* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Species Relationship notes
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
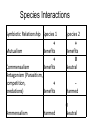
• Symbiosis is a relationship between different species in which at least one species depends upon the relationship to survive Symbiotic relationships • Symbiosis – Mutualism (+ +) – Commensalism (+ 0) – Antagonism (+ -) • Parasitism • Predation • Competition – Amensalism (- 0) Antagonism Predation • One individual (predator) captures, kills, and consumes another individual (prey) Common Defenses Against Predation • Flight • Mimicry • Camouflage • Chemicals/Physical Structures • Bright Colors Herbivore-Plant Interactions • An herbivore grazing on a plant is another example of predation. • Usually, only part of the prey is eaten by the predator. • Photo Credit: Rhett A. Butler @ mongabay.com Antagonism - Competition • Competition in an interaction between two organisms that are using the same resources • Competition within the same species= intraspecific • Competition between different species= interspecific • One organism better uses a resource leaving less for other species Example: Interspecific Competition • Two species of barnacles on rocky coasts often compete for space. • The smaller species (Chthamalus) is unable to compete as well as the larger species (Balanus). • However, Chthamalus can survive drying better than Balanus, so it can live higher up on the rocks. Experiment: Interspecific Competition • In Scotland, Joseph Connell studied interspecific competition in these two barnacles. • In places where both barnacles were present, he removed the Balanus barnacles from the rocks. Experiment: Interspecific Competition • When Balanus barnacles were removed, the Chthamalus barnacles moved down into the vacant area. • This showed that Balanus was outcompeting Chthamalus in the lower zone. Experiment: Interspecific Competition • At other sites where both barnacles were present, he removed Chthamalus barnacles from the rocks. • The vacant areas remained unoccupied. • This showed that Balanus was not able to survive in the upper zone. Antagonism - Parasitism • One individual is harmed and one benefits • Parasite feeds on the host – No immediate death Mutualism • Both species benefit – Pollination Commensalism • One species benefits and the other is not affected – Cattle Egrets and Livestock Ammensalism • one species is harmed or inhibited and the other species is unaffected – shading out of one plant by a taller and wider one – the inhibition of one plant by the secretions of another Species Interactions Symbiotic Relationship Species 1 + Mutualism Benefits + Commensalism Benefits Antagonism (Parasitism, competition, + predations) Benefits Ammensalism Harmed Species 2 + Benefits 0 Neutral Harmed 0 Neutral • http://education.nationalgeographic.org/act ivity/ecological-relationships/ • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fxrzdh Hjf0Q&list=PL0EA301D130F3DB40 – Clips 1-3