* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rocky Mountains
Survey
Document related concepts
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
Provenance (geology) wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
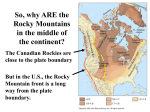
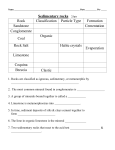
ROCKY MOUNTAIN SYSTEM Submitted By :-Your Name Add other necessary details like your roll no,college name,etc. GEOGRAPHICAL LOCATION:• The Rocky Mountains, often called the Rockies, are a mountain range in western North America • The Rocky Mountains stretch more than 3000 miles from northern most British Columbia,in Canada,to New Mexico in the United States. • Highest peak-Mount Elbert in Colorado(14,440 ft above sea level). Geological Events:• Geology of the Rocky Mountains reveals a discontinuous series of mountain ranges with distinct geological origins • The Rocky Mountains took shape during a period of intense plate tectonic activity that formed much of the rugged landscape of the western United states. • Three major mountain-building episodes reshaped the west from about 170 to 40 million years ago iods. • The Laramide orogeny, about 70–40 million years ago, was the last of the three episodes and was responsible for raising the Rocky Mountains Raising the Rockies :• The growth of the Rocky Mountains has been one of the most perplexing of geologic puzzles. • Mountain building is normally focused between 200 to 400 miles inland from a subduction zone boundary. Geologists continue to gather evidence to explain the rise of the Rockies so much farther inland; the answer most likely lies with an unusual subducting slab. • At a typical subduction zone, an oceanic plate typically sinks at a fairly high angle, and a volcanic arc grows above the subducting plate. Raising the Rockies(continuation)............... • It is postulated that the shallow angle of the subducting plate greatly increased the friction and other interactions with the thick continental mass above it. Tremendous thrusts piled sheets of crust on top of each other, building the extraordinarily broad, high Rocky Mountain range • The current Rockies were forced upwards through the layers of Pennsylvanian and Permian sedimentary remnants of the Ancestral Rocky Mountains. Such sedimentary remnants were often tilted at steep angles along the flanks of the modern range and visible in many places throughout the Rockies, included prominently along the Dakota Hogback, an early Cretaceous sandstone formation that runs along the eastern flank of the modern Rockies. The Rocks that Make Up the Rockies :• The Rockies are composed exclusively of layered sedimentary rocks. These include limestone,dolomite,sandstone and shale. • There are also a few isolated pockets of igneous (formerly molten) rocks. • Sedimentary rocks have a unique method of deposition – one layer on top of another. Digging through the layers, geologists can analyze their composition, and determine much about the climate and landscape during the time of their formation. Composition of sedimentary rocks:• Sedimentary rocks in rockies can be divided into two major groupings: inorganic and organic. • Inorganic rocks are those formed by the deposition of inorganic matter. This includes minerals as well as the remains of other older rocks that were eroded away, only to have their individual grains deposit as layered sediments. • Organic rocks are further broken down into chemical and organic origins. This group combines rocks formed from the remains of living organisms along with rocks resulting from several chemical processes. These include the limestones and dolomites that form many of our mountain summits, along with other valuable resources like coal.