* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Push Button - UCLA IEEE Micromouse
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Standby power wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
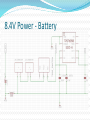
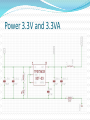
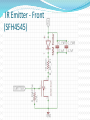
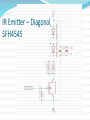
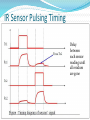
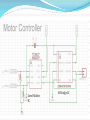
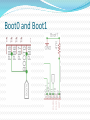
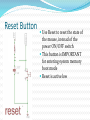
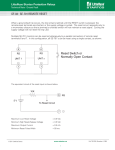
Advanced Micromouse Hardware Design Lecture Outline Microcontroller Power System Peripherals Sensor System: IR emitters and receivers Motor Controller Gyro Buzzer Display Voltage Meter LEDs Push Button Reset Button Microcontroller STM32F405RGT6 – 64 pins Timers - Generate PWM signals to motor, buzzer GPIOs – LEDs, IR emitters, push button USART – Allows “printf” to display on a terminal SPI – Prints data on alphanumeric display ADC – Convert analog voltage to a digital number 1 MB Flash – Store maze info Microcontroller Pins Multi-function pins Power System - Microcontroller Power Supply Schemes: VDD = 1.8 to 3.6 V: external power supply that will supply the voltage for GPIOs (Futura Mouse: 3.3 V) VDDA = 1.8 to 3.6 V: external analog power supply for ADC, DAC, Reset blocks, RCs and PLL (Futura Mouse: 3.3 V) VBAT = 1.65 to 3.6 V: power supply for RTC, external 32 kHz oscillator, backup registers (Futura Mouse: 3.3 V) VSSA = GND for VDDA; VSS = GND for VDD VCAP: connect 2.2 microFarad ceramic cap between this pin and GND (External capacitor that decouple power supply) Power System Power System – Power Supply Fully Charged Battery: 8.4 V (2 x 4.2 V) Motor Controller System (Level shifter + H-Bridge) 5V regulator 5V Encoders, IR Emitters (anode “+”), Alphanumeric Display 3.3 V regulator 3.3 V Microcontroller, Buzzer, USART, push buttons 3.3 VA (analog circuits) IR Receivers, Gyro 8.4V Power - Battery Power 5V Power 3.3V and 3.3VA IR Emitter - Front (SFH4545) IR Emitter – Diagonal SFH4545 IR Receiver (TEFT4300) IR Sensor Pulsing Timing Delay between each sensor reading until all residues are gone Motor Driver Level Shifter IC H-Bridge IC Gyro Buzzer - Buzzer behaves like an inductor - Diode is used to prevent inductive kickback Display Voltage Meter Keep track of the battery voltage to protect the battery from over discharging LED 2 ways to control LED with MCU The one on left is easier for wiring since ground is easier to find The way to the right is better in terms of power, since power is not drawn from the MCU Futura Mouse uses left scheme Push Button -Futura Mouse uses right scheme Boot0 Button For new MCUs, Figure 1 Figure 2 bootloading must be done just once via USART Boot mode must be entered first before bootloading Figure 2 shows how to save one button System memory boot mode - Bootloader is stored in the system memory (ROM). - To enter boot mode, set Boot0 high by holding down on the Boot0 push button, then push the reset button. Boot1 should be connected to GND. - Using USART, load application programs into FLASH. Boot0 and Boot1 Reset Button Use Reset to reset the state of the mouse, instead of the power ON/OFF switch This button is IMPORTANT for entering system memory boot mode Reset is active low References http://www.st.com/web/en/resource/technical/document/datasheet/DM00037051.pdf STM32F405 MCU datasheet http://www.seattlerobotics.org/encoder/mar97/basics.html Info about pull-up and pull-down resistors http://coactionos.com/embedded%20design%20tips/2013/10/21/Tips-UnderstandingMicrocontroller-Pin-Input-Output-Modes/ Info about pin input/output modes (i.e. push-pull, open-drain) http://www.allaboutcircuits.com/vol_3/chpt_3/9.html Info about inductive kickback https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/capacitors/application-examples Info about decoupling capacitors (filters) http://learn.parallax.com/node/258 Info about phototransistor circuits (IR receiver)