* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Principals of Pathology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
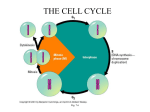
Washington & Leaver: Principles and Practice of Radiation Therapy, 3rd Edition Chapter 04: Overview of Radiobiology Additional Assignments Define the following terms. 1. Mutation frequency: 2. Doubling dose: 3. Radiobiology: 4. Homeostasis: 5. Catabolism: 6. Anabolism: 7. Protein synthesis: 8. Macromolecule: 9. Target: 10. Free radical: 11. LET (identify & define): 12. RBE (identify & define): 13. Tissue culture: 14. SLD (identify & define): 15. PLD (identify & define): 16. Radiosensitivity: 17. Differentiation: 18. Parenchyma: 19. Stroma: 20. Assay: 21. LD50: 22. TD5/5: 23. LD50/30: 24. Somatic effects: 25. Stochastic: Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Additional Assignments 26. Nonstochastic: Answer the following questions. 27. According to the Target Theory, what is the principal target of cell damage? 28. Briefly describe each component of mitosis. Prophase: Metaphase: Anaphase: Telophase: Interphase: 29. Briefly describe each component of DNA synthesis. S: G1: G2: G0: M: 30. Contrast direct action with indirect action. 31. Complete the reaction. H2O + ionizing radiation → 32. Contrast in vivo and in vitro. 33. Contrast asynchronous populations with synchronous populations. 34. Contrast radiosensitivity and radiocurability. 35. Define direct and indirect radiation effects. 36. Describe the four Rs of radiation therapy. Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 2 Additional Assignments 37. Describe mitotic delay. 38. Describe the relationship between LET and RBE. 39. Define radioprotectors and radiosensitizers. 40. During which cell cycle phase are cells most radioresistant and most radiosensitive? 41. Draw and label a typical survival curve. 42. Describe the relationship between genes, DNA, and chromosomes. 43. Describe the three possible outcomes of an irradiated cell. 44. Describe the major difference between the two types of tissue healing. 45. Define each of the following components of the mammalian survival curve. D0 Dq n 1D0 (aka D1) 46. How is growth fraction measured? 47. How and why is survival affected by changes in the dose rate? 48. Identify and describe the potential effects of radiation on DNA. 49. Identify and describe the potential effects of radiation on chromosomes. Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 3 Additional Assignments 4 50. If 300 cGy is required to reduce survival to 1% under aerobic conditions and 750 cGy under hypoxic conditions, what is the OER? 51. If 2,000 cGy is required to produce alopecia in Chinese hamsters under normal conditions and 3,500 cGy WR-2721 is administered prior to irradiation, what is the DRF? 52. If it takes 500 cGy to reduce survival to 1% under aerobic conditions and 1,150 cGy under hypoxic conditions, what is the OER? 53. If 55% of a tumor cell population is in the quiescent (nonproliferating) compartment, what is the growth fraction? 54. If a total of 70 Gy is delivered in 35 fractions of 2 Gy, calculate the BED. 55. List and describe the three types of tissue response assays. 56. List and describe the five categories of cell populations as defined by Rubin and Casarett. 57. List four potential somatic effects of radiation exposure. 58. List the three embryological divisions of pregnancy. 59. List four radiation-induced mutations of genetic material. 60. List the three functions of lipids. 61. Mouse tumors were irradiated with 2,000 cGy under normal air breathing conditions with and without the tumor clamped to make it hypoxic. If the surviving fractions for Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Additional Assignments 5 these two conditions are 0.004 (unclamped) and 0.02 (clamped), what is the hypoxic fraction of this tumor under normal conditions? 62. What is the Law of Bergonie and Tribondeua? Why is it important in radiobiology? 63. What is the Law of Ancel and Vitemberger? Why is it important in radiobiology? 64. What are parenchymal cells? 65. Why is the small bowel the most radiosensitive organ of the GI tract? 66. What is maturation depletion? 67. Who conducted experiments with fruit flies and determined that radiation increased the mutation frequency but did not cause unique mutations? 68. What is the diffusion distance of oxygen in a tissue? 69. What is thought to be the target molecule for the lethal effects of radiation, and what are four types of radiation-induced damages on it? 70. What type of radiation is used as a standard for determining the RBE? 71. Which type of radiation damage to the DNA is most likely lead to a permanent mutation? 72. You are using the in vivo dilution assay to determine the survival of an irradiated mouse tumor. If 5 cells from the control mouse tumor and 1,500 cells from the irradiated mouse tumor (4 Gy) are required to produce a tumor in 50% of the recipient mice (TD50 = 5 and 1,500), what is the surviving fraction after 4 Gy? Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Additional Assignments 6 73. Given the following data, draw and label its cell survival curve. Dose Survival 0 100 200 80 600 30 800 12.5 1,200 2.20 1,400 1.00 Match the description to the correct cell cycle stage. ____74. Most radioresistant A. G1 ____75. Cells may accumulate after irradiation B. S ____76. Greatest variation in length C. G0 ____77. Most radiosensitive D. M ____78. Cells are at rest E. G2 Match the statement to the correct survival curve parameter. ____79. Dose at which the linear and quadratic contributions to cell killing are equal. A. ____80. Dq + D0 B. ____81. Dq/D0 C. ____82. Measure of the width of the survival curve shoulder D. D0 ____83. Inversely proportional to the final slope E. Dq ____84. Thought to be related to the formation of double-strand DNA breaks F. D37 ____85. Thought to be related to the formation of single-strand DNA breaks G. log n Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Additional Assignments 7 Match the item with the parameter it is used to measure. Answers may be used more than once. ____86. Courtenay soft agar assay A. Proliferation potential ____87. Cell adhesion matrix (CAM) assay B. Reproductive integrity ____88. Tpot C. Growth assay ____89. Labeled nitroimidazoles D. Oxygen status ____90. Colorimetric microtiter well assay ____91. Polarographic electrode Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.