* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Wireless Communications and Networks
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.11 wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
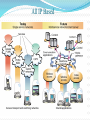
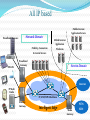
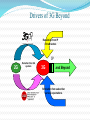
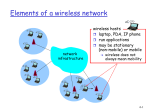
Evolution of Wireless Communication By Chandra Thapa Evolution of Wireless Systems Guglielmo Marconi invented the wireless telegraph in 1896 Communication by encoding alphanumeric characters in analog signal Sent telegraphic signals across the Atlantic Ocean First public mobile (car-based) telephone system (MTS) introduced in 1946 Analog frequency modulation High power BS tower to cover 50 miles radius Inefficient (120K spectrum for a voice connection) Evolution of Wireless Sys. (Contd) Improved mobile telephone system (IMTS) developed in 1960 Full duplex services and direct-dialing 23 FM channels with BW reduced to 25-30 KHz Cellular concept Exploits the attenuation of radio signal with distance to achieve frequency reuse. originally proposed by D. H. Ring in 1947 Bell Labs began work on cellular telephone system in the late 1960s. Evolution of Wireless Sys. (2.5G) 2G telephony is highly successful Enhancement to 2G on data service GSM: HSCSD and GPRS IS-95: IS-95b IS-136: D-AMPS+ and CDPD The improved data rate is still too low to support multimedia traffic ITU initiated 3G standardization effort in 1992, and the outcome is IMT-2000. Evolution of Wireless Sys. (1G) Handoff was not solved until the development of microprocessor, efficient remote-controlled RF synthesizer, and switching center. 1G Cellular System Designed in 1970s, deployed in early 1980s Analog, 42 control channels, 790 voice channels Handoff performed at BS based on received power AMPS in US; TACS in part of Europe; NTT in Japan; C450 in West German, and NMT in some countries. Became highly popular; AMPS still popular in US! Evolution of Wireless Sys. (2G) 2G Systems Digital cellular telephony Modest data support, incompatible GSM: a common TDMA technology for Europe; claim about 3/4 of subscribers worldwide. IS-54 and IS-136: TDMA technology in US; compatible with AMPS; IS-95: CDMA; standardized in 1993; South Korea and Hong Kong deployed it in 1995; US in 1996. Evolution of Wireless Sys. (3G) IMT-2000 comprises several 3G standards: EDGE, data rate up to 473Kbps, backward compatible with GSM/IS-136 cdma2000 (Qualcomm), data rate up to 2Mbps, backward compatible with IS-95 WCDMA (Europe), introduces a new 5MHz channel structure; data rate up to 2Mbps; TD-SCDMA (China), CDMA in TDD fashion Evolution of Wireless Sys. (4G) Problems of 3G systems Immature 3G license auction increases the financial burden Difficult to extend to higher data rates No unified standard (political factors dominate) 4G systems Research initiated, but still not well-defined Data-oriented, seamless integrated with wireline Indoor data rate up to 100 Mbps, outdoor data rate up to 20Mbps. Evolution of Mobile Radio Communications Voice Service Track 1st Generation Analog 2nd Generation Digital North America AMPS CDMA IS-95 Europe ETACS GSM 3rd Generation Wideband 4th Generation Wideband All-IP Notes: IP: Internet Protocol TCP: Transmission Control Protocol AMPS: Advanced Mobile Phone Services ETACS: European Total Access Communication System PDMA: Packet Division Multiple Access (Hanwang, China) Circuit Switching Voice & Data Service Track CDMA 2000 PDMA Circuit and Packet Switching evolving to Packet Switching WCDMA China Data Service Track Fixed Computer Network Packet Switching TDSCDMA WLAN 4G Trends in Wireless Comm. Personal Communications (Goal of mobile communications) All IP based (IPv6) (Packet switched) Flexible platform of complementary access systems( Combination of different wireless access systems, Hot spot services will be introduced by high-speed wireless access (>100mbps)) Higher system capacity (Users/Service, 5-10 times higher than 3G) Higher Transmission Data rate Higher frequency efficiency More advanced multimedia applications Improved QoS Realize high levels of security and authentication Global coverage Global roaming All IP Based All IP based Broadband Accesses Network Domain Mobility, Connection & Control Servers OWLAN Mobile Internet Application Servers Mobile Internet Application Platforms Broadband Gateway Service Domain Internet IP Multi Radio Mobility Gateway IP/ATM/MPLS Backbone Intelligent Edge Media Gateway PSTN ISDN Combination of different wireless access systems PAN Bluetooth PDMA IEEE.802.11 WLAN WPAN WLAN WWAN Network of 3G beyond Services and applications New radio interface download channel Wireline xDSL DAB DVB IP based core network return channel: e.g. GSM cellular GSM IMT-2000 UMTS WLAN type other entities short range connectivit y Transmission Data Rate Highest data rate(3G) at least 144 Kb/s in a vehicular environment, 384 Kb/s in a pedestrian environment, 2048 Kb/s in an indoor office environment. Highest data rate (4G) 2Mbps in a vehicular environment, 20Mbps in a pedestrian environment Wide Area, high velocity:100Mbps Indoor, lower velocity:1Gbps Evolution of transmission data rate Drivers of 3G Beyond 3G evolution : Difficult to extend to higher data rate with CDMA only technology; to provide various services with different QoS to have enough frequency resource to accommodate more subscribers Drawback Low system capacity Low spectrum efficiency 1800 Subscriptions (millions) 1600 1400 Mobile User Mobile Fixed Mobile Internet Fixed Internet 1200 1000 Mobile Internet User 800 600 400 200 0 1995 2000 2005 2010 Drivers of 3G Beyond Revolution from IP infrastructure IP 2G Evolution from 2G systems 3G and Beyond Revolution from subscriber service expectations Multimedia Services Internet access Shopping/banking(e-commerce) Video conferencing Video on demand Telemedicine Distance learning Challenges Unreliable Channels Scarce Spectrum and Resource Management Stringent Power Budget Security Location and Routing Interfacing with Wired Networks Health Concern Diversified Standards and Political Struggle