* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Causes of World War I and Reasons for United States Entry into the
History of the United Kingdom during the First World War wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of World War I wikipedia , lookup
History of Germany during World War I wikipedia , lookup
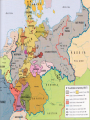
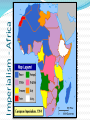
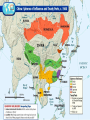
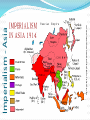
Writing Prompt The start of World War One began YEARS before 1914. In your readings, you have learned many reasons for the cause of the war. What can we learn today from the mistakes of the leaders in 1914? How can we ensure our leaders look at all information available before they make a decision? Terms militarism: The idea that a nation should build up its military forces and use them to achieve the nation’s goals. nationalism: Strong feeling of pride in and loyalty toward one’s country; the belief that the independence and interests of one’s country should come first; the reluctance to work with other nations toward a common goal. Terms Alliance: An agreement by two or more nations to act together, especially in time of war. Diplomacy: The way nations communicate with each other-how they make agreements (international relations). Causes of World War One CAUSES OF WORLD WAR I Long-Term Causes Short-Term Causes Nationalism Militarism Alliances In the late 1800s and early 1900s, certain European ethnic groups were devoted to the interests of their own nations (e.g., Germany, Italy). In order to protect colonies, European nations increased their military strength. As nations increased the size of their military, they formed alliances such as the following to protect themselves: Competition for colonies increased among European countries. Many ethnic minorities desired independence (e.g., Czechs, Slovaks, Poles, Croats, Serbs). Britain & Germany built a large navy, and Germany and Russia increased the size of their armies. Assassination of Archduke Ferdinand --Archduke of Austria was assassinated by a Serbian terrorist group, the Black Hand, on June 28, 1914. --Serbs thought that they might come under control of AustriaHungary. --Austria-Hungary sent demands Triple Alliance to the Serbian government. Serbia (Austria-Hungary, rejected the demands. With the Germany, & Italy) help of Germany, AustriaHungary declared war on Serbia, Triple Entente -Germany declared war on Russia (France, Great (ally of Serbia), and Great Britain Britain, and declared war on Germany. Russia) Diplomacy in Europe 1870-1914 Germany became a nation in 1871. Used to be over 50 small city-states and small kingdoms Unified by Otto Von Bismarck Germany used diplomacy to isolate France. Caused United Kingdom to be suspicious because Germany wanted to build a large navy to compete with England German Naval Expansion Called the “Tirpitz Plan” strengthen the Imperial Navy Started as a small coastal fleet Creating the German High Seas Fleet fleet with global capabilities. This made the United Kingdom afraid Germany would attack her trade fleet. Naval Strength 1870 Naval Strength - 1914 Dreadnaught Battle Cruiser Cruiser Destroyer Submarine/U-Boat Imperialism - Africa The European powers needed to find ways to test their new weapons. Major Powers did not want to fight a war against each other. They fought in the colonies-small battles with natives. They learned how effective their weapons really were Example: Machine Guns – killed 15,000 Zulu warriors over 7 days! http://regentsprep.org/Regents/global/themes/imperialism/africa.cfm Imperialism - Africa Imperialism - Asia Asia was also colonized by a number of European countries: Britain, the Netherlands, France, Germany, and Russia. In 1757, Britain began colonizing India; By the mid-1880s, the British also had control of Singapore, Burma, the Malay Peninsula, and North Borneo. The British brought educational reform and technological advances to these colonies, which eventually led to the colonies’ independence. Imperialism - Asia What does this cartoon say about China? http://regentsprep.org/Regents/global/themes/imperialism/africa.cfm Imperialism - Asia Imperialism and Militarism Set the Stage…. The United Kingdom Each nation thought it was the world superpower then, just as the United States is the superpower today. No one really wanted a war, but the treaties the European powers had signed was supposed to avoid war. knew what the others would do. This caused the European Powers to believe war would not come, because the “other guys” would back down from the conflict. NONE DID! Who Was On What Side Major Allied Powers: Central Powers: British Empire German Empire France Austro-Hungarian Empire Russia Quit in 1917 Had a revolution The United States Joined in 1917 Bulgaria Ottoman Empire Pictures of War…. 1914 to 1917 – Trench Warfare! Not too much movement in Trenches Massive deaths to gain several hundred FEET! The War Began…. Germany Attacked using the Schlieffen Plan. At the Start…. The fighting went swiftly Germans attacking through Belgium Open-country fighting French and British troops falling back quickly It All Changed…..At the MARNE! French, and British troops were in full retreat. Reinforcements sent from Paris in TAXIS! The Allied Armies stop to dig in at the Marne River. 1st use of trenches, would use from now on. bringing to an end the war of movement The war became a stalemate after the Allies won the Battle of the Marne. Trench Warfare Brought New Technology - Aircraft Average speed of these planes: 75 to 125 miles per hour Trench Warfare Brought New Technology - Gas Chemical weapons in World War I were primarily used to demoralize, injure and kill entrenched defenders, against whom the indiscriminate and generally slow-moving or static nature of gas clouds would be most effective. Trench Warfare Brought New Technology – Tanks! Aircraft could scout enemy positions, but not do much damage. Gas attacks – the wind could shift the gas back onto your troops. The allied created a new weapon to help break the stalemate – the TANK! The tank went in first, the infantry followed the tank over the trenches. Trench Warfare Brought New Technology – Tanks! Average speed: 5 to 10 miles per hour Trench Warfare Brought New Technology – Machine Guns 1st massive use in war REASONS FOR ENTRY OF THE UNITED STATES INTO WORLD WAR I 1-The inability to remain neutral in the face of increasing threats to the national interests of the USA. 2-The United States’ close economic and political ties to Great Britain, which compelled the United States to support Great Britain. The USA delayed entering the war because of the USA’s long history of isolationism. REASONS FOR ENTRY OF THE UNITED STATES INTO WORLD WAR I 3-The German practice of unrestricted submarine warfare February 1915: Germans used this strategy to prevent supplies from reaching Britain. German submarines would attack any ships without warning—a violation of international law. May 1915: The Lusitania left New York City for England. The German embassy warned that travelers were taking a risk. Once the ship was close to Britain, a German U-boat (an Unterseeboot or submarine) launched a torpedo attack, sinking the Lusitania. 128 Americans on board were killed. President Wilson was angry but still kept the United States out of war. He was re-elected in 1916 with the slogan, “He kept us out of war.” 4-The interception of the Zimmermann Telegram* January 1917: The German foreign secretary, Arthur Zimmermann, sent a telegram to Mexico asking Mexico to become an ally of Germany. In return, it said that Germany would help Mexico win back lands lost to the United States during the Mexican War. April 1917: Once Americans were aware of this telegram, they were outraged. President Wilson declared war on Germany. The USA delayed entering the war because of the USA’s long history of isolationism. Lusitania Sinking The German embassy warned that travelers were taking a risk. Once the ship was close to Britain, a German U-boat (an Unterseeboot or submarine) launched a torpedo attack, sinking the Lusitania. The Lusitania was spotted by U20. -The first torpedo was fired at 14.09. 1,153 passengers and crew drowned. 128 of them were Americans Zimmerman Telegram http://www.archives.gov/education/lessons/zimmermann/#documents Zimmerman Telegram Mexico to become an ally of Germany. In return, it said that Germany would help Mexico win back lands lost to the United States during the Mexican War. 1917 -The Allies lose Russia Due to losses to Germany on the Eastern Front, Russian Army collapses. The Royal Family takes the blame. Germany sends Vladimir Lenin to Russia Leads a communist revolution! Lenin speaking to crowds 1917 -The Allies lose Russia Russia quickly dives deep into revolution Several small revolutions begin in major cities, soon entire empire is in revolt. After a bloody conflict, Communists make peace with Germany. Germany took over One million troops Back to the Western Front! 1918 – One Last Push The Germans made one last powerful attack. 2nd Battle of the Marne At first, Germans doing VERY well! Looked like war would be won by Germany. Allies threw in United States Marines and Army soldiers, stopped the Germans, and then beat the Germans Back. This loss led to the collapse of the German Army American Hero – Alvin York He received the Medal of Honor for leading an attack on a German Machine Gun nest, his fellow solders saying he captured 32 machine guns, killing 28 German soldiers and capturing 132 others. From rural Tennessee. Had 9 months of schooling 11 November 1918 – 11pm… Germany signed Armistice, and at 11pm on 11/11/1918 the fighting stopped. Next….Versailles!