* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Algebra 1 Study Guide Answer Section
Polynomial greatest common divisor wikipedia , lookup
Cubic function wikipedia , lookup
Gröbner basis wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental theorem of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Polynomial ring wikipedia , lookup
Eisenstein's criterion wikipedia , lookup
Quartic function wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic equation wikipedia , lookup
Factorization of polynomials over finite fields wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
History of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Factorization wikipedia , lookup
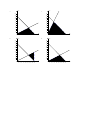
Algebra 1 Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. What is each expression written using each base only once? 1) a b c d What is the simplified form of each expression? 2) a b c d Find the simplified form of the expression. Give your answer in scientific notation. 3) a 1.5 1012 b 5.6 1012 c 1.5 1029 d What is the simplified form of the expression? 4) a b c d a b c d 5) What is the simplified form of each expression? 6) a b c d What is the simplified form of the expression? 7) a b What is the sum or difference? c d 5.6 1029 8) 3x8 – 7x8 a –4x16 b –21x8 c –4x8 c 2n3 + 6n + 8 n2 + 5n + 4 d 10x8 Simplify the product. 9) 2n(n2 + 3n + 4) a 2n3 + 6n2 + 8n b 2n3 + 3n + 4 d Factor the polynomial. 10) 42w10 + 24w6 a w6(42w4 + 24) b 6w6(7w4 + 4) c d 6(7w10 + 4w6) 6w5(7w5 + 4w) What is the factored form of the expression? 11) 15g3 + 20g2 – 18g – 24 a (5g2 + 4)(3g – 6) b (5g2 – 6)(3g + 4) c d (5g2 + 6)(3g – 4) (5g2 – 4)(3g + 6) What is the factored form of the expression? Factor completely. 12) 6x4 – 9x3 – 36x2 + 54x a b 3x(x2 – 6)(2x – 3) 3x(x2 + 6)(2x + 3) c d 6x(x2 – 6)(2x – 3) 6x(x2 + 6)(2x + 3) What are the coordinates of the vertex of the graph? Is it a maximum or minimum? 13) 4 y 3 2 1 –4 –3 –2 –1 1 2 3 4 x –1 –2 –3 –4 a b (2, 0); minimum (0, 2); minimum c d (2, 0); maximum (0, 2); maximum What is the solution of the system? Use substitution. 14) 3x + 2y = 7 y = –3x + 11 a (6, –3) b (6, –7) c d (5, –4) d (–9, –9) What is the solution of the system? Use elimination. 15) 3x – 4y = 9 –3x + 2y = 9 a (3, 9) b (–27, –9) c (–3, –6) What is the solution of the system? Use a graph. 16) y = x + 5 y = –5x – 1 a c y –4 y 4 4 2 2 –2 2 4 x –4 –2 –2 d 17) 4 x y 4 (–1, 4) 2 2 2 4 x (4, –1) –4 –2 –2 –2 –4 –4 Graph the inequality. 2 –4 (0.67, –4.35) 4 –2 x –2 y –4 4 (–1.5, –2.5) –4 b 2 a c y –4 –2 4 4 2 2 O 2 4 x –2 O –2 –4 –4 d y –2 –4 –2 b –4 y 4 2 2 2 4 x –4 –2 O –2 –2 –4 –4 Find the GCF of the terms of the polynomial. 18) 30x3 + 16x5 a 16x b 2x3 c 2x5 c –3, 9 –3, –9 d What are the solutions of the equation? 19) a b 3, 9 3, –9 d Simplify the expression. 20) a b Solve the equation. Check your solution. 21) c 4 x 2 4 x y 4 O 2 d x3 a 6 b 36 c 3 d 6 b 16 c 58 d 23 22) a 40 23) Solve the equation. Then check your solution. a b c 11 –1 d 9 1 24) Graph the system of equations. Then determine whether the system has no solution, one solution, or infinitely many solutions. If the system has one solution, name it. a c no solution infinitely many y –6 b –4 y 6 6 4 4 2 2 –2 2 4 6 x –6 –4 –2 –2 –2 –4 –4 –6 –6 d one solution; (4, 1) –4 6 x 2 4 6 x y 6 6 4 4 2 2 –2 4 one solution; (1, 4) y –6 2 2 4 6 x –6 –4 –2 –2 –2 –4 –4 –6 –6 25) Graph the system of equations. Then determine whether the system has no solution, one solution, or infinitely many solutions. If the system has one solution, name it. a c no solution one solution; (–2, –1) y –6 b –4 y 6 6 4 4 2 2 –2 2 4 6 x –6 –4 –2 –2 –2 –4 –4 –6 –6 one solution; (–1, –2) d –4 6 x 2 4 6 x y 6 6 4 4 2 2 –2 4 infinitely many y –6 2 2 4 6 x –6 –4 –2 –2 –2 –4 –4 –6 –6 26) The cost of 3 large candles and 5 small candles is $6.40. The cost of 4 large candles and 6 small candles is $7.50. Which pair of equations can be used to determine, t, the cost of a large candle, and s, the cost of a small candle? a c b d 27) The sum of two positive integers is less than 80 and their difference is more than 10. Write a system of inequalities to represent this situation. a c b d 28) Find the degree of the polynomial. a b 7 4 c d 12 8 29) Find the degree of the polynomial. a b 23 15 c d 30) Find the sum or difference. a b c d 31) Find the sum or difference. a b c d 32) Solve the equation. a c b d 33) Solve the equation. a c b d 34) Solve the equation. 14 13 a c b d 35) Find the product. a c b d 36) Find the product. a b c d 37) Factor the monomial completely. a b c d 38) Factor the trinomial. a c b d 39) Solve the equation. Then check your solution. a c b d 40) The Washington family is hosting a cookout. They decide to serve chicken and pork. They determine that they will need at most 20 pounds of meat, and they want to have at least twice as much chicken as pork. Make a graph showing the amount of each type of meat that satisfies the requirements. a c pork pork 22 22 20 20 18 18 16 16 14 14 12 12 10 10 8 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 2 b 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 chicken 2 d pork 22 20 20 18 18 16 16 14 14 12 12 10 10 8 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 chicken 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 chicken 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 chicken pork 22 2 4 2 Algebra 1 Study Guide Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1) ANS: REF: OBJ: TOP: 2) ANS: REF: OBJ: TOP: DOK: 3) ANS: REF: OBJ: TOP: DOK: 4) ANS: REF: STA: DOK: 5) ANS: REF: STA: DOK: 6) ANS: OBJ: TOP: 7) ANS: OBJ: TOP: 8) ANS: OBJ: TOP: DOK: 9) ANS: OBJ: TOP: DOK: 10) ANS: OBJ: TOP: 11) ANS: OBJ: TOP: DOK: 12) ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: L2 7-3 Multiplying Powers With the Same Base 7-3.1 To multiply powers with the same base STA: MA.912.A.4.1 7-3 Problem 1 Multiplying Powers DOK: DOK 1 B PTS: 1 DIF: L2 7-3 Multiplying Powers With the Same Base 7-3.1 To multiply powers with the same base STA: MA.912.A.4.1 7-3 Problem 2 Multiplying Powers in Algebraic Expressions DOK 1 B PTS: 1 DIF: L2 7-3 Multiplying Powers With the Same Base 7-3.1 To multiply powers with the same base STA: MA.912.A.4.1 7-3 Problem 3 Multiplying Numbers in Scientific Notation DOK 1 D PTS: 1 DIF: L2 7-4 More Multiplication Properties of Exponents OBJ: 7-4.1 To raise a power to a power MA.912.A.4.1 TOP: 7-4 Problem 1 Simplifying a Power Raised to a Power DOK 1 C PTS: 1 DIF: L3 7-4 More Multiplication Properties of Exponents OBJ: 7-4.1 To raise a power to a power MA.912.A.4.1 TOP: 7-4 Problem 1 Simplifying a Power Raised to a Power DOK 1 B PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 7-5 Division Properties of Exponents 7-5.1 To divide powers with the same base STA: MA.912.A.4.1 7-5 Problem 1 Dividing Algebraic Expressions DOK: DOK 1 A PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 7-5 Division Properties of Exponents 7-5.2 To raise a quotient to a power STA: MA.912.A.4.1 7-5 Problem 3 Raising a Quotient to a Power DOK: DOK 1 C PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 8-1 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials 8-1.1 To classify, add, and subtract polynomials STA: MA.912.A.4.2 8-1 Problem 2 Adding and Subtracting Monomials KEY: monomial | degree of a monomial DOK 1 A PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 8-2 Multiplying and Factoring 8-2.1 To multiply a monomial by a polynomial STA: MA.912.A.4.2| MA.912.A.4.3 8-2 Problem 1 Multiplying a Monomial and a Trinomial KEY: polynomial | trinomial | monomial DOK 1 B PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 8-2 Multiplying and Factoring 8-2.2 To factor a monomial from a polynomial STA: MA.912.A.4.2| MA.912.A.4.3 8-2 Problem 3 Factoring Out a Monomial DOK: DOK 1 B PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 8-8 Factoring by Grouping 8-8.1 To factor higher-degree polynomials by grouping STA: MA.912.A.4.3 8-8 Problem 1 Factoring a Cubic Polynomial KEY: factoring by grouping DOK 1 A PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 8-8 Factoring by Grouping 13) 14) 15) 16) 17) 18) 19) 20) 21) 22) 23) OBJ: 8-8.1 To factor higher-degree polynomials by grouping STA: MA.912.A.4.3 TOP: 8-8 Problem 2 Factoring a Polynomial Completely KEY: factoring by grouping DOK: DOK 1 ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 9-1 Quadratic Graphs and Their Properties OBJ: 9-1.1 To graph quadratic functions of the form y = ax^2 and y = ax^2 + c STA: MA.912.A.7.1| MA.912.A.7.6| MA.912.A.7.8 TOP: 9-1 Problem 1 Identifying a Vertex KEY: quadratic function | parabola | maximum | minimum | vertex DOK: DOK 1 ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 6-2 Solving Systems Using Substitution OBJ: 6-2.1 To solve systems of equations using substitution STA: MA.912.A.3.14| MA.912.A.3.15 TOP: 6-2 Problem 1 Using Substitution KEY: substitution method DOK: DOK 1 ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 6-3 Solving Systems Using Elimination OBJ: 6-3.1 To solve systems by adding or subtracting to eliminate a variable STA: MA.912.A.3.14| MA.912.A.3.15 TOP: 6-3 Problem 1 Solving a System by Adding Equations KEY: elimination method DOK: DOK 1 ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 6-1 Solving Systems By Graphing OBJ: 6-1.1 To solve systems of equations by graphing STA: MA.912.A.3.13| MA.912.A.3.14| MA.912.A.3.15 TOP: 6-1 Problem 1 Solving a System of Equations by Graphing KEY: consistent | independent | solution of a system of linear equations | system of linear equations DOK: DOK 1 ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 6-5 Linear Inequalities OBJ: 6-5.1 To graph linear inequalities in two variables STA: MA.912.A.3.5| MA.912.A.3.12 TOP: 6-5 Problem 2 Graphing an Inequality in Two Variables KEY: linear inequality DOK: DOK 1 ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 8-2 Multiplying and Factoring OBJ: 8-2.2 To factor a monomial from a polynomial STA: MA.912.A.4.2| MA.912.A.4.3 TOP: 8-2 Problem 2 Finding the Greatest Common Factor DOK: DOK 1 ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 9-4 Factoring to Solve Quadratic Equations OBJ: 9-4.1 To solve quadratic equations by factoring STA: MA.912.A.1.8| MA.912.A.7.2| MA.912.A.7.8 TOP: 9-4 Problem 2 Solving by Factoring KEY: Zero-Product Property DOK: DOK 2 ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 10-3 Operations With Radical Expressions OBJ: 10-3.1 To simplify sums and differences of radical expressions STA: MA.912.A.6.2 TOP: 10-3 Problem 1 Combining Like Radicals KEY: like radicals DOK: DOK 1 ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 10-4 Solving Radical Equations OBJ: 10-4.1 To solve equations containing radicals STA: MA.912.A.6.2 TOP: 10-4 Problem 1 Solving by Isolating the Radical KEY: radical equation DOK: DOK 1 ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 10-4 Solving Radical Equations OBJ: 10-4.1 To solve equations containing radicals STA: MA.912.A.6.2 TOP: 10-4 Problem 1 Solving by Isolating the Radical KEY: radical equation DOK: DOK 1 ANS: D To solve an equation with more than one operation, undo operations by working backward. Feedback A B C D How did you undo the operation in the first step? Be careful with sign rules. What operation did you try to undo first? Correct! PTS: 1 DIF: Average REF: Lesson 2-3 OBJ: 2-3.1 Solve equations by involving more than one operation. STA: MA.912.A.3.1 | MA.912.A.3.5 | MA.912.A.10.3 TOP: Solve equations involving more than one operation KEY: Solve Equations | Equations 24) ANS: D Graph each line. The point where the two lines intersect is the solution. Check the solution by replacing x and y in the original equations with the values in the ordered pair. Feedback A B C D Did you graph the second line correctly? Remember that the x-coordinate comes first in an ordered pair. Graph both lines. Correct! PTS: 1 DIF: Average REF: Lesson 6-1 OBJ: 6-1.2 Solve systems of equations by graphing. STA: MA.912.A.3.13 | MA.912.A.3.14 | MA.912.A.3.15 | MA.912.A.10.2 | MA.912.A.10.3 TOP: Solve systems of equations by graphing KEY: System of Equations | Graphing 25) ANS: B Graph each line. The point where the two lines intersect is the solution. Check the solution by replacing x and y in the original equations with the values in the ordered pair. Feedback A B C D Did you graph the second line correctly? Correct! Remember that the x-coordinate comes first in an ordered pair. Graph both lines. PTS: 1 DIF: Average REF: Lesson 6-1 OBJ: 6-1.2 Solve systems of equations by graphing. STA: MA.912.A.3.13 | MA.912.A.3.14 | MA.912.A.3.15 | MA.912.A.10.2 | MA.912.A.10.3 TOP: Solve systems of equations by graphing KEY: System of Equations | Graphing 26) ANS: A Write a system of equations for the situation. Feedback A B C D Correct! Check the first equation. Check the second equation. Check the coefficients of t and s in the first equation. PTS: 1 DIF: Basic REF: Lesson 6-4 OBJ: 6-4.2 Solve real-world problems involving systems of equations. STA: MA.912.A.3.14 | MA.912.A.3.15 TOP: Solve real-world problems involving systems of equations. KEY: System of Equations | Real-World Problems 27) ANS: C Translate the words into mathematical symbols. The endpoints are not included in the inequalities. Feedback A B C D The endpoints are not included in the inequalities. These inequalities do not fit the situation. Correct! These inequalities do not fit the situation. PTS: 1 DIF: Average REF: Lesson 6-8 OBJ: 6-8.2 Solve real-world problems involving systems of inequalities. STA: MA.912.A.3.14 | MA.912.A.3.15 | MA.912.A.10.3 TOP: Solve real-world problems involving systems of inequalities KEY: System of Inequalities | Real-World Problems DOK: 1998 Lesson 8-5 28) ANS: A Add the exponents of the variables only. Feedback A B C D Correct! Add both exponents. Add only the exponents. Add the exponents of the variables. PTS: 1 DIF: Basic REF: Lesson 7-4 OBJ: 7-4.1 Find the degree of a polynomial. STA: LA.910.1.6.1 TOP: Find the degree of a polynomial KEY: Polynomials | Degree of Polynomial 29) ANS: C Add the exponents of the variables for each monomial. The degree of the polynomial is the highest degree of any of its monomials. Feedback A B C D Add exponents of each monomial, not each exponent in like variables. Only add the exponents of the variables. Correct! Add the exponents of all 3 monomials. PTS: 1 DIF: Average REF: Lesson 7-4 OBJ: 7-4.1 Find the degree of a polynomial. STA: LA.910.1.6.1 TOP: Find the degree of a polynomial KEY: Polynomials | Degree of Polynomial 30) ANS: D Group like terms together and then add like terms. The power stays the same. Feedback A B C Be careful with your signs. Group like terms together. Subtract the other a. D Correct! PTS: 1 DIF: Average REF: Lesson 7-5 OBJ: 7-5.1 Add polynomials. STA: MA.912.A.4.2 TOP: Add polynomials KEY: Polynomials | Add Polynomials 31) ANS: D Group like terms together. Subtract like terms, making sure you subtract negatives (add). The power stays the same. Feedback A B C D Be careful with your signs. Be careful with your signs. Be careful with your signs. Correct! PTS: STA: KEY: 32) ANS: 1 DIF: Average REF: Lesson 7-5 OBJ: 7-5.2 Subtract polynomials. MA.912.A.4.2 TOP: Subtract polynomials Polynomials | Subtract Polynomials D Feedback A B C D Be careful subtracting 12 from both sides. Subtract 10x from both sides. Multiply the number outside the parentheses by EACH monomial inside. Correct! PTS: OBJ: TOP: 33) ANS: Either If If 1 DIF: Basic REF: Lesson 7-6 7-6.2 Solve equations involving polynomials. Solve equations involving polynomials C or . , then . , then . Feedback A B Watch your signs. Remember, either r – 3 = 0 or r + 6 = 0. STA: MA.912.A.4.2 KEY: Polynomials | Solve Equations C D Correct! Remember, either r – 3 = 0 or r + 6 = 0. PTS: OBJ: STA: KEY: 34) ANS: 1 DIF: Basic REF: Lesson 8-2 8-2.2 Solve quadratic equations in the form ax^2 + bx = 0. MA.912.A.1.8 | MA.912.A.4.3 TOP: Solve quadratic equations of the form ax^2 + bx = 0 Quadratic Equations | Solve Equations A Feedback A B C D Correct! Watch your division. Watch your division. Watch your division. PTS: OBJ: STA: KEY: 35) ANS: 1 DIF: Average REF: Lesson 8-2 8-2.2 Solve quadratic equations in the form ax^2 + bx = 0. MA.912.A.1.8 | MA.912.A.4.3 TOP: Solve quadratic equations of the form ax^2 + bx = 0 Quadratic Equations | Solve Equations B Feedback A B C D Use the FOIL method. Correct! Use the FOIL method. Watch your signs. PTS: OBJ: TOP: 36) ANS: 1 DIF: Basic REF: Lesson 7-7 7-7.1 Multiply two binomials by using the FOIL method. STA: MA.912.A.4.2 Multiply two binomials by using the FOIL method KEY: Multiply Binomials | FOIL Method A Feedback A B C D Correct! Multiply each number in the binomial by each number in the polynomial, adding exponents. Then add numbers of like powers. Multiply each number in the binomial by each number in the polynomial, adding exponents. Then add numbers of like powers. Watch your signs. PTS: 1 DIF: Average REF: Lesson 7-7 OBJ: 7-7.2 Multiply two polynomials by using the Distributive Property. STA: MA.912.A.4.2 TOP: Multiply two polynomials by using the Distributive Property KEY: Multiply Polynomials | Distributive Property 37) ANS: B The prime factors of 70 are . The prime factors of are . The prime factors of are . Thus, is factored into . Feedback A B C D How many b's are there? Correct! You want the prime factors. How many a's are there? PTS: 1 DIF: Average REF: Lesson 8-1 OBJ: 8-1.1 Find prime factorizations of monomials. STA: LA.910.1.6.1 TOP: Find prime factorizations of monomials KEY: Prime Factorization | Monomials 38) ANS: C Two variables, and , exist such that . and . Make a table to find the possible solutions. The correct factors are 2 and –13. Feedback A B C D Remember, m + n = the middle number and m n = the last number. Watch your signs. Correct! Remember, m + n = the middle number and m n = the last number. PTS: 1 DIF: Average REF: Lesson 8-3 OBJ: 8-3.1 Factor trinomials of the form x^2 + bx + c. STA: MA.912.A.4.3 | MA.912.A.7.2 | MA.912.A.1.8 | MA.912.A.7.8 | MA.912.A.10.2 TOP: Factor trinomials of the form x^2 + bx + c KEY: Factor Trinomials 39) ANS: C Divide both sides of the inequality by the constant on the left. Remember to flip the inequality sign since you are dividing by a negative number. Feedback A Remember to flip the inequality sign since you are dividing by a negative number. B C D Use division instead of multiplication to solve this. Correct! Use division instead of subtraction to solve this. PTS: OBJ: STA: TOP: 40) ANS: 1 DIF: Average REF: Lesson 5-2 5-2.2 Solve linear inequalities by using division. MA.912.A.3.4 | MA.912.A.3.5 | MA.912.A.10.3 Solve linear inequalities by using division A Graph the inequalities and KEY: Linear Inequalities | Division . The solution is the shaded area. Feedback A B C D Correct! Did you use the correct inequality signs? There must be at least twice as much chicken as pork. Double-check this inequality. A dotted line means that the points on the line are not included in the solution. PTS: OBJ: STA: TOP: KEY: 1 DIF: Average REF: Lesson 6-8 6-8.2 Solve real-world problems involving systems of inequalities. MA.912.A.3.14 | MA.912.A.3.15 | MA.912.A.10.3 Solve real-world problems involving systems of inequalities System of Inequalities | Real-World Problems DOK: 1998 Lesson 8-5