* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation
Historiography of the causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
United States home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War I wikipedia , lookup
American entry into World War I wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Article 231 of the Treaty of Versailles wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War I wikipedia , lookup
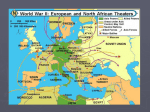
General Information… • Started on July 28, 1914 • Ended on November 11, 1918 • Almost 8,000,000 dead. *** Russia the most = 1.7 million • Almost 22,000,000 wounded….. • Map of Europe greatly changed. WWI War Goals • France – – – – regain Alasace/Lorraine, Saar Basin (coal region) create a DMZ (Rhineland) as a buffer cripple Germany’s military get German & Turkish colonies in Africa & Mid-East • Great Britain – get German & Turkish colonies in Africa & Mid-East • Italy – wanted land from Austria-Hungary WWI War Goals • Russia – wanted control of the Dardenelle & Bosporus Straits • Austria-Hungary – self preservation • Germany – part of France, Luxembourg, Belgium, western Russia – A-H and the Balkans as a “sphere of influence” – take over French and British colonies in Africa • United States – win an end to the war – Wilson’s 14 Points • New aspect of “Total War” • Targeting “neutral merchant” ships Submarines • Germans announce submarine blockade • Part physical, part psychological weapon • Draws Allied resources away from offensive operations • Civilian control of production • Sinking of ships with US passengers is major factor in US’s eventual entry into the war www.nrotc.net/310/17.ppt 1915 • May 7 Sinking of the passenger ship Lusitania • Killed 1200, 123 Americans • May 23 Italy declares war on Austria-Hungary • August 30 Germany responds to U.S. anger by ceasing to sink ships without warning • December 28 Allies begin withdrawal of troops from Gallipoli www.nrotc.net/310/17.ppt The Gallipoli Disaster, 1915 Major Battles Continued • Gallipoli Campaign – Feb. 1915-Jan. 1916 – Britain attacked Turkish forts along the Dardanelles – Both sides suffer heavy casualties, but the British eventually withdrew all troops. (although Winston Churchill recommended sending more troops) Verdun – February, 1916 German offensive. Each side had 500,000 casualties. Major Battles Continued • Battle of Verdun – Known as the greatest and longest battle in world history-due in part to the great number of men fighting over such a small piece of land – Battlefield was 10 square kilometers – Lasted from Feb. 1916 to Dec. 1916 – French and German troops fighting for prestige – Over 700,000 casualties The Somme – July, 1916 60,000 British soldiers killed in one day. Over 1,000,000 killed in 5 months. Major Battles Continued • Battle of the Somme – July-Oct. 1916 – This battle has come to symbolize the horrors of modern WWI warfare and the futility of trench warfare. – The British attempted to relieve the French who had suffered great losses at Verdun. The British try to advance over a 25 mile front to the German trenches. – This battle is also known for the massive amount of British casualties (420,000) Major Battles Continued • Battle of Meuse-Argonne – Also known as the Battle of Argonne Forest – September-Nov. 11, 1918 – Final Allied offensive of WWI, also known as the Grand Offensive. – All major allied powers were involved in breaking through German lines. – Fresh U.S. troops are credited with tipping the scale to victory. Map 31.1: Major U.S. Operations in France, 1918 Figure 31.1: Approximate Comparative Losses in World War I The Treaty of Versailles June 1919 What did France want from the treaty? Security Revenge Reparations Clemenceau : The Tiger Clemenceau wanted to make sure that Germany could not invade France in the future. He was determined that Germany should be made to pay for the damage that had been caused in northern France by the invading German armies. What did Britain Want? In public Lloyd-George said he wanted to punish the Germans. The British public was very anti-German at the end of the war. In private he realised that Britain needed Germany to recover because she was an important trading partner. David Lloyd-George He was also worried about the “disease from the east”, communism. The Russian government had been overthrown by a communist revolution in 1917. Lloyd-George believed that the spread of communism had to be stopped. A strong Germany would be a barrier against it. What did America Want? Woodrow Wilson wanted the treaty to be based on his Fourteen Points He believed Germany should be punished but not severely. He wanted a just settlement that would not leave Germany feeling resentful Wilson wanted to set up an international organisation called The League of Nations which would settle disputes Woodrow Wilson The American public did not support him. They were fed up with involvement in European affairs. The USA became more isolationist. What were the terms of the Treaty of Versailles? To do with Germany’s armed forces : The German army was to be reduced to 100,000 men. It was not allowed to have tanks. Germany was not allowed an airforce The area known as the Rhineland was to be de-militarised The Allies were to occupy the west bank of the Rhine for fifteen years The German navy was to have no submarines or large battleships The War Guilt Clause "The Allied and Associated Governments affirm, and Germany accepts, the responsibility of Germany and her Allies for causing all the loss and damage to which the Allied and Associate Governments and their nationals have been subjected as a consequence of a war imposed upon them by the aggression of Germany and her Allies." Article 231 GERMANY ACCEPTED RESPONSIBILITY FOR STARTING THE WAR REPARATIONS Germany agreed to pay for the damage caused by her armies during the war. The sum she had to pay was later fixed at £6.6 billion ($33 billion US dollars) Germany was forbidden to unite with Austria How did Germans React to the Treaty? Germans thought the Treaty was a “diktat” : a dictated peace. They had not been invited to the peace conference at Versailles and when the Treaty was presented to them they were threatened with war if they did not sign it. The Treaty was NOT based on Wilson’s Fourteen Points as the Germans had been promised it would. Most Germans believed that the War Guilt Clause was unjustified. The French and British had done just as much to start the war The loss of territory and population angered most Germans who believed that the losses were too severe. Many Germans believed the German economy would be crippled by having to pay reparations.