* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A Simplified Database System Environment
Serializability wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Access wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Ingres (database) wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Functional Database Model wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
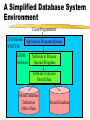
Database A database is a logically coherent collection of data with some inherent meaning e.g. address book A database is designed, built, and populated with data for a specific purpose Database A database may be generated and maintained manually, for example, a library card catalog. A computerized database is usually maintained by a set of programs. Data Hierarchy File (Collection of related records) Record (data elements that relate to a particular object or activity) Data element (smallest unit of data) Traditional Approach Programming with files or file-processing Files linked to a specific application Structure of data files is embedded in the application programs File Processing Disadvantages File structure changes usually result in program changes Data redundancy or duplication Wasted space Naming problems Inconsistency because of lack of synchronization in updating the duplicated data File Processing Disadvantages Diffused data ownership programmers “own” data accessed by their programs Result - inconsistent, inaccurate, and unreliable information Database Approach A single repository of data which is accessed by various users Database system contains the database and a complete description of the database called meta-data Database Approach Advantages Program - data independence Ability to change data structure without making changes to the programs User is not constrained by the physical organization of data Database Management System (DBMS) DBMS is a collection of programs that enables users to create and maintain a database DBMS is a general-purpose software that facilitates the process of defining constructing and manipulating databases for various applications DBMS (Contd.) DBMS functions Defining a database (data types, structures, and constraints) Constructing the database (storing the data) Manipulating the database (querying, updating and report generation) DBMS software + database = database system A Simplified Database System Environment Users/Programmers DATABASE Application Programs/Queries SYSTEM DBMS Software Software to Process Queries/Programs Software to Access Stored Data Stored Database Definition (Meta-Data) Stored Database DBMS (Contd.) Data hierarchy in a Database Approach Database (collection of interrelated files) File • Record – Data element Means to integrate the contents of files that have logical relationship Database Structures Logical integration of files through explicit relationships - for example, “link” fields in a hierarchical structure Implicit relationships - relationships that can be implied from existing record data as in a relational structure Database Approach “Disadvantages” Need for DBMS software which could be expensive Larger hardware configuration may be needed Dedicated staff Database Staff Database Administrator (DBA) authorizes access to the database co-ordinates and monitors database use acquires software and hardware resources accountable for security and response time problems Database Staff (Contd.) Analysts/Database designers get user requirements identify data to be stored choose appropriate structures develop a “view” of the database that meets user requirements Programmers