* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download biology plant test
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
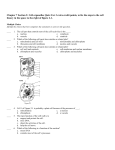
BIOLOGY PLANT TEST Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ____ ____ 1. Plant cells all have a _____ composed of cellulose. a. cell wall c. nucleus b. cell membrane d. cytoplasm 2. Both algae and plants store their food in the form of _____. a. glycogen c. cellulose b. glucose d. proteins 3. Although all plants produce spores only _____ produce flowers. a. Anthophytes c. Coniferophytes b. Anthocerophytes d. Ginkgophytes Figure 21-3 ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 4. Refer to Figure 21-3. Removing which structure would cause this plant to fall over? a. A c. C b. B d. D 5. Refer to Figure 21-3. Which structure is used for the transportation of nutrients? a. A c. C b. B d. D 6. Refer to Figure 21-3. Removing which structure would cause this plant to starve? a. A c. C b. B d. D 7. Refer to Figure 21-3. Which structure collects water? a. A c. C b. B d. D 8. Which division of seed plants is represented by only one living species? a. Cycadophyta c. Ginkgophyta b. Gnetophyta d. Coniferophyta 9. Bryophytes tend to be found in moist environments because _____. a. they rely on osmosis and diffusion for transport of nutrients b. they contain vascular tissue c. they are both small plants d. they don't produce seeds 10. In most seed plants, fertilization does not require _____. ____ 11. ____ 12. ____ 13. ____ 14. ____ 15. ____ 16. ____ 17. ____ 18. ____ 19. ____ 20. a. a film of water to carry the sperm to the egg b. alternation of generations c. the production of eggs d. a gametophyte generation Which of the following is not a dicotyledon? a. lettuce c. grass b. maple tree d. dandelion An anthophyte differs from a conifer in that _____. a. it is deciduous c. its seeds are enclosed in a fruit b. it produces seeds d. it has vascular tissue Parallel veins in a leaf would indicate that the plant is a _____. a. dicotyledon c. perennial b. biennial d. monocotyledon What is the primary function of plant leaves? a. to support the plant c. to take in water b. to produce flowers d. to trap sunlight for photosynthesis A plant is probably a dicot if it has _____. a. netted veins c. parallel veins b. one seed leaf within the seed d. flower parts in multiples of three Sugars and other organic compounds are transported throughout the plant by the _____. a. tracheids c. phloem b. guard cells d. xylem Guard cells close the _____ to prevent excess water loss. a. stomata c. epidermis b. trichomes d. collenchyma What is the most likely seed-dispersal mechanism for a seed with winglike structures? a. eaten by animals c. wind b. catch in animal fur d. water What is the most likely seed-dispersal mechanism for an apple seed? a. eaten by animals c. wind b. catch in animal fur d. water What is the most likely seed-dispersal mechanism for a seed with hooks? a. eaten by animals c. wind b. catch in animal fur d. water Completion Complete each statement. 21. Most photosynthesis occurs in the ____________________ of the plant. 22. The waxy, waterproof covering found on the plant stems and leaves is called the ____________________. 23. A plant with needlelike or scaly leaves that produces seeds in cones would most likely belong to the ____________________ division. 24. Some plants such as radishes and sweet potatoes store starch reserves in their ____________________. 25. Nonvascular plants have to rely on ____________________ and ____________________ for transport of their water and nutrients. 26. ____________________ are small bryophytes with leafy stems that usually grow in dense carpets or tufts. 27. Nonvascular plants must have adaptations to keep them from ____________________. 28. The ____________________ is the female structure of the flower. 29. The beginning of the development of the embryo into a new plant is called ____________________. 30. The ____________________ of a flower develops into the fruit. Short Answer 31. Explain the difference between the following: A. Vascular and Non vascular plants B. Gymnosperms and Angiosperms C. Monocots and Dicots(tell 1 characteristic that makes these plants different) 32. Fill in the chart below __________________ ____________-__________________ _______________ ________________ _______________ ________________ BIOLOGY PLANT TEST Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: NAT: 2. ANS: NAT: 3. ANS: NAT: 4. ANS: NAT: 5. ANS: NAT: 6. ANS: NAT: 7. ANS: NAT: 8. ANS: NAT: 9. ANS: NAT: 10. ANS: NAT: 11. ANS: NAT: 12. ANS: NAT: 13. ANS: NAT: 14. ANS: NAT: 15. ANS: NAT: 16. ANS: NAT: 17. ANS: NAT: 18. ANS: NAT: 19. ANS: NAT: 20. ANS: NAT: A C5 | C6 | F3 B C5 | C6 | F3 A C5 | E2 | F1 D C5 | F3 | F4 B C5 | F3 | F4 A C5 | F3 | F4 D C5 | F3 | F4 C C1 | C3 | C5 A C1 | C3 | C5 A C1 | C3 | C5 C C1 | C3 | C5 C C1 | C3 | C5 D C2 | C3 | C5 D C3 | C4 | C5 A C2 | C3 | C5 C C3 | C4 | C5 A A1 | C1 | C5 C C4 | C5 | C6 A C4 | C5 | C6 B C4 | C5 | C6 PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: 1 15 | 16 | 19 1 15 | 16 | 19 1 15 | 16 | 19 1 16 | 19 | 22 1 16 | 19 | 22 1 16 | 19 | 22 1 16 | 19 | 22 1 15 | 16 | 19 1 19 | 37 | 38 1 15 | 16 | 19 1 15 | 16 | 19 1 15 | 16 | 19 1 19 | 34 | 37 1 19 | 34 | 37 1 19 | 34 | 37 1 19 | 34 | 37 1 19 | 33 | 37 1 19 | 37 | 38 1 19 | 37 | 38 1 19 | 37 | 38 DIF: B OBJ: 21-1 DIF: B OBJ: 21-1 DIF: B OBJ: 21-5 DIF: A OBJ: 21-2 DIF: A OBJ: 21-2 DIF: A OBJ: 21-2 DIF: A OBJ: 21-2 DIF: B OBJ: 22-5 DIF: B OBJ: 22-3 DIF: B OBJ: 22-5 DIF: B OBJ: 22-5 DIF: B OBJ: 22-5 DIF: B OBJ: 23-3 DIF: B OBJ: 23-4 DIF: B OBJ: 23-3 DIF: B OBJ: 23-4 DIF: B OBJ: 23-2 DIF: B OBJ: 24-6 DIF: B OBJ: 24-6 DIF: B OBJ: 24-6 COMPLETION 21. ANS: leaves PTS: 1 STA: 16 | 19 | 22 22. ANS: cuticle DIF: B OBJ: 21-2 NAT: C5 | F3 | F4 PTS: 1 DIF: B STA: 16 | 19 | 22 23. ANS: Coniferophyta OBJ: 21-2 NAT: C5 | F3 | F4 PTS: 1 STA: 15 | 16 | 19 24. ANS: roots DIF: B OBJ: 21-5 NAT: C5 | E2 | F1 PTS: 1 DIF: B STA: 16 | 19 | 22 25. ANS: osmosis, diffusion OBJ: 21-2 NAT: C5 | F3 | F4 PTS: 1 STA: 15 | 16 | 19 26. ANS: Mosses DIF: B OBJ: 21-4 NAT: C4 | C6 | E2 PTS: 1 STA: 15 | 16 | 19 27. ANS: drying out DIF: B OBJ: 21-5 NAT: C5 | E2 | F1 PTS: 1 STA: 16 | 19 | 22 28. ANS: pistil DIF: B OBJ: 21-2 NAT: C5 | F3 | F4 PTS: 1 STA: 19 | 36 | 37 29. ANS: germination DIF: B OBJ: 24-3 NAT: C4 | C5 | C6 PTS: 1 STA: 19 | 37 | 38 30. ANS: ovary DIF: B OBJ: 24-6 NAT: C4 | C5 | C6 PTS: 1 STA: 19 | 36 | 37 DIF: B OBJ: 24-3 NAT: C4 | C5 | C6 SHORT ANSWER 31. ANS: v PTS: 1 32. ANS: n PTS: 1