* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sperm - mrsoto
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
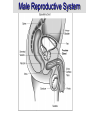
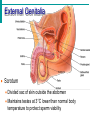
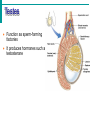
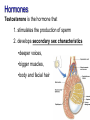
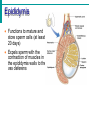
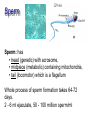
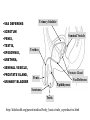
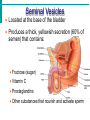
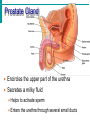
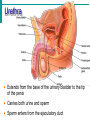
Male Reproductive System • Aim: Understand the major structures of the male reproductive system and explain the functions Vocabulary: Penis, urethra, seminal vesicle, prostate gland, urinary bladder, testis, epididymus. • Do Now: List 3 things you already know about the male reproductive system. The male reproductive system • Three main functions: – To produce gametes (the sperm cells) – To produce hormones (testosterone) – To deposit the sperm cells it produces inside the female. Male Reproductive System External Genitalia Scrotum Divided sac of skin outside the abdomen Maintains testes at 3°C lower than normal body temperature to protect sperm viability Testes Function as sperm-forming factories It produces hormones such as testosterone Hormones Testosterone is the hormone that 1. stimulates the production of sperm 2. develops secondary sex characteristics •deeper voices, •bigger muscles, •body and facial hair Epididymis Functions to mature and store sperm cells (at least 20 days) Expels sperm with the contraction of muscles in the epididymis walls to the vas deferens Sperm Sperm: has • head (genetic) with acrosome, • midpiece (metabolic) containing mitochondria, • tail (locomotor) which is a flagellum Whole process of sperm formation takes 64-72 days. 2 - 6 ml ejaculate, 50 - 100 million sperm/ml Processes of Spermatogenesis Spermatogenesis takes 64 to 72 days Urinary bladder •VAS DEFERENS •SCROTUM Seminal Vesicle •PENIS, •TESTIS, •EPIDIDYMIS, Urethra •URETHRA, •SEMINAL VESICLE, •PROSTATE GLAND, •URINARY BLADDER Prostate Gland Penis Vas Deferens Epididymus Scrotum Testis http://kidshealth.org/parent/medical/body_basics/male_reproductive.html Seminal Vesicles Located at the base of the bladder Produces a thick, yellowish secretion (60% of semen) that contains: Fructose (sugar) Vitamin C Prostaglandins Other substances that nourish and activate sperm Prostate Gland Encircles the upper part of the urethra Secretes a milky fluid Helps to activate sperm Enters the urethra through several small ducts Urethra Extends from the base of the urinary bladder to the tip of the penis Carries both urine and sperm Sperm enters from the ejaculatory duct Semen Mixture of sperm and accessory gland secretions Advantages of accessory gland secretions Fructose provides energy for sperm cells Alkalinity of semen helps neutralize the acidic environment of vagina Semen inhibits bacterial multiplication Elements of semen enhance sperm motility