* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Aztecs vs. Inca
Bernardino de Sahagún wikipedia , lookup
Texcoco, State of Mexico wikipedia , lookup
Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire wikipedia , lookup
National Palace (Mexico) wikipedia , lookup
Templo Mayor wikipedia , lookup
Fall of Tenochtitlan wikipedia , lookup
Human sacrifice in Aztec culture wikipedia , lookup
Aztec warfare wikipedia , lookup
Aztec cuisine wikipedia , lookup
Aztec Empire wikipedia , lookup
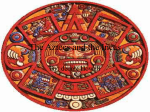
AZTEC VS. INCA AP World History Victoria Rains RISE OF THE AZTECS • Aztecs migrate to Lake Texcoco in central Mexico around 1325 • Founded city of Tenochtitlan in 1325 • Empire started in 1434 • Aztec kings represented civil power and served as a representative AZTEC GOVERNMENT • City-states ruled by a speaker chosen from the nobility • The Great Speaker, ruler of Tenochtitlan, was in effect an emperor • Increasingly considered a living god • The Aztecs made the people they conquered pay tribute, or give them cotton, gold, or food. AZTEC RELIGION • Aztec maintained traditional deities of Mesoamerica • 128 major deities • Huitzilopochtli (right) was the Aztec tribal patron and patron god of the cult of sacrifice and warfare • Quetzalcoatl (meaning feathered serpent) was the one who would create humans. HUMAN SACRIFICE • Human sacrifice was a typical part of Mesoamerican religion • Aztec expand practice into a cult where military supplied war captives for sacrifice • Why? • Political purposes • Population control • Cannibal kingdom TENOCHTITLAN • Captial of the Aztec Empire • Built in the middle of a lake on an island • Aztecs called it the “foundation of Heaven” • By 1519 had a population of 150,000 • Connected by causeways and canals AZTEC ECONOMY • Agriculture • Food often provided as tribute • Built chinampas • Pochteca was a special merchant class which specialized in long-distance luxury trade • Cacao beans and gold dust were used as currency; bartering was most common AZTEC SOCIETY • Originally divided into seven clans called calpulli • Calpulli redistributed land, organized labor gangs & military units, maintained temples & schools • Eventually a class of nobility emerged • Nobility controlled the priesthood & military AZTEC SOCIETY • Women’s primary role was the household • Women spent six hours a day grinding corn; restricted women’s rights • Marriages were arranged • Polygamy existed amongst the nobility • Women could inherit property AZTEC SCIENTIFIC ACHIEVEMENTS • The Aztecs studied astronomy and created a calendar much like the Mayan calendar. • The Aztecs also knew many different uses for plants. They knew of 100 different plants that could be used for medicine. Lippia dulcis- used to treat coughs & colds Mexican poppy- used for depression & anxiety Aztec calendar Mayan Calendar RISE OF INCA • Founded by Quechua speaking clans (ayllus) living near Cuzco around 1350 • Inca (ruler) Pachacuti expanded the empire from 1438-1471 • Built Machu Picchu • Expansion continued after Pachacuti’s death MACHU PICCHU CONQUEST & RELIGION Temple of the Sun in Machu Picchu • Expansion motivated by split inheritance • Polytheistic • Sun God was the primary god • Influenced by animism • Mountains, rivers, etc. were considered holy shrines INCAN GOVERNMENT • The Incas established an official language, Quechua • Divided empire into four provinces • Developed a bureaucracy run by nobles • Nobility drawn from the ten ayllus • Local rulers maintained their positions • Colonized conquered areas • Made conquered leaders move out of their villages and move in with leaders who were loyal to the Inca government INCA ECONOMY • • • • • • • • Unlike Aztecs, not a lot of trade Tried to be self-sufficient Primarily agricultural Terrace farming & complex irrigation Over 200 types of potatoes Inca Socialism Used forced labor for massive projects Mita TERRACE FARMING They carved steps of flat land up the side of the mountain to create flat land for farming. The terraces also helped to keep rainwater from running off. They reduced erosion. The government built raised aqueducts to carry water to farmlands for irrigation. INCA SOCIETY • Inca emphasis on military reinforced gender inequality • Women worked in the fields, wove cloth, and cared for the household • Women worshipped fertility deities • Recognize parallel descent • Women passed rights and property to their daughters INCA TECHNOLOGY • Built a complex system of roads and bridges • 2500 miles of roads • Used a system of runners to carry messages throughout the empire • Beautiful pottery, cloth, and metalworking • Quipu • Masonry BRIDGES AND ROADS QUIPU INCA METALWORKING AZTEC ART • Ancient Aztec art was primarily a form of religious expression and a means for paying tribute to their gods • Showed their deep religion through a variety of sculptures made of stones • Pottery was not only useful to the Aztecs; it was also an important religious craft within the Aztec arts INCA ART • Sculpted pottery which featured geometric designs painted in black, red, brown, yellow, and white. • Metalworkers make ornaments, tools, and weapons out silver, copper, gold, and bronze. • Inca weavers wove beautiful textiles from alpaca, llama, and vicuña wool and from cotton. AZTEC VIDEO http://www.history.com/videos/the-aztecs#the-aztecs