* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Antibiotic Selection and Resistance: A Pharmacist`s perspective
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
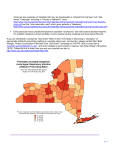
Jennifer Ott, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, Infectious Diseases Eastern Maine Medical Center Bangor, ME [email protected] The use of antibiotics is the single most important factor leading to antibiotic resistance Up to 50% of all antibiotics prescribed are not needed or are not optimally effective as prescribed CDC. Threat Report 2013. http://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/threat-report-2013/ 85 200 80 150 75 100 70 50 65 0 60 1990 1991 1992 Patients with VRE Kim NJ. JID 1999;179:163 1993 1994 DDD vancomycin 1995 Defined daily doses of vancomycin/1000 patient days Number of patients with VRE 250 The Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project Individuals prescribed an antibiotic in primary care for a respiratory or urinary infection develop resistance to that antibiotic Greatest effect in the month immediately following treatment but may persist for up to 12 months Costelloe, C. et al. BMJ 2010: 340:c2096. Costelloe C et al. BMJ. 2010;340:c2096. 1 Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, Long Term Care Minimum Data Set, Resident profile table as of 05/02/2005. Baltimore. MD. 2 Loeb, M et.al. Antibiotic use in Ontario facilities that provide chronic care. J Gen Intern Med 2001; 16: 376-383. 3 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health statistics, 1999 National Nursing Home Survey. Nursing Home Residents, number, percent distribution, and rate per 10,000, by age at interview, according to sex, race, and region: United States, 1999. http://www.cdc.gov/getsmart/campaign-materials/week/images/resistance.png Data pooled from 4 studies Gram-negative pneumonia Ciprofloxacin resistance associated with AUC/MIC <100 Thomas JK, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998;42:521-527. Penicillin half-life is only 30-45 minutes Retrospective review of Streptococcal infective endocarditis Penicillin given every 4 hours was associated with successful treatment vs every 6 hours (OR 2.79; 95%CI 1.43-5.62) Sandoe JAT, et al. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013; June 13 [Epub ahead of print] Shea KM, et al. Ann Pharmacother 2009;43:1747-1754 Cefepime Tertiary references suggest a dose of 1-2 g q8-12h Susceptibility breakpoints are based on 1 g q8h (= 2g q12h) Meaning: using 1 g q12h for pneumonia does not optimize the dosing of cefepime and risks undertreating the patient CDC. Threat Report 2013. http://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/threat-report-2013/ Boucher HW, et al. Clin Infect Dis 2009;48:1-12. http://www.rff.org/RFF/Documents/ETC-06.pdf Accessed Jan 1, 2013 Promotion of appropriate and responsible use of anti-infective agents Optimize anti-infective therapy Drug Dose Route Duration Patient tolerance and safety Limit preventable adverse events Drug-drug or drug-disease interactions CDC. Threat Report 2013. http://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/threat-report-2013/ Antibiotic overuse promotes resistance Goal – use most narrow spectrum agent for appropriate duration Increased resistant organisms are on the rise Inappropriate antibiotic dosing may promote resistance Antibiotic pipeline is diminishing What to do Promote appriopriate anti-infective use Use most narrow spectrum anti-infective agent at optimal doses for the appropriate duration