* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TEST BANK ~ Cardiovascular System
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
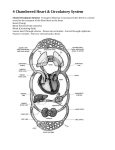
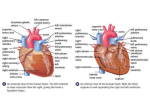
10/15/06 Dr. Vince Scialli BSC 1086 EXAM 2 ~ TEST BANK ~ Cardiovascular System 1. The portion of the intrinsic cardiac conduction system located in the interatrial septum is the ? a. AV node b. SA node c. Tricuspid node d. Purkinje fibers e. none of the above 2. Which is/are true about extrinsic stimulation of the heart? a. sympathetic stimulation increases force of contraction. b. vagus nerve stimulation increases heart rate c. sympathetic stimulation decreases heart rate d. exercise increases ventricular filling time e. all of the above 3. Freshly oxygenated blood is first received by the? a. vena cava b. right atrium c. pulmonary artery d. left ventricle e. right ventricle 4. Baroreceptors located in the carotid sinus and aortic arch? a. sense changes in O2 and CO2 blood levels b. sense changes in Ca+ blood levels c. sense changes in venous pressure d. sense changes in arterial pressure e. sense chemical & mechanical changes 5. Which statement does not accurately describe veins? a. veins have less elastic tissue and less smooth muscle than arteries b. veins contain more fibrous tissue than arteries c. most veins in the extremities have valves d. all veins carry deoxygenated blood e. veins can contain up to 65% of the bodies blood volume 6. Which of the following tissue is responsible for vasoconstriction of blood vessels? a. elastic tissue b. smooth muscle c. tunica externa d. collegen tissue e. adipoise tissue 7. Peripheral tissue & vascular resistance? a. is inversely related to the diameter of the arterioles b. tends to increase if blood viscosity increases c. is directly proportional to the length of the vascular bed d. increases with sympathetic stimulation due to vasoconstriction e. all of the above 10/15/06 Dr. Vince Scialli BSC 1086 8. Which of the following could lead to decreased venous return of blood to the heart? a. increased muscular activity b. an increase in blood volume c. an increase in venous pressure d. damage to the venous valves e. sympathetic stimulation 9. Arterial blood pressure increases in response to? a. catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla b. increase in stroke volume c. increase in heart rate d. artheriosclerosis e. all of the above 10. The structure of a capillary wall differs from that of a vein or an artery because? a. It has a single tunic, only the tunica interna b. it has two tunics instead of three tunics c. it is less fragile than artery or vein walls d. the diameter is larger than arteries and veins e. all of the above 11. The chemoreceptors in the carotid and aortic bodies are sensitive to? a. changes in arterial pressure b. changes in carbon dioxide, pH, and oxygen blood levels c. decrease in venous blood pressure d. changes in arterial elasticity e. all of the above 12. The myocardium receives its blood supply directly from? a. pulmonary arteries b. coronary arteries c. aorta d. coronary sinus e. the carotid arteries 13. Blood flow in the capillaries is slow & intermittent because of? a. venous valves which plugs up the capillaries b. large diameter of each individual capillary c. large cross sectional area of the total capillary bed d. thin walls of veins e. very high blood pressure in capillaries compared to arteries 14. Which occurs when a depolarization wave travels through the myocardium? a. decreased Na+ influx, increased Ca+ influx, increased K+ influx b. decreased Na+ influx, increased Ca+ influx, increased K+ efflux c. increased Na+ influx, decreased Ca+ influx, increased K+ influx d. increased Na+ influx, increased Ca+ influx, increased K+ influx e. increased Na+ influx, increased Ca+ influx, increased K+ efflux 10/15/06 Dr. Vince Scialli BSC 1086 15. Which of the following statements about the left side of the heart is false? a. deoxygenated blood returns to the left atrium b. the left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood c. a bicuspid valve or mitral valve is between the left atrium and left ventricle d. the left ventricle pumps blood into the systemic circulation e. the left sided heart failure results in fluid build up in the lungs causing pulmonary edema 16. Which circuit is under the greatest hydrostatic (fluid) pressure? a. pulmonary circuit b. systemic circuit c. short circuit d. sympathetic circuit e. parasympathetic circuit 17. Which type of artery is found closest to the heart? a. arteriole b. distributing artery c. elastic artery d. muscular artery e. metarteriole 18. When the semilunar (Aortic & Pulmonic) valves are open, which of the following are occurs? a. AV valves are closed b. ventricles are in systole c. blood enters the aorta d. blood enters the pulmonary artery e. all of the above 19. An ECG or EKG provides information about? a. movement of an electrical excitation wave across the heart b. coronary circulation c. valve impairment d. cardiac output e. all of the above 20. The sequence of depolarization of the heart chambers, as reflected by the EKG, is/are? a. right atrium, right ventricle, left atria, left ventricle b. both atria together, followed by both ventricles together c. left ventricle followed by right ventricle d. left atria, left ventricle, right atria, right ventricle e. both ventricles followed by both atria 21. The fact that the left ventricle wall is thicker than the right ventricle wall reveals that it? a. pumps a greater volume of blood b. pumps blood through a smaller diameter valve c. pumps blood a greater distance & against a greater resistance d. pumps blood a short distance to the lungs e. pumps blood to a lower pressure systemic system 22. A uniqueness about the coronary artery blood flow is that? a. the coronary artery contains venous unoxygenated blood being pumped to the lungs b. the coronary artery contains venous oxygenated blood returning to the left atrium c. the coronary artery contains arterial unoxygenated blood returning to the right atrium d. coronary artery blood flow occurs during ventricular diastole or ventricular filling e. coronary artery blood flow occurs during ventricular systole or ventricular emptying 10/15/06 Dr. Vince Scialli BSC 1086 23. The chordae tendineae? a. closes the AV valves b. opens the semilunar valves c. prevents the AV valve flaps from everting or umbrellering into the atria d. attaches the heart muscle to the mediastinum e. are the major sites of coronary artery blockage 24. In the heart, which one of the following applies? a. heart contractility is controlled only by extrinsic stimulation form the brain b. cardiac muscle can contract for long periods without oxygen due to pacemakers c. spontaneous depolarization of cardiac cells can occur in the absence of nerve stimulation due to pacemakers d. the AV node sets the pace or heart rate in a normal heart e. heart is controlled mainly by extrinsic endocrine stimulation & release of hormones 25. The valve between the right atrium and right ventricle is called the? a. bicuspid valve b. mitral valve c. tricuspid valve d. semilunar valve e. left AV valve 26. If the connections between the vagus nerve and the heart are severed, the? a. heart will beat slower b. stroke volume will increase c. ventricular filling will increase d. nodal fibers will depolarize more slowly e. heart will beat faster 27 What effect would compressing the vena cava have where it enters the right atrium? a. stroke volume would increase due to more blood flowing into the right ventricle b. heart rate would increase to compensate for lower volume of blood returning to the heart c. heart rate would decrease due to volume overload of blood returning to the heart d. cardiac output would increase due to more blood returning to the right atrium e. heart rate would decrease since less blood volume is returning to the heart 28. The great cardiac vein drains blood from the heart muscle into the? a. left ventricle b. right ventricle c. right atrium d. pulmonary artery e. left atrium 29. The autonomic extrinsic centers for cardiac function are located in the? a. myocardial tissue of the heart b. medulla oblongata c. adrenal medulla d. SA node e. AV node 10/15/06 Dr. Vince Scialli BSC 1086 30. The serous membrane covering the inner surface of the heart & heart valves is the? a. parietal pericardium b. visceral or serous pericardium c. serous pericardium d. epicardium e. endocardium 31. The simple squamous epithelium and areolar connective tissue covering the heart valves and blood vessels is commonly called? a. mesothelium b. endothelium c. myothelium d. epithelium e. perithelium 32. The structure in the fetal heart that allows blood flow from the right atrium to the left atrium while the lungs develop prior to birth is the? a. foramen ovale b. foramen magnum c. fossa ovalis d. ventricular septal defect e. interatrial septum 33. Blood leaves the right ventricle into the pulmonary artery by passing through the? a. aortic pulmonic valve b. mitral valve c. tricuspid valve d. right AV valve e. pulmonic valve 34. The p-wave of the EKG appears as the? a. ventricles depolarize b. atria depolarize c. ventricles repolarize d. ventricles contract e. atria fill 35. During diastole, a chamber of the heart? a. relaxes and fills with blood b. contracts and pushes blood into the adjacent chamber c. experiences a sharp increase in volume pressure d. reaches a pressure of 120mmHG on the right side e. reaches a pressure on 8mmHG on the left side 36. During the cardiac cycle, the amount of blood ejected from the left ventricle each time the semilunar valve opens, is? a. three to five times greater in volume than in the right ventricle b. the stroke volume c. end-diastolic volume d. end-systolic volume e. the cardiac output 10/15/06 Dr. Vince Scialli BSC 1086 37. The cells of the nodal conducting system of the heart send out impulses in the following order? a. AV node, SA node, bundle of his, bundle branches, purkinje fibers b. AV node, internodal pathway, SA node, bundle of his, bundle branches, purkingi fibers c. SA node, internodal pathway, AV node, bundle branches, bundle of his, purkinji fibers d. SA node, internodal pathway, AV node, bundle of his, bundle branches, purkinji fibers e. SA node, AV node, bundle branches, bundle of his, purkinji fibers 38. Extremely rapid muscle contractions usually do not occur in normal cardiac muscle cells because? a. cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own b. there is no neural or hormonal stimulation to cardiac muscles c. the plateau effect of Ca+ ion influx extends the refractory period until the muscle cell relaxes d. the refractory period ends before the muscle cell reaches peak tension e. the rapid efflux of Na+ ion initiates depolarization prior to repolarization 39. The amount of blood forced (stroke volume) out of the heart during systole depends on? a. the degree of stretching at the end of ventricular systole b. the contractility of the atria during diastole c. the contractility of the ventricle at the beginning of diastole d. the degree of stretching at the end of ventricular diastole e. the cardiac output 40. The cardiac output cannot increase indefinitely because? a. the available filling time becomes shorter as the heart rate increases b. the rate of spontaneous depolarization is totally contolled by the AV nodes c. the ion concentration of pacemaker cell membranes decreases over time d. cardiac output is totally dependent on stroke volume e. cardiac output is totally dependent on heart rate 41. The portion of the intrinsic cardiac nodal conduction system flowing through the interventricular septum is/are the ? a. AV node b. SA node c. Tricuspid node d. Purkinje fibers e. Right & Left Bundle Branches 42. The layer of the arteriole that provides the properties of contractility & elasticity is the? a. tunica adventitia b. tunica media c. tunica externa d. tunica intima e. tunica interna 43. Blood vessels that supply the walls of arteries and veins with blood are? a. coronary arteries b. coronary sinuses c. portal vessels d. vasa vasorum e. microarterioles 10/15/06 Dr. Vince Scialli BSC 1086 44. Two way exchange of substances between blood & body tissue cells occurs mostly through? a. b. c. d. e. arterioles capillaries veins endothelial cells b&d 45. Large molecules such as peptides and proteins move into and out of the bloodstream by way of? a. continuous capillaries b. fenestrated capillaries c. thoroughfare channels d. gap junctions e. intercalated discs 46. The blood vessels that collect blood from all tissues and organs regardless of oxygenation level, and return it to the heart are? a. veins b. arteries c. arterioles d. capillaries e. plasma membranes 47. Blood is normally transported through the venous system and back to the heart by means of? a. gravity b. muscle contractions c. the respiratory pump d. standing on ones head e. b & c 48. The most important single factor in determining vascular resistance is? a. viscosity of the blood b. diameter of blood vessels c. turbulence due to irregular surfaces of blood vessels d. length of blood vessels e. all of the above are most important 49. The vein that collects most of the venous blood from below the diaphragm is the? a. superior vena cava b. pulmonary artery c. pulmonary vein d. aorta e. inferior vena cava 50. Elevated levels of the hormone ANP will produce? a. increased fluid loss through the kidneys b. increased aldosterone release and water retention c. increased blood volume d. increased blood pressure e. increased venous return to the heart 10/15/06 Dr. Vince Scialli BSC 1086 51. The secretion of ADH & aldosterone to retain fluid are typical of the body’s long-term compensation following? a. a heart attack b. hypertension c. sodium and fluid retention d. serious hemorrhage, dehydration or shock e. high blood pressure 52. The pectinate muscles are? a. prominent muscular ridges in the walls of the ventricles b. papillary muscles in the walls of the ventricles that prevent umbrellering of the AV valves c. prominent muscular ridges that run along the surfaces of the auricles d. muscles that close tha semilunar valves e. muscles connected by chordae tendineae that support the AV valves 53. The cusps of the AV valves are attached to the papillary muscles by the? a. pectinate muscles b. trebaculae carneae c. chordae tendineae d. intratrial septa e. interventricular speta 54. The visceral or inner layer of the pericardium makes up the? a. myocardium b. endocardium c. epicardium d. outermost layer of the heart wall e. c & d 55. The atrioventricular valve on the side of the heart that receives venous blood from the systemic circulation is the? a. mitral valve b. bicuspid valve c. tricuspid valve d. aortic semilunar valve e. pulmonic valve 56. Compared to the right ventricle, the left ventricle has all the following characteristics, except? a. a thicker wall b. is rounder in cross section c. relaxes more slowly d. develops much higher pressure when it contracts e. produces 6-7 times more force during systole 10/15/06 Dr. Vince Scialli BSC 1086 57. The following is a list of structures associated with the heart. 1. right atrium 2. left atrium 3. right ventricle 4. left ventricle 5. vena cava 6. aorta 7. pulmonary artery 8. pulmonary veins 9. mitral valve 10. aortic valve 11. pulmonic valve 12. tricuspid valve 13. lung capillaries What is the correct order for the flow of blood entering from the systemic circulation? a. 5, 1, 12, 3, 11, 8, 13, 7, 2, 9, 4, 10, 6 b. 5, 1, 12, 3, 11, 7, 8, 13, 2, 9, 4, 10, 6 c. 5, 2, 12, 3, 11, 7, 13, 8, 1, 9, 4, 10, 6 d. 5, 1, 12, 3, 11, 7, 13, 8, 2, 9, 4, 10, 6 e. 5, 1, 9, 3, 11, 7, 13, 8, 2, 12, 4, 10, 6 58. The heart is innervated by what nerves? a. parasympathetic nerves predominantly b. sympathetic nerves predominantly c. both sympathetic & parasympathetic nerves d. the vagus nerve only e. neither sympathetic or parasympathetic nerves since the heart has its own intrinsic authyryhthmic system of nodes called pacemakers 59. In cardiac muscle, the depolarization phase of the action potential is the result of? a. increased membrane permeability to sodium ions b. increased membrane permeability to calcium ions c. increased membrane permeability to potassium ions d. decreased membrane permeability to potassium ions e. decreased membrane permeability to calcium ions 60. In cardiac muscle, the plateau phase of the cardiac muscle action potential, is due to? a. the efflux & movement of fewer sodium ions across the membrane b. the calcium channels remaining open longer than the sodium channels c. the increased membrane permeability to potassium resulting in K+ influx d. a decrease in the amount of calcium diffusing out of the cell e. an increase in the membrane permeability to sodium ions 61. During ventricular systole, the? a. atria are contracting b. blood is entering the ventricles c. AV valves are closed d. pressure in the ventricles declines e. ventricles are relaxed 62. When a clot forms on the plaque in a coronary vessel and obstructs blood flow to the muscle, the clot formation & blockage, is referred to as a(n)? a, angioplasty b. myocardial infection c. coronary thrombosis d. angina pectoris e. pulmonary embolism 10/15/06 Dr. Vince Scialli BSC 1086 63. Abnormally slow conduction through the ventricles would change the shape of the? a. p wave b. t wave c. QRS complex d. P-R interval e. S-T segment 64. If the conduction between the SA node and AV node becomes blocked? a. the ventricles will beat faster b. the ventricles will beat more slowly c. the ventricular rate of contraction will not change d. the stroke volume will decrease e. the cardiac output will increase 65. The first heart sound is heard when the? a. AV valves open b. AV valves close c. semilunar valves close d. atria contract e. blood enters the aorta 67. The volume of blood ejected from each ventricle during a contraction is called the? a. end-diastolic volume b. end-systolic volume c. stroke volume d. cardiac output e. cardiac reserve 68. The cardiac output is equal to the? a. difference between end-diastolic volume and end-systolic volume b. the product of heart rate and stroke volume c. difference between the stroke volume at rest and stroke volume during exercise d. stroke volume less the end-systolic volume e. product of heart rate and blood pressure 69. Each of the following would increase heart rate, except? a. increased sympathetic stimulation of nodal fibers b. increased parasympathetic stimulation of nodal fibers c. increased levels of epinephrine in the blood d. increased permeability of the myocardium to sodium ions e. inhibition or blockage of the vagus nerve 70. In which of the following situations would the end-systolic volume be the greatest? a. when sympathetic stimulation of the heart is increased b. when parasympathetic stimulation of the heart is increased c. when the force of myocardial contraction is increased d. when the intracellular stores of calcium are increased within the heart cell e. when stroke volume is increased 10/15/06 Dr. Vince Scialli BSC 1086 71. In which case would the stroke volume be the greatest? a. when venous return is the greatest thus increasing EDV b. when venous return is decreased thus decreasing EDV c. when the force of contraction is decreased thus increasing ESV d. when the difference between end-diastolic and end-systolic volume is small e. when calcium channels are blocked preventing depolarization & contractility 72. If one suffers from damaged or regurgitating mitral valve insufficiency, this condition could cause? a. increased cardiac output from the right ventricle b. increased cardiac output from the left ventricle c. decreased heart rate d. fluid congestion in the lungs resulting from left sided failure e. fluid accumulation in tissues resulting from right sided failure 73. Compared to arteries, veins? a. are more elastic b. have more smooth muscle in their tunica media c. have a pleated epithelium d. have thinner walls and valves e. hold their shape better when cut 74. The blood vessels that play the most important role in regulation of blood flow to tissue and susceptible to the effects of blood pressure, are the? a. arteries b. arterioles c. veins d. venules e. capillaries 75. The following is a list of the vessels that contains blood moving too & from the heart: 1. venules 2. arterioles 3. capillaries 4. elastic arteries 5. medium veins 6. large veins 7. muscular arteries The correct order in which blood passes through these structures leaving the heart and returning is? a. 7,4,2,3,1,5,6 b. 6,5,1,3,2,7,4 c. 5,6,1,3,2,7,4 d. 2,7,6,3,1,5,6 e. 4,7,2,3,1,5,6 76. The blood vessels whose walls permit the majority of exchange between the blood and surrounding tissue are a. arteries b. arterioles c. veins d. veinules e. capillaries 10/15/06 Dr. Vince Scialli BSC 1086 77. Blood moves forward through veins by all of the following, except? a. pressure in veins is lower than in arteries b. contraction-relaxation pumping & pulsation of smooth muscle in walls of veins c. with the aid of the thoraco-abdominal (thoracic)pump d. valves in veins prevent backflow of blood e. aid of contraction of skeletal muscle 78. Blood flow through the circulatory system is affected by all of the following, except? a. the presence or absence of collateral portal systems b. the viscosity of blood c. the amount of friction in blood vessels d. the length and diameter of blood vessels e. pressure differences 79. Vascular resistance is related to all of the following, except? a. length of a blood vessel b. solute concentration of interstitial fluids c. nature of & turbulence of blood flow d. viscosity or thickness of the blood e. diameter of a blood vessel 80. As blood travels from the aorta toward the capillaries, the? a. pressure increases b. resistance increases c. flow increases d. viscosity increases e. diameter of blood vessels increase 81. Blood pressure is influenced by all of the following, except? a. age b. sex c. capillary density of the skin d. time of the day e. body size 82. Blood pressure increases with all of the following, except? a. increased cardiac output b. peripheral resistance c. blood volume d. parasympathetic stimulation e. force of cardiac contraction 83. The difference between the systolic and diastolic pressure is called? a. critical pressure b. mean arterial pressure c. pulse pressure d. blood pressure e. circulatory pressure 10/15/06 Dr. Vince Scialli BSC 1086 84. Which one of the following will not result in a decrease in blood pressure? a. peripheral vasodilation b. decreased blood volume c. decreased peripheral resistance d. increased levels of ANP (atrial natriuretic peptice) e. increased levels of aldosterone 85. Which one of the following will not result in increased blood flow to tissue? a. increased blood volume b. increased vessel diameter c. increased blood pressure d. increased peripheral resistance e. increased heart rate 86. Blood flow velocity is the slowest in which one of the vessels listed below? a. capillaries b. arterioles c. venules d. arteries e. veins 87. To which organ(s) is/are the volume blood flow the highest during exercise? a. heart muscle b. skeletal muscle c. brain d. skeletal muscle & brain e. skeletal muscle, brain, & heart muscle 88. To which organ(s) is/are the volume blood flow the highest during rest?? a. brain b. heart muscle c. skeletal muscle d. abdominal organs e. kidneys & skeletal muscle 89. The goal of cardiovascular regulation includes all of the following, except? a. ensure blood flow changes occur at the appropriate times b. ensure blood flow changes occur in the appropriate areas c. ensure sufficient numbers of blood cells are in the blood to meet emergency situations d ensure changes occur without drastically altering blood pressure e. ensure changes occur without drastically altering blood flow to vital organs 90. Cardiovascular function is regulated by all of the following, except? a. cerebral cortex b. medulla oblongata c. intrinsic or autorhythmic factors d. endocrine factors e. neural factor 10/15/06 Dr. Vince Scialli BSC 1086 91. Stimulation of the aortic baroreceptors, due to a change in blood pressure, first results in? a. stimulation of the cardioaccelerator center in the adrenal medulla b. changes in sympathetic centers within the heart c. changes in parasympathetic centers within the heart d. stimulation of the vasomotor center resulting in vasoconstriction or vasodilation e. possible adjusting changes in cardiac output 92. Elderly individuals usually have all of the following, except? a. reduction in cardiac output b. changes in nodal activity and conducting cells c. progressive atherosclerosis d. vessel walls become less tolerant to sudden pressure changes e. increased elasticity of vessel walls increasing the risk of aneurysm 93. Factors that increase the risk of atherosclerosis include all of the following, except? a. smoking b. lack of exercise c. high fat diets d. family history of hypotension e. obesity 94. Which of the following conditions would have the greatest effect on peripheral resistance? a. doubling the length of a vessel b. doubling the diameter of a vessel c. doubling the viscosity of the blood d. doubling the turbulence of the blood e. doubling the number of formed elements in the blood 95. Which of the following factors will not increase peripheral resistance? a. increased sympathetic stimulation b. elevated levels of catecholamines c. vasodilation d. irregularities in the walls of blood vessels caused by plaques e. factors that cause increase hematocrit or packed cell volume of RBC’s 96. Which of the following factors will not increase cardiac output? a. increase venous return b. decreased parasympathetic stimulation of the heart c. increase sympathetic stimulation to the heart d. increased blood concentrations of insulin e. stimulation of the heart by catecholamines 97. Edema or fluid entering the tissue would likely occur when? a. the concentration of protein in the blood increases b. hemorrhage or decreased blood volume occurs c. the heart becomes insufficient as a pump d. blood hydrostatic pressure in the capillaries decreases e. blood hydrostatic pressure in a capillary is equal to the blood osmotic pressure 10/15/06 Dr. Vince Scialli BSC 1086 98. When a person rises quickly from a prone or sleeping position? a. the carotid baroreceptors become less active b. venous return is increased c. reflex vasoconstriction of peripheral blood vessels occurs d. heart rate decreases e. the cardioaccelerator center in the medulla oblongata becomes less excitable 99. If a person has a blood pressure of 120 / 80, their mean arterial pressure would be? a. 200 b. 120 c. 80 d. 40 e. 93 100. If someone falls and badly cuts a leg and severs several major vessels, one would expect to observe all of the following, except? a. compensatory increased heart rate b. increase in blood pressure due to severe loss of fluid volume c. increased secretion of renin by the kidney to retain sodium & increase fluid volume d. lower blood pressure due to a loss of fluid volume e. increased secretion of aldosterone & ADH to retain fluid Matching Determine if blood in the vessel/organ indicated in the left column is oxygenated blood (indicate with “A”) or unoxygenated blood (indicate with “B”). If mixed, indicate with a “C”. A = Oxygenated B = Un-oxygenated C = Mixed 101. __________ Right Atrium 102. __________ Pulmonary Artery 103. __________ Pulmonary Veins 104. __________ Aorta 105. __________ Right Ventricle 106. __________ Left Ventricle 107. __________ Left Atrium 108. __________ Coronary Artery 109. __________ Thoracic Artery 110. __________ Carotid Artery 111. __________ Azygus Vein 112. __________ Pulmonary Trunk 113. __________ Aortic Arch 114. __________ Nose Bleed 115. __________ Capillaries __________ Blood from skin cut Fill in the Blanks 116. _________________________ Major mechanism of aldosterone release? 117. _________________________ Hormone produced by heart that lowers blood pressure and helps to fine tune blood pressure? (direct antagonist to aldosterone) 10/15/06 Dr. Vince Scialli BSC 1086 118. _________________________ Phase of cardiac cycle when ventricular filling occurs? Also name the phase when ventricular contraction occurs? (Name in order asked) 119. _________________________ If the stroke volume is 100 ml/beat and the heart rate is 55 beats/minute, what is the cardiac output? 120. ___________/______________ What is the average normal systolic pressure in an adult? What is the normal average diastolic pressure? (Indicate as systolic / diastolic) 121. _________________________ Calculate the mean arterial pressure if the blood pressure = 150/90? 122. __________________________ The difference between systolic and diastolic pressure is called the? 123. _________________________ What is the name for abnormal heart sounds caused by abnormal heart blood flow? 124. _________________________ Component of the EKG that signifies atrial contraction and emptying. (atrial depolarization)? 125. _________________________ Component of the EKG signifies ventricular contraction (ventricular depolarization)? 126. _________________________ Condition where impulses sent through the atria do not reach the ventricles? 127. _________________________ What does an EKG show if the SA node is not firing impulses? 128. _________________________ A very erratic, bizarre, irregular EKG signifies what dangerous ventricular arrhythmia? 129. _________________________ General term used to describe an abnormally fast heart rate > 100 beats/minute? 130. _________________________ General term used to describe a slow heart rate < 60 beats/minute? 131. _________________________ Name the heart disease condition when the pumping efficiency of the heart is inadequate to meet tissue needs? 132. _________________________ Name the congestive condition that occurs when the left side of the heart fails? 133. _________________________ Name the congestive condition that occurs when the right side of the heart fails? 10/15/06 Dr. Vince Scialli BSC 1086 134. _________________________ What anatomical features do veins of the extremities contain which prevent blood from flowing downhill? 135. _________________________ Name a condition in which vein valves fail to function properly resulting in vein pooling of blood? 136. _________________________ A condition where the diastolic pressure is 90 or more or the systolic pressure is 140 or more? 137. _________________________ Name a reflex controlled by baroreceptors that prevents fainting as a result of rapid posture changes? 138. _________________________ The volume of blood that remains in the ventricles after systole is called the? 139. _________________________ Name the vein which is the longest vein in the body and used in coronary by-pass surgery? 140. _________________________ Name the artery that is used most often for taking a routine pulse? 141. _________________________ Thin sheet of endothelium that lines chambers, valves & vessels? 142. _________________________ Name the event that causes a plateau in cardiac action potential? 143. _________________________ Special cells in the roof of the right atrium that produces pacemaker potentials? 144. _________________________ Neonatal structure remaining open after birth causing a left to right shunt from left atrium to right atrium? 145. _________________________ Neonatal structure remaining open after birth causing a left to right shunt from aorta to pulmonary artery? 146. _________________________ Congenital defect remaining open after birth causing a left to right shunt from left ventricle to right ventricle? 147. _________________________ Congenital defect resulting in a VSD, pulmonic stenosis, dual aortas off both ventricles & enlarged right ventricle? 148. _________________________ A premature or extra contraction of the ventricles due to an excitable condition is called?