* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Wall of eyeball
Corrective lens wikipedia , lookup
Contact lens wikipedia , lookup
Dry eye syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial optic neuropathies wikipedia , lookup
Keratoconus wikipedia , lookup
Diabetic retinopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cataract surgery wikipedia , lookup
Eyeglass prescription wikipedia , lookup
Corneal transplantation wikipedia , lookup
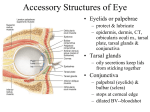
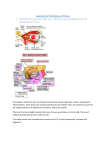
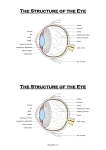
Part Ⅳ Sensory Organs SHANDONG UNIVERSITY Liu Zhiyu The Sensory Organs Sensory organs include • receptors • accessory organs The receptors may be divided into three kinds: • exteroceptors :receive stimuli such as touch, temperature, pain, light and sound from the external environment • interoceptors :pick up information about internal environment • proprioceptors :receive stimuli from muscles, tendons, joints and ligaments chapter 1 The Visual Organ The Visual Organ consist of eyeball accessory organs of eyeball Section 1 Eyeball Ⅰ. Shape of eyeball anterior and posterior poles anterior pole Axis of eyeball :a line joining the two poles Optic axis :a line joining the center of the pupil to the fovea centralis Equator : an imaginary line encircling the eyeball, midway between anterior and posterior poles posterior pole Ⅱ.Structure of eyeball 1. Walls of eyeball Fibrous tunic of eyeball Vascular tunic of eyeball Cornea Sclera Iris Cilliary body Choroid Pars iridica retinae Retina Pars ciliaris retinae Pars optica retinae Pars caeca retinae Wall of eyeball (1) Fibrous tunic (outer layer) Cornea : anterior 1/6; a nonvascular, transparent portion; Ⅱ supplied richly by nerves; because it is curved, the cornea helps focus light. Walls of eyeball (1) Fibrous tunic Sclera: posterior 5/6, consists of fibrous connective tissue having protection and surpporting for eyeball, posteriorly it contineus with the sheath of optic n. sinus venous sclerae : lies beneath the junction of cornea and sclera, and is irregular circular canal. cribriform plate of sclera cornea Sinus venous sclerae sclera Wall of eyeball (2) Vascular tunic (middle layer): iris lies the anterior part of the vascular tunic, and is a thin contractile membrane with a central opening, the pupil iridocorneal angle sphincter pupillae dilator pupillae eyeball Ciliary body : Behind the iris,may be divided into a) ciliary ring b) ciliary processes : 60~80, producing aqueous humor ciliary muscle ciliary zonules ciliary zonules eyeball choroid Thin, highly vascular in posterior 2/3 of eye Contains brown pigmented cells and dense capillary plexus function: Nutrition Absorb the disperse light Wall of eyeball (3) Internal tunic of eyeball— retina division: ora serrata a. Pars caeca retinae: pars iridica retinae pars ciliaris retinae b. Pars optica retinae: Wall of eyeball 2) structure: The retina consists of two layers: pigment epithelial layer nervus layer:consist of three layers of cells Photoreceptor cells: Cone cell Rod cell Rod cell Cone cell Pigment cell layer Wall of eyeball bipolar cell ganglion cell, whose axons form the optic n. fibers Ganglion cell Bipolar neuron Rod cells Cone cells Pigment cell layer Wall of eyeball Optic disc (blind spot), located medial to posterior pole of eye, and consists of optic nerve fibers and at where there are central a.and v. of retina Macula lutea – Lies lateral about 3.5 mm to optic disc, a shallow depression, and is yellowish in color Wall of eyeball – Fovea centralis, is an aera of greatest visual acuity and is completely free of blood vessels (concentration of cone cells). The pigment epithelial layerabsorbs light that enter the eyeball preventing backscatter (blurring of vision) 2. Contents of eyeball (1) Aqueous humor 1) Chamber of eye: lies between cornea and lens, and divided by iris into: anterior chamber posterior chamber Contents of eyeball 2) Aqueous humor •A clear watery fluid that fills chamber of eye,secreted by ciliary body. Functions • Helps focus light • Helps maintain constant pressure in eyeball • Helps nourish the lens and cornea Production and circulation of aqueous humor: secreted by the ciliary body anterior chamber pupil posterior chamber iridocorneal angle sinus venosus sclera anterior ciliary vein sinus venosus sclera ophthalmic vein Contents of eyeball (2) Lens position : lis behind the iris , anterior to the vitreous body shape: Transparent biconvex structure, covered by an elastic transparent capsule which is connected by the ciliary zonules (suspensory lig.)to the ciliary process Contents of eyeball Structure: lens capsule cortex of lens lens nucleus Its shape is changed by the ciliary muscle: for near vision, the ciliary muscle contracts and the lens rounds up, while for distant vision the lens flattens out, so that the eye may be focused on distant objects Contents of eyeball (3) Vitreous body Consists of colorless, transparent jelly-like substance in which there is a meshwork of fine fibrils, occupies the space between lens and retina Helps maintain the shape of eyeball and supports the retina Contents of eyeball (4) Refractive media:include Cornea 、 aqueous humor 、lens vitreous body Bend entering light waves and focus them on the retina Section2. Accessory organs Ⅰ. Eyelids: upper and lower ,consist of 5 layers, ①Skin ②subcutaneous adipose tissue, ③musclar layer: orbicularis oculi ④tarsus: formed by dense connective tissue (tarsal glands) ⑤ palpebral conjunctiva Accessory organs of eye Ⅱ.Conjunctiva : thin mucous membrane 3 parts: • Palpebral conjunctiva : lining inner surface of eyelids; • Bulbar conjunctiva : lining anterior part of sclera; • Conjunctival fornix (superior and inferior): the reflected part of the conjunctiva from the superior and inferior eyelids onto the eyeball. Conjunctival sac Accessory organs of eye Ⅲ.Lacrimal apparatus 1. Lacrimal gland: 2. Lacrimal passages: lacrimal punctum: on each eyelid margin near medial angle lacrimal ductules : in each lid, pass medially, join and enter lacrimal sac Lacrimal sac : in fossa for lacrimal sac, opening into nasolacrimal duct Nasolacrimal duct : opening into inferior nasal meatus Accessory organs of eye Ⅳ.Extraocular m. : 7 levator palpebrae superioris: elvates the upper eyelid. Rectuses: 4 superior rectus inferior rectus medial rectus lateral rectus Obliquuses : 2 Superior obliquus Inferior obliquus Accessory organs of eye Muscle levator palpebrae superioris Action N. supply elvates upper eyelid Ⅲ Superior rectus turns eyeball superomedially Ⅲ Inferior rectus turns eyeball inferomedially Ⅲ Medial rectus turns the eyeball medially Ⅲ Lateral retus turns the eyeball laterally Ⅵ Superior obliquus turns eyeball inferolaterally Ⅳ Inferior obliquus turns eyeball superolaterally Ⅲ Accessory organs of eye Accessory organs of eye Ⅴ. Connective Tissues in the Orbit 1. adipose body of orbit lies between sheath of eyeball and the orbit acts as a protective cushion and shock sorber for the eyeball 2. orbital fasciae a. periorbita b. fascial sheath of eyeball c. sheath of ocular muscles d . orbital septum Section 3. The vessels and nerves of eye Ⅰ. Vessels of eye 1. Artery (1)Ophthalmic a. : Arises from the internal carotid a. Branches: 1) central a. of retina Enters optic nerve, passes toward the optic disk and then fans out to supply the retina The vessels and nerves of eye 1) central a. of retina branches: superior nasal arteriole of retina inferior nasal arteriole of retina superior temporal arteriole of retina inferior temporal arteriole of retina The vessels and nerves of eye 2) short posterior ciliary a. : Choroidal artery 3) long posterior ciliary a. 4) anterior ciliary a. The vessels and nerves of eye Ⅱ.Vein (1) central v. of retina (2) vortex vein (3)anterior ciliary veins (4)Ophthalmic v. a)Superior ophthalmic v. b) Inferior ophthalmic v The vessels and nerves of eye Ⅲ.Nerves optic nerve: oculomotor n. trochlear n. abducent n. ophthalmic n. facial n. superior temporal arteriole of retina superior nasal arteriole of retina inferior temporal arteriole of retina inferior nasal arteriole of retina Sinus venosus sclerae Ciliary Muscle Iridocorneal angle Dilator Pupillae Sphincter Pupillae Lens ciliary zonule Ciliary Processes chapter14 视器The Visual Organ composition fibrous tunic : cornea sclera iris walls vascular tunic: ciliary body choroid retina: Eyeball choroidal part: pars opticaretinae pars ciliaris pars iridiac aqueous humor lens vitreous body accessory organs of eyeball pars caeca retinae