* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1 - NEHSMath
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Cardinal direction wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
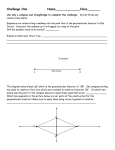
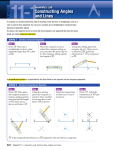
Section 1-5: Constructions SPI 32A: Identify properties of plane figures TPI 42A: Construct bisectors of angles and line segments Objective: • Use a compass and straight edge to construct and bisect congruent segments and angles Perpendicular Lines Two lines that intersect to form right angles. Perpendicular Bisector A line, segment, or ray that is perpendicular to the segment at its midpoint, thereby bisecting the segment into two congruent segments. 2 congruent segments midpoint Angle Bisector Ray that divides an angle into two congruent coplanar angles. • Its endpoint is the angle vertex • Say… Ray or Segment bisects the angle Tools used for Geometric Constructions Straight Edge Ruler with no markings Compass Tool used to draw circles or arcs Next, you will learn to construct: 1. Congruent Segments 2. Congruent Angles 3. Perpendicular Bisectors 4. Angle Bisectors Construct Congruent Segments with Straight Edge and Compass Construct a segment congruent to a given segment. Given: AB Construct: CD so that CD AB Step 1: Draw a ray with endpoint C A C Step 2: Open a compass to the length AB Step 3: With the same compass setting, put the compass point on point C. Draw an arc that intersects the ray. Label the point of intersection D. CD AB B Construct Congruent Angles using Straight Edge and Compass Construct an angle congruent to a given angle. Given: A Construct: S so that S A Step 1: Draw a ray with endpoint S. A S Step 2: With the compass point on point A, draw an arc that intersects the sides of A. Label the points of intersection B and C. Step 3: With the same compass setting, put the compass point on point S. Draw an arc and label its point of intersection with the ray as R. Step 4: Open the compass to length BC. Keeping the same compass setting, put the compass point on R. Draw an arc to locate point T. Step 5: Draw ST. Construct Perpendicular Bisector Construct the perpendicular bisector of a segment. Given: AB Construct: XY so that XY AB at the midpoint M of AB Step 1: Put the compass of point A and draw a long arc as shown. Be sure the opening is greater than ½ AB. Step 2: With the same compass setting, put the compass point on point B and draw another long arc. Labe the points where the two arcs intersect as X and Y. Step 3: Draw XY. The point of intersection of AB and XY is M, the midpoint of AB. XY AB at the midpoint of AB, so XY is the Perpendicular bisector of AB. A B Construct Angle Bisector Construct the bisector of an angle Given: A Construct: AX, the bisector of A Step 1: Put the compass of vertex A. Draw an arc that intersects the sides of A. Label the points of intersection B and C. Step 2: Put the compass point on point C and draw an arc. With the same compass setting, draw an arc using point B. Be sure the arcs intersect. Label the intersection as X. Step 3: Draw AX. AX is the bisector of CAB. Construction and Vocabulary Activity 1. Use your compass to draw a circle. 2. Locate three points A, B, and C on the circle. 3. Construct perpendicular bisectors of AB and BC. 4. Label the intersection of the two perpendicular bisectors as point O. 5. Make a conjecture about point O.















![PH_Geo_3-8_Constructing_parallel_lines[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001202465_1-91ca6e9d9e8948ba2229cefd106376ad-150x150.png)