* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
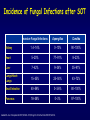
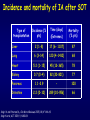
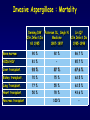
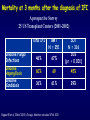
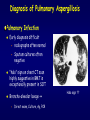
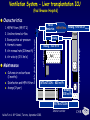
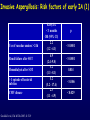
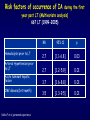
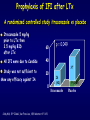
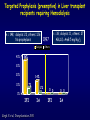
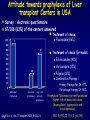
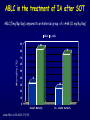
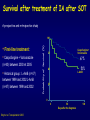
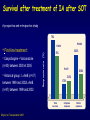
Aspergillosis in Transplant patients Pr Faouzi SALIBA faouzi.saliba@ pbr.aphp.fr Faculté de Médecine Paris Sud Réanimation - Centre Hépato-Biliaire Hôpital Paul Brousse - Villejuif- France Incidence of Fungal Infections after SOT Invasive Fungal Infections Aspergillus Candida 1.4–14% 0–10% 90–100% Heart 5–20% 77–91% 8–23% Liver 7–42% 9–34% 35–91% Lungs/HeartLungs 15–35% 25–50% 43–72% Small Intestine 40–59% 0–3.6% 80–100% Pancreas 18–38% 0–3% 97–100% Kidney Gabardi S. et al. Transplant Int 2007;20:993–1015, Singh N. Clin Infect Dis 2000:31;545–53. Outcome of Patients according to the presence of Fungal Infections after LT 667 LT (1999-2005) 91% 85% 69% 77% No Fungal Infection QuickTime™ et un 69% décompresseur sont requis pour visionner cette image. 48% Fungal Colonisation Treated fungal infection Logrank p <0.0001 years Saliba F et al, European Society of Organ transplantation (ESOT), Paris Sept 2009 Saliba F et al, International Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (ICAAC) San Francisco, Sept 2009 Incidence and mortality of IA after SOT Incidence (% pts) Time (days) (Extremes) Mortality (% pts) Liver 2 (1-8) 17 (6- 1107) 87 Lung 6 (3-14) 120 (4-1410) 68 Heart 5.2 (1-15) 45 (12-365) 78 Kidney 0.7 (0-4) 82 (20-801) 77 Pancreas 1.1-2.9 - 100 Intestine 2.2 (0-10) 289 (10-956) 66 Type of transplantation Singh N. and Paterson DL, Clin Microb Reviews; 2005, 18, N°1: 44-69. Singh N et al, AJT 2009; 9, S180-191 Invasive Aspergillose : Mortality Denning DW Clin Infect Dis till 1995 Paterson DL, Singh N Medicine 1987-1997 Lin QY Clin Infect Dis 1995-1999 Bone marrow 90 % 92 % 86.7 % AIDS/HIV 81 % - 85.7 % Liver transplant. 93 % 87 % 67.6 % Kidney transplant. 70 % 75 % 62.5 % Lung Transplant. 77 % 55 % 62.5 % Heart transplant. 50 % 78 % 43.6 % 100 % - Pancreas transplant Mortality of IA after LT 1985 - 1997: 26/1307 patients (2 %) 24/26 (92 %) patients Death directly related to aspergillosis : 16 patients (68 %) Other causes of death : Technical Complications: Recurrent disease : Sepsis : 2 patients 1 patient 5 patients 13/24 patients had autopsy : 7 positive 4 confirming the diagnosis 3 revealing the diagnosis Saliba F. et al, Paul Brousse expeirence C.H.B. Mortality at 3 months after the diagnosis of IFI A prospective Survey 25 US Transplant Centers (2001-2002) Invasive Fungal Infections Invasive Aspergillosis Invasive Candidosis Total IFI BMT N = 251 46% 67% 60% 69 45% 36% 61% 29% Pappas PG et al, ICAAC 2003, Chicago, Abstract actualisé N° M-1010 SOT N = 316 30% (p= < 0.001) Invasive Fungal Infections: Time of occurrence Earlier Reports Most of the cases occurred within the first three months (CNS involvement++) Recent studies* * 55% of the cases occurred > 3 months ** 43% of the cases occurred > 3 months * Singh N, Clin Infect Dis 2003; 36:46–52 ** Gavaldà J et al, Clin Inf Dis 2005; 41:52-9 Invasive Aspergillosis : Time of diagnosis A retrospective case-control study : - 156 cases of proven or probable invasive aspergillosis - 11 Spanish centers (RESITRA) - Since the start of the centers’ transplantation programs to December 2001 Gavaldà J et al, Clin Inf Dis 2005; 41:52-9 Pattern of Fungal Infections in SOT Patients • Immunosuppression impairs inflammatory response Scarcity of clinical and/or radiologic signs associated with inflammation Progress of infection prior to clinical presentation • Infection often advanced at time of diagnosis • Rapidly progressive • Absence of surrogate markers that could allow early diagnosis • Efficacy of therapeutic agents limited by toxicity and drug interactions Diagnosis of Pulmonary Aspergillosis Pulmonary Infection Early diagnosis difficult radiographs often normal Sputum cultures often negative "halo" sign on chest CT scan highly suggestive in BMT is exceptionally present in SOT Broncho-alveolar lavage ++ Direct exam, Culture, Ag, PCR Halo sign ?? Galactomannan for Diagnosis of IA Meta-analysis 1996- 2005: 27 studies Sensitivity (%) Specificty (%) 70 92 BMT 82 86 Pediatric BMT + malignancy 89 85 Solid organ transplant 22 84 Population Hematologic malgnancy • Real-time PCR performed on the first positive GM increased sensitivity to 62% (Botterel F et al, Transpl Infect Dis 2008, 10: 333-8.) Pfeiffer CD et al, Clin Infect Dis 2006; 42: 1417-27 Risk factors of IA Invasive Aspergillosis : role of the environement Old ICU New protected ICU E n v i r o n e m e n t culture + + + - + - - - - - 12/767 pts (1.6 %) Saliba F et al. 40th ICAAC, Toronto 2000. 4/541 pts (0.7 %) C.H.B. Ventilation System - Liver transplantation ICU (Paul Brousse Hospital) Noise Double vitrage + store intérieur Reduction 3. Room positive air pressure 4. Hermetic rooms 5. Air renewal rate (20times/h) 6. Air velocity (2.5-3m/s) Maintenance Cultures air and surfaces (3 months) Disinfection and HEPA filter change (1/year) Double glass + interior storage 2. Unidirectionnel airflow HEPA Filtre Blowing filtered air Trappe Blowing Blowing : 800 m3/h rail support 1. HEPA Filters (99.97 %) Bed EXTRACTION : 800 m3/h Blowing 300 m3/h Double glass + interior storage Characteristics Double vitrage + store intérieur EXTRACTION Saliba F et al. 40th ICAAC, Toronto, September 2000. Interior corridor C.H.B. Risk Factors for IFI in Liver Transplant Recipients Clinical parameters Fungal Infections Retransplantation Aspergillus spp + Candida spp Need for hemodialysis Aspergillus spp + Candida spp Prophylaxis of SBP Candida spp Dysfunction of the graft Aspergillus spp CMV Infection Aspergillus spp + Candida spp HHV6 Infection Aspergillus spp + Candida spp C.H.B. Invasive Aspergillosis: Risk factors of early IA (1) Use of vascular amines > 24h Renal failure after SOT Hemodialysis after SOT > 1 episode of bacterial infetion CMV disease Gavaldà J et al, Clin Inf Dis 2005; 41:52-9 Early IA < 3 months OR (95% CI) 2.2 (1.2 - 4.1) 4.9 (2.4 -9.8) 3.2 (1.3 - 8.1) 3.2 (3.2 - 17.4) 2.3 (1.1 - 4.9) p < 0.0001 < 0.0001 0.014 < 0.006 < 0.029 Invasive Aspergillosis : Risk factors of late IA (2) Age > 50 years Renal failure after SOT High levels of CNI > 1 episode of bacterial De novo cancer Chronic graft rejection Gavaldà J et al, Clin Inf Dis 2005; 41:52-9 infetion Late IA > 3 months OR (95% CI) p 2.5 (1.3 - 5.1) 0.009 3.9 (1.9 -7.8) 2.5 (1.2 - 5) 7.5 (3.2 - 17.4) 69.3 (6.4 - 75.3) 5 (1.9 - 13) < 0.0001 0.01 < 0.0001 < 0.0001 0.001 Risk factors of occurrence of IA during the first year post LT (Multivariate analysis) 667 LT (1999-2005) Hemodialysis prior to LT Arterial Hypertension prior to LT Acute fulminant hepatic failure CMV disease (1rst month) Saliba F et al, personnal experience RR 95% CI p 2.7 [1.1-6.8] 0.03 2.7 [1.2-5.9] 0.01 3.7 [1.6-8.8] 0.01 3.5 [1.3-9.5] 0.01 Risk factors of IA after Lung transplantation Early Fungal Infections Single lung transplant Surgical factors include: Lung/airway denervation anastomotic ischemia provides nidus for fungal infection Stents predispose to tracheal infection Diffuse airway ischemia Acute allograft rejection CMV infection Pre and post transplant Aspergillus colonisation Acquired hypogammagloblinemia (IgG < 400mg/dl) Transmission with the allograft Late Fungal Infections Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome ? Risk factors of IA after Heart transplantation Isolation of Aspergillus from redspiratory tract cultures Reintervention CMV disease Hemodialysis Existence of an episode of IA in the program in the program 2 months before or after heart transplant Overall mortality : 67% Munoz P et al, Curr Opin Infect Dis 2006; 19: 365-370 Singh N et al, Am J Transplant 2009, 9, S180-S191 . Risk factors of IA after Renal transplantation High doses or prolonged duration of corticosteroids Graft failure requiring Hemodialysis Potent immunosuppressive therapy for rejection Overall mortality : 67-75 % Singh N et al, Am J Transplant 2009, 9, S180-S191 . Prophylaxis Targeted prophylaxis Preemptive Therapy Fungal Prophylaxis after Liver transplantation Drugs that have been shown to non efficaceous in preventing IFI after transplantation Nystatin Fungizone Conventional low dose of Amphotericin B 0.2 - 0.5 mg/kg/day x 7 - 21 days Prophylaxis of IFI after LTx A randomized controlled study itraconazole vs placebo Itraconazole 5 mg/kg prior to LTx then 2.5 mg/kg BID after LTx All IFI were due to Candida Study was not sufficient to show any efficacy against IA 60 p = 0.049 40 20 0 Colby WD. 39th ICAAC, San Francisco, 1999 Abstract N°1650. 37 24 (24%) 1 (4%) 9 Itraconazole Placebo Prophylaxis with Liposomal Amphotericin B after Liver Transplantation • Randomized study of liposomal amphotericin B (1 mg/kg/day x 5 days) vs placebo Placebo (n=37) Liposomal amphotericin B (n=40) Infection (1 month) 6 (16 %) 0 Infection (>1 month to 1 year) 5 (IA:1) 4 (IA:3) 78% 80% 3 1 Survival (1 year) Mortality (1 year) due to IFI Tollemar JG, et al. Transplant Proc 1995;27:1195-8 Targeted Prophylaxis (preemptive) in Liver transplant recipients requiring Hemodialysis n = 148; dialysis: 22, others: 126 No prophylaxis 1997 Dialysis 40% n = 38; dialysis: 11, others: 27 ABLC/L-AmB 5 mg/kg/j Others 36% 30% 20% 10% 0% 14% 7% IFI Singh N et al, Transplantation 2001 2% IA 0 0 IFI 0 0 IA Fungal prophylaxis Prophylaxis was targeted to high-risk patients mainly ALF, Retransplantation, End-stage cirrhosis in the ICU A total of 198 high-risk patients received a fungal prophylaxis 146 high-risk patients (21.9%) received Amphotericin B lipid complex (ABLC) fungal prophylaxis Dosage: 1mg/kg/day x 1w then 2.5 mg/kg biw Day 1 to day 7 (mean) : 76 ± 16 mg Cumulated dose (mean) : 955 ± 609 mg Mean duration : 23 ± 12 days 50 patients received Fluconazole Mean dose : 245 ± 108 mg/day (median : 200 mg) Mean duration : 18 ± 11 days Saliba F et al, European Society of Organ transplantation (ESOT), Paris Sept 2009 Saliba F et al, International Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (ICAAC) San Francisco, Sept 2009 Results : Candida infection No prophylaxis Fungal prophylaxis 100 90 80 70 60 p= NS 50 p=0.0002 p=0.0001 p=0.009 p= 0.03 40 33,3 32,4 30 18,7 17,7 20 10,9 11,5 6,1 10 4,5 2,5 2,5 0 Candida Candida Candidemia Candiduria Candida infection treated Abdominal infection Saliba F et al, European Society of Organ transplantation (ESOT), Paris Sept 2009 Saliba F et al, International Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (ICAAC) San Francisco, Sept 2009 Results : Aspergillosis ABLC prophylaxis : 1mg/Kg/day x 3 weeks 50 45 No prophylaxis 40 ABLC prophylaxis 35 30 25 P= NS 20 15 10 5 0 5,5 5,5 Aspergillosis 3,2 4,1 Probable Aspergillosis 2,8 1,4 Proven Aspergillosis Saliba F et al, European Society of Organ transplantation (ESOT), Paris Sept 2009 Saliba F et al, International Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (ICAAC) San Francisco, Sept 2009 Prophylaxis with Caspofungin in High-risk Liver Transplant Recipients • A prospective multicentre Spanish study • Duration of prophylaxis: 21 days (range 5–54 days) • Successful response: 88.7% • 2 patients developed IFI after end of therapy: Mucor and Candida albicans Fortun J and GESITRA study group. Transplantation 2009;87:424-37 Attitude towards prophylaxis of Liver transplant Centers in USA Survey : electronic questionnaire 67/106 (63%) of the centers answered 100 90 Traitement of choice: Fluconazole (86%) 91 80 72 70 60 50 40 28 30 20 10 0 Traitement of choice for moulds: Echinocandins (41%) Voriconazole (25%) Polyene (18%) Combination therapy : Antifungal Prophylaxis Universal prophylaxis High-risk patients prophylaxis Singh N et al, Am J Transplant 2008, 8:426-31. Primary therapy for IA: 47% For salvage therapy IA: 80% Prophylaxis Fluconazole vs non-Fluconazole Higher rate of mould infections (Aspergillosis, zygomycosis and scedosporiosis) RR 1.5 (95% CI 1.0-2.2; p=0.04) Prophylaxis of high-risk patients after Liver transplantation (Recommendations of the AST Infectious disease Community of Practice) Lipid formulation of AmB (II 2) 3-5 mg/kg/day Or an Echinocandin (II 3) Duration 3-4 weeks or until resolution of risk factors Singh N et al, Am J Transplant 2009, 9, S180-S191 . Prophylaxis for high-risk patients after Lung transplantation (recommendations of the AST Infectious disease Community of Practice) Inhaled amphotericin B 6-30 mg/day 25 mg/day Inhaled lipid formulations of amphotericin B Nebulized ABLC (II 3) 50 mg/every 2 days for 2 weeks Once a week x 13 weeks (minimum) Nebulized L-AmB 25 mg three times per week x 2 months Then once a week x 6 months Then twice per month In high-risk patients Voriconazole* : 400 mg/day x 4 months Itraconazole*: 400 mg/day x 4 months Monitor liver enzymes and azole and Immunosuppressive drugs +++ Singh N et al, Am J Transplant 2009, 9, S180-S191 . Voriconazole for Prophylaxis after Lung transplantation IFI NonAspergillus infections at 1 year Voriconazole N= 65 Targeted prophylaxis Itraconazole or Inhaled ampho B N= 30 p 1 (1.5%) 7 (23%) 0.001 2 (3%) 7 (23%) 0.004 Husain S et al, AJT 2006; 6:3008-16 Prophylaxis for high-risk patients after Heart transplantation (Recommendations of the AST Infectious disease Community of Practice) Voriconazole 200mg BID for 50-150 days Singh N et al, Am J Transplant 2009, 9, S180-S191 . Management of Invasive Fungal Infection • Early specific diagnosis often requires invasive procedure • Effective therapy must take into consideration: Common altered liver and kidney functions Drug toxicities Liver, kidney, brain… Drug interactions Immunosuppressive drugs: Calcineurine inhibitors: Cyclosporine, tacrolimus mTOR inhibitors: sirolimus, everolimus Antimicrobials Glycopeptides, aminoglycosides, rifampicin… ABLC in the treatment of IA after SOT ABLC (5mg/Kg/day) compared to an historical group of c-AmB (1.1 mg/kg/day) ABLC 90 c-AmB 83 76 80 Mortality (%) 70 60 50 40 33 25 30 20 10 0 Linden PK et al, CID 2003; 37:17-25 Overall Mortality IA- related mortality Survival after treatment of IA after SOT A prospective and retrospective study • First-line treatment : • Caspofungine + Voriconazole (n=40) between 2003 et 2005 • Historical group : L-AmB (n=47) between 1999 and 2002 L-AmB (n=47) between 1999 and 2002 Probability of Survival (%) 100 Caspofungine + Voriconazole 75 67% 51% 50 L-AmB 25 0 0 Singh et al. Transplantation 2006 50 Days after the diagnosis 100 Survival after treatment of IA after SOT A prospective and retrospective study 70% • Caspofungine + Voriconazole (n=40) between 2003 et 2005 • Historical group : L-AmB (n=47) between 1999 and 2002L-AmB Response rate (%) • First-line treatment : P=0.048 P=0.08 52,5% 51% P=0.79 17,5% 29,8% 21,3% (n=47) between 1999 and 2002 Total success Singh et al. Transplantation 2006 Complete response Partial response Caspofungine for treatment of IA after SOT •A retrospective study : 81 SOT patients with IFI •IA : 22 patients, 19 treated with Caspofungine •Proven : 7 patients •Probable 12 patients Survived Total treated patients 20 18 16 14 74% 12 10 8 6 4 78% 70% CASPO monotherapy CASPO combination 2 0 Winkler M et al, Transplant inf Dis 2010 Total Conclusion Invasive Aspergillosis has a major impact on patient survival Risk factors for developping IA are now well known Serum, sputum and BAL galactomannan could be of help but need further evaluation Prophylaxis should be administered only to high-risk patients Further multicenter trials are needed to evaluate their efficacy Echinocandins are currently under evaluation Management of IA is comparable to the non-transplant setting