* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Induction motor control
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
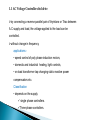
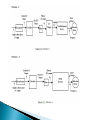
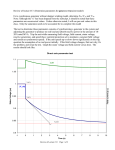
UNIT-3 1.Stator voltage control The speed can be controlled by varying the stator voltage. Here the supply frequency is constant. Equivalent circuit of induction motor R1& X1 - the stator side resistance & reactance. V1 - stator voltage (or) supply voltage. f1 - the supply frequency. I1, I2 - the stator and rotor side current respectively. R2 & X2 - the rotor resistance & reactance respectively. 3I 22 R2 Torque T = S S -------------------------- (3.1) Therefore the equation (3.3) becomes Results The starting torque α Square of stator voltage, rotor resistance. 1/α The square of the leakage reactance. A small change in stator voltage results in a relatively large change in torque. the slip at maximum torque remains unchanged Figure 3.2. Speed Vs Torque of Induction motor under stator voltage It is not a function of voltage. This method is not used for wide range of speed control and constant torque load. Consider The induction motor has no stator copper loss, friction loss, windage and core loss. Electrical power converted into mechanical power (developed power in the rotor). Pm = Total air gap power transferred across the air gap for a three phase induction motor (Pag) – copper loss in the rotor (Pcur) From equation (3.6) For low speed, slip will be very high. Therefore Efficiency will be poor. It is an excellent method for reducing starting current and increasing the efficiency during light load conditions. The losses are reduced, mainly core losses, which are proportional to the square of the voltage. This method is only suitable for speed control below the rated speed, since the terminal voltage cannot exceeds rated value to prevent the damage of the winding’s insulations. We have seen that the torque is directly proportional to the transformation ratio K. 1.1 AC Voltage Controllers fed drive by connecting a reverse parallel pair of thyristors or Triac between A.C supply and load, the voltage applied to the load can be controlled. without change in frequency. applications:• speed control of poly phase induction motors, • domestic and industrial heating, light controls, • on load transformer tap changing static reactive power compensators etc. Classification • depends on the supply. single phase controllers. Three phase controllers. Figure 3.3. Three phase Y connected AC voltage controller circuit In the delta connection, the phase current is 1 3 times of line current, Thyrsitor current rating is reduced by a factor of 3 Under normal operation Figure 3.4.Three phase delta connected AC voltage controller circuit Each thyristors is the above circuits are fired in the sequence of their numbers with a phase difference of 60 degree like three phase full converter. Let Rin – Resistance in the induction motor. Xin – Inductive reactance in the induction motor. 1 Xin Therefore, the phase angle tan Rin For the firing angle , the motor terminal voltage remains constant and nearly equal to the supply voltage. Both motor voltage and current are sinusoidal. For higher values of firing angle , the current flows discontinuously and the motor voltage decreases with an increase in .The zero motor voltage and current are reached at =150 degree and 180 degree As per the emf equation. Various Schemes of induction motor speed control