* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Zener diode and regulators
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Optical rectenna wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
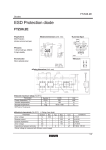
Zener Diode Zener diode and regulators Zener diodes are used to maintain a fixed voltage. They are designed to 'breakdown' in a reliable and non-destructive way so that they can be used in reverse to maintain a fixed voltage across their terminals. The diagram shows how they are connected, with a resistor in series to limit the current. Cont.… • A Zener Diode is a special kind of diode which permits current to flow in the forward direction as normal, but will also allow it to flow in the reverse direction when the voltage is above a certain value - the breakdown voltage known as the Zener voltage. • Commonly available Zener diodes are available with breakdown voltages (“Zener voltages”) anywhere from 1.8 to 200 V. History of Zener The device was named after Clarance Melvin Zener, who discovered the Zener effect. Zener reverse breakdown is due to electron quantum tunneling caused by a high strength electric field. Zener V-I characteristics Cont.… The illustration above shows this phenomenon in a Current vs. Voltage graph. With a zener diode connected in the forward direction, it behaves exactly the same as a standard diode - i.e. a small voltage drop of 0.3 to 0.7V with current flowing through pretty much unrestricted. In the reverse direction however there is a very small leakage current between 0V and the Zener voltage - i.e. just a tiny amount of current is able to flow. Then, when the voltage reaches the breakdown voltage (Vz), suddenly current can flow freely through it. For example if you pass a reverse 5V through a 3V zener diode and measure the voltage across the zener diode, that voltage will be 3V. Cont.… • The Zener voltage of a standard diode is high, but if a reverse current above that value is allowed to pass through it, the diode is permanently damaged. • Zener diodes are designed so that their zener voltage is much lower - for example just 2.4 Volts. When a reverse current above the Zener voltage passes through a Zener diode, there is a controlled breakdown which does not damage the diode. • The voltage drop across the Zener diode is equal to the Zener voltage of that diode no matter how high the reverse bias voltage is above the Zener voltage. Cont.… • Zener diodes can be distinguished from ordinary diodes by their code and breakdown voltage which are printed on them. • Zener diode codes begin BZX... or BZY... Their breakdown voltage is printed with V in place of a decimal point, so 4V7 means 4.7V for example. • Zener diodes are rated by their breakdown voltage and maximum power: •The minimum voltage available is 2.4V. •Power ratings of 400mW and 1.3W are common. Circuit symbol and construction Circuit symbol Physical identification Cont.… If the zener diode’s voltage is 12.6 volts and the power supply’s voltage is 45 volts, there will be 32.4 volts dropped across the resistor (45 volts - 12.6 volts = 32.4 volts). 32.4 volts dropped across 1000Ω gives 32.4 mA of current in the circuit. Uses of Zener Diodes • Since the voltage dropped across a Zener Diode is a known and fixed value, Zener diodes are typically used to regulate the voltage in electric circuits. • Using a resistor to ensure that the current passing through the Zener diode is at least 5mA (0.005 Amps), the circuit designer knows that the voltage drop across the diode is exactly equal to the Zener voltage of the diode. Types of Zener Diodes • There are many different kinds of Zener diodes. At Future Electronics we stock many of the most common types categorized by power dissipation, nominal working voltage, forward (drive) current, forward voltage, packaging type and maximum reverse current. • The parametric filters on our website can help refine your search results depending on the required specifications. • The most common values for nominal working voltage are 5.1 V, 5.6 V, 6.2 V, 12 V and 15 V. We also carry Zener diodes with nominal working voltage up to 1 kV. Forward (drive) current can have a range from 200 uA to 200 A, with the most common forward (drive) current being 10 mA or 200 mA. Applications for Zener Diodes: • Zener diodes can be found in several applications. Some of these are: voltage stabilizers or regulators (in shunt mode), surge suppressors for device protection, peak clippers, switching operations, reference elements and in meter protection applications. • The constant reverse voltage of a Zener diode renders it a very useful component in regulating the output voltage against variations in the load resistance or variations in the input voltage from an unregulated power supply. The current through the Zener diode will change in order to keep the voltage within the threshold limits of Zener action and the maximum power that it can dissipate. Waveform clipper Two Zener diodes facing each other in series will act to clip both halves of an input signal. Waveform clippers can be used to not only reshape a signal, but also to prevent voltage spikes from affecting circuits that are connected to the power supply. Voltage shifter A Zener diode can be applied to a circuit with a resistor to act as a voltage shifter. This circuit lowers the input voltage by a quantity that is equal to the Zener diode's breakdown voltage. Voltage regulator A Zener diode can be applied to a circuit to regulate the voltage applied to a load, such as in a linear regulator. Choosing the Right Zener Diode: • When you are looking for the right Zener diodes, with the FutureElectronics.com parametric search, you can filter the results by various attributes: by Forward (Drive) Current (200 uA, 10 mA, 200 mA, 250 mA, 1A,…), Forward Voltage (700 mV, 900 mV, 1.1 V, 1.2 V, 1.5V,…) and Power Dissipation (from 100 mW to 1.5 kW) to name a few. • You will be able to find the right semiconductor chip when designing a circuit that requires a Zener diode regulator, power Zener diode, 5v Zener diode, 12v Zener diode, 18v Zener diode, 24v Zener diode, high voltage Zener diode, low voltage Zener diode, Zener diode rectifier, 3v Zener diode or for designing any Zener diode circuits. Voltage clamps: Limiting signals with Zener diodes Thank you for listening