* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download tissues
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Stem-cell therapy wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Nerve guidance conduit wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
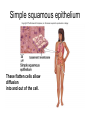
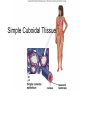
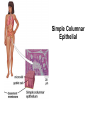
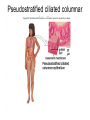
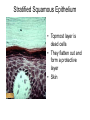
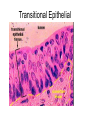
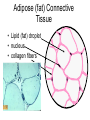
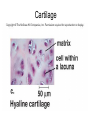
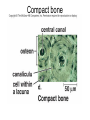
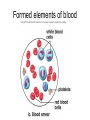
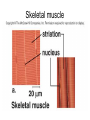
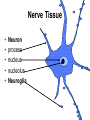
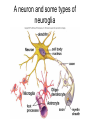
Chapter 5: Tissue Types of Tissues • A tissue is composed of specialized cells that perform a function in the body. • The human body has four major types of tissues: The 4 types are: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous Some Cancers that occur in tissue are: • • • • Carcinomas – cancers of epithelial tissue Sarcomas – cancers of connective tissue Leukemia – cancer of blood Lymphomas – cancers of lymphatic tissue 1. Epithelial Tissue Characteristics of epithelial tissue: • Epithelial tissue is made of highly packed cells that line the body surface and inner body cavities. • Epithelial tissue functions in protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, and filtration. Obj. #1: Describe the types of Epithelial Tissue 1. Simple Squamous epithelium • a single layer of of flattened cells • is found lining the lungs and blood vessels. • Allows substances to pass into and out of tissue…when oxygen enters blood stream Simple squamous epithelium These flatten cells allow diffusion into and out of the cell. 2. Cuboidal epithelium • contains cube-shaped cells • is found lining the kidney tubules and glands • functions to store secretions Simple Cuboidal Ttissue 3. Simple Columnar epithelium • has elongated cells with nuclei at the bottom of cells • is found in the digestive tract. • secretes digestive fluid • absorbs nutrients • cells have microvilli on ends to increase absoption • has goblet cells that make mucus Simple Columnar Epithelial 4. Pseudostratified Columnar epithelial• Long cells with cilia on end • Lines respiratory tract and reproductive tract • Promotes movement of mucus in repiratory tract • Promotes movement of egg in oviducts Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium 5. • • • • • Stratified Squamous Found in outer skin and lines the mouth Occurs in layers- stacks of flatten cells Oldest layer is on top…youngest on bottom Protects body from invasion Outer layer sloughs off as cells die Stratified Squamous Epithelium • Topmost layer is dead cells • They flatten out and form a protective layer • Skin 6. Transitional epithelial tissue • Stretches • Found in bladder Transitional Epithelial Obj. #2 Describe Connective Tissue Characteristics: • binds organs together, provides support and protection, fills spaces, produces blood cells, and stores fat. • matrix material is the material that fills the cell. It is a semifluid or solid. • Different types of fibers float in matrix Types of Connective Tissue . 1. Loose fibrous-supports epithelium and many internal organs. • Wrinkles form when loose fibrous tissue ages. • Sun exposure cause fibers in loose to break much like a rubber band breaks.. this leads to wrinkles forming Loose fibrous connective tissue 2. Dense fibrous-is found in tendons and ligaments. • Very tightly packed cells • Has very little blood supply..so when a person injures a ligament or tendon…it will take a long time to heal Dense Connective Tissue 3.Adipose tissue is found beneath the skin and around certain internal organs. • • • Functions: Cushions Insulates Stores energy-cells look empty…but contain fat droplets Adipose (fat) Connective Tissue • Lipid (fat) droplet • nucleus • collagen fibers 4. Cartilage Cartilage found in outer ear, nose, and between bones. Function: • Flexible • Protects Cartilage 5. Bone • Bone is the most rigid connective tissue with its matrix of calcium and other inorganic salts and protein fibers. • Compact bone makes up the shafts of long bones and consists of ring-linke circels called osteons which contain blood vessels and nerves. Compact bone 6. Blood • Blood is a fluid connective tissue containing blood cells in liquid plasma. • Blood has many functions: • Keeps body chemistry within limits • Transports nutrients and wastes to cells • Distributes heat Blood, a fluid tissue Formed elements of blood Obj. #3 Describe Muscle Tissue There are 3 types 1. Skeletal muscle, under voluntary control, is attached by tendons to bones and allows for movement. - have striations which are bands of fibers Skeletal muscle 2. Smooth (visceral) muscle is involuntary and nonstriated. • Long, tapered cells, • Smooth muscle is found in walls of organs. • Smooth muscle contracts more slowly than skeletal muscle but can remained contracted for a longer period. Smooth muscle 3. Cardiac muscle is found only in the walls of the heart and functions to pump blood. • Cardiac muscle has striations but is involuntary. • Cardiac muscle fibers are branched and have a single nucleus. Cardiac muscle 4. Nervous Tissue • Nervous tissue found in the brain and spinal cord is made up of cells called neurons. • Neurons have three parts: • Dendrites – carry impulses to the neuron • Cell body – houses nucleus • Axon – carries impulse away from cell Nerve Tissue • • • • • Neuron process nucleus nucleolus Neuroglia A neuron and some types of neuroglia