* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Respiratory System Review
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
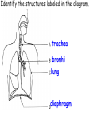
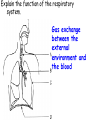
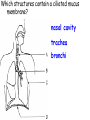
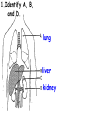
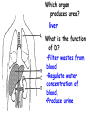
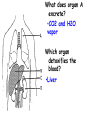
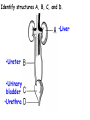
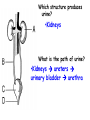
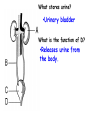
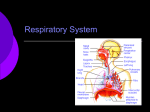
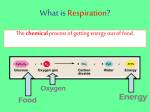
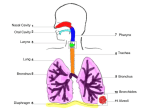
Respiratory and Excretory System Review 1. The tubes that branch from the trachea are the bronchi 2. The dome shaped muscle below the chest cavity is called the diaphragm 3. During swallowing, the air passage of the pharynx is covered by the epiglottis 4. Alveoli in the lungs are connected to the bronchi by a network of tiny tubes called bronchioles 5. Breathing is controlled by the chemistry of your blood as it interacts with the carbon dioxide Explain what happens to carbon dioxide and oxygen inside the alveoli. Alveoli fills up with oxygen and diffuses into the capillaries (blood). Carbon dioxide and water in the blood diffuses out of the capillaries into the alveoli. Which is the correct sequence for the path of oxygen through the respiratory system? a) nasal cavity, bronchi, trachea, bronchioles, cells, blood, alveoli b) cells, blood, alveoli, bronchioles, bronchi, trachea, nasal cavity c) nasal cavity, blood, alveoli, bronchi, cells, trachea, bronchioles d) nasal cavity, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, blood, cells 1. Where are the vocal cords located in the body? larynx 2. Breathing is an involuntary process controlled by the which part of the brain? medulla 3.What prevents the trachea from collapsing? rings of cartilage 4. Where does the actual exchange of gases occur? alveoli 5. During gas exchange where does the oxygen and carbon dioxide go? O2 diffuses into capillaries. CO2 diffuses out of capillaries and into alveoli. 1. Explain what happens to the diaphragm and rib cage do during inhalation. Diaphragm contracts (pulls down). Rib cage expands. 2. Explain what happens to the diaphragm and rib cage muscles do during exhalation. Diaphragm relaxes (pushes up). Rib cage relaxes. Identify the structures labeled in the diagram. trachea bronhi lung diaphragm Explain the function of the respiratory system. Gas exchange between the external environment and the blood Which structures contain a ciliated mucus membrane? nasal cavity trachea bronchi The ______ is a long straight tube that carries air from the back of the throat to the lungs. trachea What structures trap foreign particles and bacteria in the nose and trachea? cilia 1.Identify A, B, and D. lung liver kidney Which organ produces urea? liver What is the function of D? •Filter wastes from blood •Regulate water concentration of blood. •Produce urine What does organ A excrete? •CO2 and H2O vapor Which organ detoxifies the blood? •Liver What are metabolic wastes? Examples? •Wastes from your cells. •CO2, H2O, salts, urea Identify structures A, B, C, and D. •Liver •Ureter •Urinary bladder •Urethra Which structure produces urine? •Kidneys What is the path of urine? •Kidneys ureters urinary bladder urethra What stores urine? •Urinary bladder What is the function of D? •Releases urine from the body. Which human excretory structure aids in the maintenance of normal body temperature? •Skin Why is the skin also an excretory organ? It excretes water, salts and urea in the form of perspiration. What are metabolic wastes?