* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Phet Lab: Circuits - Oakland Schools Moodle
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
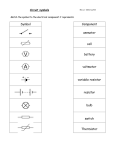
Phet Lab: Circuits with Diagrams DO NOT PRINT; SUBMIT TO MOODLE Name_____________________________ Block____ Save this document to your own folder, calling it: NAME Phet Circuit Diagrams 1) Create a circuit with a battery, one resistor, and a closed switch. You may use either lifelike or schematic view. Use Control-PrtScn (Print screen function) to copy your drawing, and paste it into this paper in the space below. Click on the picture, and then crop the picture using the button so it only includes your circuit. Expand the picture to be easily readable. 2) Click on non-contact ammeter, and move it so the crosshairs are over a wire in the circuit. Adjust the properties of the battery by right-clicking on it. Set its resistance to zero, and then adjust the voltage so the current is as close to 2.0 Amperes as you can get. Paste your diagram here. 3) a) Add a second resistor in series with the first one. Change the resistance of each resistor to approximately 8 Ohms, and adjust the voltage of the battery to 48 Volts. b) Record actual values here: R1 = R2 = c) Use a calculator to calculate V/Total R: Total R = V= I= It should match the measured current above. d) Click on all circuit elements to “show value”, and then copy and paste the diagram below. 4) Create a new parallel circuit. Give yourself room to work! a) Each branch should have one resistor, and one switch controlling only that branch. Hint: Think of our road system, with a lot of different possible routes from 7 Mile to 8 Mile. b) You should insert a regular ammeter in each branch of the circuit which shows the current through that branch, and one ammeter near the battery which will show the total current through the whole circuit. c) Be sure to click “Show Values” d) After you paste in the diagram, you should use Ohm’s law to calculate the current through each ammeter, and see if it matches the actual values on the screen. CALCULATIONS: Resistor 1: Resistor 2: Resistor 3: