* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name: Class: Date:______ Physics Forces Exam Part 1: Multiple
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
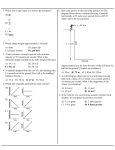
Name:________________________ Class:______________ Date:________ Physics Forces Exam Part 1: Multiple Choice ___ 1. Which object weighs approximately 1 newton? a. b. c. d. ___ 2. Which terms represent a vector quantity and its respective unit? a. b. c. d. ___ 3. less mass and more inertia. more mass and more inertia. less mass and less inertia. more mass and less inertia. Two forces are applied to a 2.0-kilogram block on a frictionless horizontal surface, as shown in the diagram below. What is the acceleration of the block? a. b. c. d. ___ 5. momentum - newton mass - kilogram weight - kilogram force - newton Compared to 25 kilograms of feathers, 20 kilograms of gold has: a. b. c. d. ___ 4. golf ball dime physics student paper clip 4.0 m/s2 to the left 2.5 m/s2 to the right 2.5 m/s2 to the left 1.5 m/s2 to the right A 2,400-kilogram car is traveling at a speed of 20 meters per second. Compared to the magnitude of the force required to stop the car in 12 seconds, the magnitude of the force required to stop the car in 6.0 seconds is: a. b. c. d. half as great. twice as great. four times as great. the same. ___ 6. Sand is often placed on an icy road because the sand: a. b. c. d. ___ 7. The graph below represents the relationship between the forces applied to an object and the corresponding accelerations produced. What is the inertial mass of the object? a. b. c. d. ___ 8. 1.0 kg 2.0 kg 0.50 kg 1.5 kg Which of the following is a derived unit? a. b. c. d. ___ 9. increases the coefficient of friction between the tires of a car and the road. increases the normal force of a car on the road. decreases the coefficient of friction between the tires of a car and the road. decreases the gravitational force on a car. kilogram newton second meter A 2.0-kilogram mass weighs 10.-newtons on planet X. Which of the following is the approximate acceleration due to gravity on planet X? a. b. c. d. 5.0 m/s2 20. m/s2 0.20 m/s2 9.8 m/s2 ___ 10. Two cars having different weights are traveling on a level surface at different constant velocities. Within the same time interval, greater force will always be required to stop the car that has the greater: a. b. c. weight. velocity. kinetic energy. d. momentum. ___ 11. A wooden block is at rest on a horizontal steel surface. If a 10.-newton force applied parallel to the surface is required to set the block in motion, how much force is required to keep the block moving at a constant velocity? a. b. c. d. greater than 10. N no force exactly 10. N less than 10. N ___ 12. A series of unbalanced forces was applied to each of two blocks, A and B. The graph below shows the relationship between unbalanced force and acceleration for each block. Compared to the mass of block A, the mass of block B is: a. b. c. d. four times as great. the same. twice as great. half as great. ___ 13. A 50.-newton horizontal force is needed to keep an object weighing 500. newtons moving at a constant velocity of 2.0 meters per second across a horizontal surface. The magnitude of the fric-tional force acting on the object is: a. b. c. d. 450. N. 500. N. 0 N. 50. N. ___ 14. A different force is applied to each of four 1-kilogram blocks to slide them across a uniform steel surface at constant speed as shown below. In which diagram is the coefficient of friction between the block and steel smallest? a. b. c. d. ___ 15. In the diagram below, a box is on a frictionless horizontal surface with forces F1 and F2 acting as shown. If the magnitude of F1 is greater than the magnitude of F2, then the box is: a. b. c. d. moving at constant speed in the direction of F2. moving at constant speed in the direction of F1. accelerating in the direction of F2. accelerating in the direction of F1. ___ 16. Which two graphs represent the motion of an object on which the net force is zero? a. b. c. d. ___ 17. The table below lists the coefficients of kinetic friction for four materials sliding over steel. Material Coefficient of Kinetic Friction aluminum 0.47 brass 0.44 copper 0.36 steel 0.57 A 10.-kilogram block of each of these materials is pulled horizontally across a steel floor at constant velocity. Which block requires the smallest applied force to keep it moving at constant velocity? a. b. c. d. aluminum brass copper steel ___ 18. The magnitude of the force that a baseball bat exerts on a ball is 50. newtons. What is the magnitude of the force that the ball exerts on the bat? a. b. c. d. 250 N 5.0 N 10. N 50. N ___ 19. The diagram below shows a granite block being slid at constant speed across a horizontal concrete floor by a force parallel to the floor. Which pair of quantities could be used to determine the coefficient of friction for the granite on the concrete? a. b. c. d. frictional force and speed of the block frictional force and normal force on the block mass and speed of the block mass and normal force on the block ___ 20. A 70-kilogram astronaut has a weight of 560 newtons on the surface of planet X. What is the acceleration due to gravity on planet X? a. b. c. d. 0.0 m/s2 9.8 m/s2 80. m/s2 8.0 m/s2 ___ 21. The diagram below shows a horizontal 8.0-newton force applied to a 4.0-kilogram block on a frictionless table. What is the magnitude of the block’ s acceleration? a. b. c. d. 32m/s2 2.0 m/s2 0.50 m/s2 9.8 m/s2 ___ 22. A net force of 25 newtons is applied horizontally to a 10. kilogram block resting on a table. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the block? a. b. c. d. 0.0 m/s2 0.26 m/s2 0.40 m/s2 2.5 m/s2 ___ 23. In which situation is the net force on the object equal to zero? a. b. c. d. an automobile braking to a stop a pitched baseball being hit by a bat a satellite moving at constant speed around Earth in a circular orbit a bicycle moving at constant speed on a straight, level road ___ 24. If the sum of all the forces acting on a moving object is zero, the object will: a. b. c. d. accelerate uniformly. slow down and stop. change the direction of its motion. continue moving with constant velocity. ___ 25. A net force of 10. newtons accelerates an object at 5.0 meters per second2 . What net force would be required to accelerate the same object at 1.0 meter per second2 ? a. b. c. d. 5.0 N 2.0 N 1.0 N 50. N ___ 26. A 1,200-kilogram car traveling at 10. meters per second hits a tree and is brought to rest in 0.10 second. What is the magnitude of the average force acting on the car to bring it to rest? a. b. c. d. 1.2x102 N 1.2x105 N 1.2x103 N 1.2x104 N ___ 27. A spring scale reads 20. newtons as it pulls a 5.0-kilogram mass across a table. What is the magnitude of the force exerted by the mass on the spring scale? a. b. c. d. 49 N 4.0 N 20. N 5.0 N ___ 28. The diagram below shows a block sliding down a plane inclined at angle 98 with the horizontal. As angle 98 is increased, the coefficient of kinetic friction between the bottom surface of the block and the surface of the incline will: a. b. c. d. increase by a factor of four. decrease to zero. remain the same. increase by a factor of two. ___ 29. A man standing on a scale in an elevator notices that the scale reads 30 newtons greater than his normal weight. Which type of movement of the elevator could cause this greater-than-normal reading? a. b. c. d. moving downward at constant speed moving upward at constant speed accelerating downward accelerating upward ___ 30. When a 12-newton horizontal force is applied to a box on a horizontal tabletop, the box remains at rest. What is the magnitude of the force of static friction acting on the box? a. b. c. d. greater than 12 N 12 N between 0 N and l2 N 0N ___ 31. Which person has the greatest inertia? a. b. c. d. a 70-kg long-distance runner traveling at 5 m/s a 110-kg wrestler resting on a mat a 90-kg man walking at 2 m/s a 50-kg girl sprinting at 10 m/s ___ 32. Which of the following best illustrates Newton’ s First Law of Motion? a. b. c. d. a volleyball being “ spiked” across the net a bowling pin being struck by a bowling ball an ice hockey puck sliding along the ice after being hit by a player’ s stick a collision between a running back and a linebacker in football ___ 33. An object rolling across a level floor without any horizontal net force acting on it will: a. b. c. d. have unbalanced forces. keep moving forever. speed up. slow down. ___ 34. An object falling to Earth in the absence of air resistance: a. b. c. d. falls with a constant speed of 9.8 m/s. falls with a constant speed of 32 m/s. slows down. falls with constant acceleration of 9.8m/s2 . ___ 35. A constant net force acting on an object causes the object to move with constant: a. b. c. d. velocity. momentum. speed. acceleration. ___ 36. Which of the following is not one of Newton’ s Laws of Motion? a. b. c. d. An object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. A constant net force acting on an object produces a change in the object’ s motion. Energy is neither created not destroyed; it simply changes form. ___ 37. Newton’ s First Law is known as the law of: a. b. c. d. inertia. acceleration. impetus. resistance. ___ 38. A volleyball hits the floor. What is the “ reaction” force from Newton’ s Third Law? a. b. c. d. the force of the volleyball on the floor the force of the floor on the volleyball the force of the player hitting the volleyball the force of the player’ s arm on the player’ s hand ___39. A block is pulled by a horizontal force along a rough surface. The Force pulling the block is 75 N. The mass of the block is 5 kg. The coefficient of friction (μ) between the block and the surface is 0.6. What is the acceleration of the block? ___ 40. A 30 kg puppy is pulled across a surface with a μ of 0.775 with a force of 500 N. What force of friction is acting on the puppy?