* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download New Emerging Infectious Diseases
Swine influenza wikipedia , lookup
Taura syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Canine distemper wikipedia , lookup
Canine parvovirus wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Avian influenza wikipedia , lookup
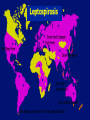
NEW EMERGING AND REEMERGING DISEASES • Definitions •New Emerging infectious diseases newly identified or previously unknown infections •Re-emerging infectious diseases re-appearance of, or increase in number of, infections from a disease previously known 2 New Emerging Infectious Diseases: Definition Diseases of infectious origin whose incidence in humans has increased within the recent past or threatens to increase in the near future, including: previously unknown infectious diseases; known but appearing in new geographic areas; or increase abruptly; 3 4 Infectious Diseases: A World in Transition 5 6 7 •The human species Continues to change and to change its surroundings: the ways we live, work, relax; the places we go; the foods we eat ... •The changing nature of our interactions with each other and with our environment alters the dynamics of disease epidemiology and exposes us to new threats. 8 9 10 11 ENVIRONTMENT 12 13 14 15 EMERGING DISEASES ARE NOT NEW TO MANKIND 16 17 NEWLY IDENTIFIED PHATOGENS (1973- 1989) 1973 Rotavirus 1975 Parvovirus B19 1976 Cryptosporidium parvum 1977 Ebola virus, Legionella pneumophilia, Hantaan virus, Campylobacter jejuni 1980 HTLV-1 1981 Staphylococcus toxin 1982 E. coli O157, HTLV-2, Borrelia burgdoferi 1983 HIV virus, Helicobacter pylori 1988 HHV-6, Hepatitis E 1989 Ehrlichia chaffeensis, Hepatitis C 18 Newly identified pathogens (1990 - 1999) 1990 Guanarito virus 1991 Encephalitozzon hellem 1992 Vibrio cholerae O139 1992 Bartonella henselae 1993 Sabia virus 1995 Hepatitis G virus 1995 Human herpesvirus-8 1996 TSE causing agent (nvCJD) 1997 Avian influenza (Type A H5N1) 1999 Nipah virus, Avian Influenza H9N1, Stealth viruses 19 Newly identified pathogens (1997 – 2009) •1998 Nipah encephalitis •2003 SARS •2004 Avian influenza H5N1 •2006 Chikungunya- re-emergence •2009 Pandemic influenza A H1N1 20 Since 1973 39 newly identified pathogens, examples : 1973 Rotavirus 1977 Ebola virus, Hantaan virus 1980 HTLV-1 1983 HIV virus H pylori 1988 Hepatitis E 1992 Vibrio cholerae O139 1996 Avian influenza A (H5N1) 1999 Nipah virus 2003 SARS Others re-emerged Dengue/DHF Cholera Malaria Chikungunya J. Encephalitis Leptospirosis N.meningitidis 21 Current estimates1,415 microbes are infectious for human. Of these, 868 (61%) considered zoonotic. 70% of newly recognized pathogens are zoonoses. 22 Current estimates1,415 microbes are infectious for human. Of these, 868 (61%) considered zoonotic. 70% of newly recognized pathogens are zoonoses. 23 Risk factors for emerging zoonoses: close human animal interface in Asia 24 Examples of recent emerging and re-emerging diseases 25 Emergence of HPAI (H5N1) 2003-June 2008 a total of 385 cases with 243 deaths 26 GEOGRAPHIC DISTRIBUTION OF PROBABLE CASES 27 SARS: THE FIRST EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASE OF THE 21ST CENTURY 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 EMERGENCY DENGUE FEVER/DENGUE HAEMORRHAGIC FEVER 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55