* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5 - ChemWeb (UCC)
Sol–gel process wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Bond valence method wikipedia , lookup
Metal carbonyl wikipedia , lookup
Jahn–Teller effect wikipedia , lookup
Stability constants of complexes wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Spin crossover wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
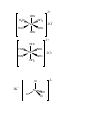
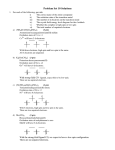
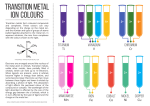
Exercise Complete and balance the following equations. Name the reaction type in each case: (a) N2 + H2 (b) P4 + 3O2 (c) SO2 + H2O 5. Transition Elements Section 23.7, p. 1010 - 1013 Elements in Groups 3 to 11 are the transition elements or transition metals. The valence shell of 1st row transition elements consists of the 4s and the 3d subshells. The valence electrons are the associated electrons. e.g. Cobalt, Co, [Ar]4s2 3d7 has 9 valence electrons. 5.1 Compounds of transition elements. Most transition metal compounds contain covalent bonds between ligands and central metal atom. Some are simple polyatomic ions, e.g. permanganate [MnO4]-, a polar covalent compound. Electrons - shared between central Mn and O ligands. However most are "complex compounds" or “complexes”. These contain more complicated ligands like H2O, NH3. E.g. Fe forms complexes with six H2O molecules, [Fe(OH2)6]Cl2, [Fe(OH2)6]SO4. Bonding involves donation of an electron pair from an atom of the ligand to an empty orbital on the metal. e.g. in [Fe(OH2)6]Cl2, each bond formed by donation of one of the lone pairs on the O of the H2O to an empty orbital on the Fe. 5.2. Shape compounds of transition element Incompletely filled d orbitals, cannot use VSEPR. Compounds where the metal has a coordination number of 6, i.e. 6 atoms or groups bonded to it, are octahedral, e.g. [Fe(OH2)6]Cl2, [Fe(NH3)6]Cl2, [Fe(OH2)6]SO4. See handout. Compounds where the metal has a coordination number of 4, i.e. 4 atoms or groups bonded to it are tetrahedral, e.g. K2[FeCl4], K2[FeBr4]. 2+ OH2 H2O OH2 Fe H2O 2Cl- OH2 OH2 2+ NH3 H3N NH3 Fe H3N NH3 2Cl- NH3 2- Cl 2K+ Fe Cl Cl Cl 5.3 Hybridisation Cannot use VSEPR for compounds with incompletely filled d shells so determine hybridisation by ‘inspection’. Octahedral complexes Six electron pairs around the transition element centre, so need 6 hybrid orbitalsformed from one s, three p, and two d a.o.’s so the T.E. is sp3d2 hybridised. e.g. [Fe(NH3)6]Cl2 Fe is sp3d2 hybridised. Tetrahedral complexes Four electron pairs around the transition element centre, so need 4 hybrid orbitals – formed from one s, and three p a.o.’s so the T.E. is sp3 hybridised. e.g. K2[FeCl4] Fe is sp3 hybridised 5.4 Oxidation states (O.S.s) of transition elements Same rules as before apply. For example, MnF2 O.S. F = -1; Thus O.S. Mn = +2 KMnO4 O.S. O = -2; O.S. K = +1. Thus O.S. Mn =+7 K2[FeCl4] O.S. Cl = -1; O.S. K = +1. Thus O.S. Fe = +2 [Fe(NH3)6]Cl2 O.S. Cl = -1; Note: NH3 ligand has no overall charge. O.S. Fe = +2 Question: Calculate the O.S. of Fe in [Fe(OH2)6]Cl2. Reactions of Transition Elements and Their Compounds E.g. Iron, Fe 1. Redox reactions Examples: (a) 2Fe + 3Cl2 2FeCl3 O.S. Fe goes from 0 to +3, i.e. Fe is oxidised O.S. Cl goes from 0 to –1, i.e. Cl is reduced (b) Fe + 2FeCl3 3FeCl2 (c) 2Fe + O2 2FeO Question: Calculate the O.S. of all the elements in reactions (b) and (c) above. Hence, identify the species being oxidised and the species being reduced in each reaction. 2. Reactions with H2O – hydrolysis. Examples: FeCl2 + 6H2O [Fe(OH2)6]Cl2 FeCl3 + 6H2O [Fe(OH2)6]Cl3In both reactions, the Fe-containing products are octahedral, i.e contain the [Fe(OH2)6]n+ cation. 3. Precipitation reactions In the practical you do: [Fe(OH2)6]2+(aq) + 3[C2O4]2[Fe(C2O4)3]4-(s) + 6H2O (l) (aq) [Fe(C2O4)3]4- is insoluble in water forming a precipitate. The ligand [C2O4]2- has exchanged with the H2O ligands around Fe. Questions 1. Give the O.S. of the transition element in the following complexes: (a) [Fe(NH3)6]Cl3 (b) [Ni(H2O)6]F2 (c) Na2[CoCl4] 2. Draw the structure of the transition element part of the following complexes and name the type of geometry. (a) [Fe(NH3)6]Cl3 (b) Na2[CoCl4] 3. Give the hybridisation of the transition element in: (a) [Fe(NH3)6]Cl3 (b) Na2[CoCl4]