minimum • • • • 3 ports of entry Smuggling Demand for Chinese goods Does not industrialize Merchant class at the bottom of society • Offended Chinese Confucian beliefs • Economy favored agriculture High taxes on manufacturing Christian missionaries • Matteo Ricci made an impact Qing Dynasty Ming dynasty collapsed • Mandate of Heaven Manchuria- the Manchus invaded • Took over and became the Qing Dynasty Rule 260 years- add Taiwan, Chinese central Asia, Mongolia and Tibet Qing Dynasty Continued Non-Chinese • Resisted, rebellions Men had to wear a hat and pigtail as submission to rule Kept Confucian beliefs Made frontiers safe Made China prosperous again Kanxi and Qian-long Emperor 1661, ruled for 60 years • Reduced government expenses and lowered taxes • Offered intellectuals government positions Qian-long (grandson) ruled 17361795 • Reached greatest size and prosperity More Isolation Trading countries must follow Chinese rules • Dutch kowtowed and paid tribute • Made trading partners Brought tea • British didn’t like restrictions Letter from King George III asking for better trade agreement • would allow British goods • Refused to kowtow China refused the deal Korea Manchus conquered Korea before China • Vassal state • Like China • More nationalistic feelings after Japan attacked and Manchus took it over Life Rice production Population doubled Most were farmers • Irrigation and fertilizers increased • New crops- corn potatoes Nutrition and diet improved Women Sons favored over daughters • Son could carry on religious beliefs Raised family and took care of parents Females killed Men over females • Inferior footbinding Culture Mainly traditional forms • Dream of the Red Chamber by Cao Zhan looked at upperclass Manchu society Portrayed females well • Painted in traditional styles Technique over creativity • Drama Plays about Chinese history Japan 1467-1568 civil war and chaos Sengoku Period (warring states) • Samurai (daimyo) seize feudal estates Offer peasants protection for loyalty Emperor becomes figurehead in Kyoto Constant fighting Order Restored Oda Nobunaga seized control of capital in 1568 • Eliminated enemies • Not able to unify Japan • Committed seppuku when own generals turned on him Toyotomi Hideyoshi- best general • By 1590 controlled most of the country Invaded Korea When he died the troops left Korea Tokugawa Shogunate Tokugawa Ieyasu • Unified Japan by defeating his rivals • Gained loyalty of daimyo • Became sole leader or shogun Moved capital to Edo (Tokyo) Made daimyo spend every other year at capital to keep them under control Families kept as hostages when they returned to their land Ruled by law • Tokugawa Shogunate lasted until 1867 Society Stable, prosperous and isolated Plenty of food, population rose • Merchants and the rich prospered Confucian values • Peasants mostly taxed Left for cities • Shift to urban society by 1700’s Edo largest city in the world Large commercial centers- jobs for women, most restricted in the home Culture Traditional themes • Dramas with tragic themes • Ancient warriors • Paintings from classical literature Kabuki theater- elaborate costumes, used music, dance and mime about modern urban life • Paintings with woodblock prints Popular stories about self made merchants • Urban fiction • Haiku- presents images in poetry 5-7-5 Portugal and Japan Europeans welcomed at first 1543 first contact • Merchants followed • Brought items from Europe from trade • Japanese merchants liked the new goods • Daimyo welcomed the Europeans Especially their muskets and cannons Switch from sword to musket in battle Christian Missionaries Arrived in 1549 Japanese associated them with muskets and goods, so were welcomed • Francis Xavier, a Jesuit converted about 100 • 300,000 Japanese converted by 1600 Upset Tokugawa Ieyasu • Missionaries came out against traditional beliefs and got involved in politics • Banned Christianity in 1612 and tried to get rid of them After a rebellion in 1637 led by Christiansruthlessly persecuted • Christianity disappeared Isolationism Did not Europeans way, but liked their trade • Sealed borders and started a closed country policy • Nagasaki remained open Only Dutch and Chinese could trade Tokugawa shoguns controlled port Isolated for 200 years • Self-sufficient Columbus Nina, Pinta, and Santa Maria left Spain August 3, 1492 • October 12, 1492 spotted land Columbus promised to first spot land would receive a reward Called the people who greeted the shipsIndians since he believed himself to be in India, really were the Taino Landed in the Bahamas- claimed for Spain and named it San Salvador Columbus in Spain Reported journey to monarchs in 1493 • Left some sailors behind • Monarchs will agree to finance more troops • Set off again in September 17 ships and several hundred armed soldiers 1000 settlers Create colonies- lands controlled by another nation • Other explorers will follow to take the unclaimed lands Other Explorers 1500 Portuguese explorer Pedro Alvares reached Brazil 1501 Amerigo Vespucci- an Italian sailing for Portugal explored the coast of South America • Claimed land was not part of Asia but a new continent • 1507 the continents are named after Vespucci- The Americas Continued 1519 Ferdinand Magellan attempted to circumnavigate the world • • • • 230 men and five ships Sailed around South America No land for months, food ran out Finally reached the Philippines Involved in a local war- Magellan killed 18 men and one ship made it back Spanish Explorer Vasco Nunez de Balboa first European to see Pacific after crossing Panama Cortes Hernando Cortes landed in Mexico to claim new lands for Spain • Conquistadors (conquerors) • Looking for gold and silver • Found Aztec Empire Cortes and 600 men found capital of Tenochtitlan Montezuma II believed he was a destined God at first • Gave gold • Cortes forced the Aztecs to mine for gold and silver Aztecs rebelled in 1520 1521 Spanish win • Superior weaponry • Used other natives groups to fight • smallpox Disease Measles, mumps, smallpox and typhus • No immunity to these extinct diseases • Syphilis • Died by the hundreds of thousands • More devastating that warfare Pizarro 1532 Francisco Pizarro marched a small force into South America • Conquered Inca Empire 200 men met the Inca ruler Atahualpa who had 30,000 men Atahualpa came unarmed Spanish crushed the force and kidnapped Atahualpa until the Incas filled an entire room once with gold and twice with silver They then killed the king Forces retreated Incas Left demoralized without king Pizarro marched on Capital of Cuzco • Took it without a struggle Others conquered native people in the Yucatan and Guatemala Conquest Used techniques from the reconquista in Spain • Live among the people and impose culture upon them Groups of people • Peninsulares- mostly men and born in Spain Married native women • Created mestizo class – mixed Oppressed the natives • Labor system- ecomienda- natives farmed, ranched or mined for Spanish landlords Landlords had the right to native labor from Spain Promised to act fairly, most were abused and worked to death Portuguese in Brazil Only area in Americas out of Spanish control • 1500 Cabral claimed land for Portugal No gold or silver Grew sugar- demand in Europe was great Moved further west and produced more sugar Killed off the natives with disease and slavery Conquistadors push North Explored southwestern US • 1513 Ponce de Leon explored Florida and claimed it for Spain • 1540 Francisco Vasquez de Coronado explored AZ, NM, TX, OK and KS Looked for a wealthy empire Mostly priests will explore and colonize the US • Catholic priests came to convert the heathens 1609-1610 Pedro de Peralta led settlers to the upper Rio Grande and built a capital called Sante Fe or Holy Faith Opposition Priests pushed for better treatment of native Americans • Criticized encomienda system Dominican monk Bartolome de Las Casas wrote in complaint of system • Spanish government abolished encomienda system in 1542 • Switched to Africans for workers Resistance Even Columbus met with resistance from the natives Taino revolted off and on Late 17th century natives in New Mexico fought back because forced to give up their culture 1680 Pope, a Pueblo ruler led a rebellion of 17,000 against the Spanish • Drove the Spanish back for 12 years New France Giovanni da Verrazzano- Italian exploring for France • Looked for sea route in north to the Pacific Discovered New York Harbor Frenchman Jacques Cartier explored the St. Lawrence River and followed inward to modern day Montreal Samuel de Champlain claimed Quebec which would become the base of New France French Exploration 1673 Priest Jacques Marquette and trader Louis Joliet explored the Great Lakes and upper Mississippi River • Sieur de La Salle explored the lower Mississippi in 1680’s Claimed entire area for France and named it the Louisiana territory after Louis XIV Mostly traders and priests- small population in New France African Slavery 1500 European enslavement of Africans began • Had existed before • Slave trade began with the spread of Islam Prisoners of war 4.8 million enslaved in Africa- prisoners of war and criminals west to Southwest Asia • • • • • Domestic servants Had legal rights and opportunity for social mobility Could be in power, could own their own slaves Could marry into the family they served Not hereditary Desire For Africans