* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
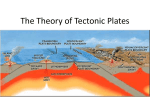
8.4 Note-taking Guide B 1. The place where two plates push together; one plate sinking beneath another; continental-continental collision, oceanic-continental subduction, oceanic-continental subduction. 2. Where two continental plates push together; how mountains form. 3. Denser oceanic plate sinks into the asthenosphere; sinking plate is melted; sometimes the melted rock rises back to the surface and forms volcanoes; if both are oceanic plates, the older sinks; if continental and oceanic plates meet, the oceanic plate sinks because it is more dense. 4. Deep-ocean trench forms along coastline. Coastal mountains form as continental plate buckles, folds, and rises up. Some mountains become volcanoes as magma rises up. 5. Students should draw mountains on the left plate, near the point where the plates meet. The X can be put anywhere between the mountains and the trench, an oceanic-continental subduction boundary. 6. The plate on the right; Oceanic plates are more dense, therefore they sink beneath continental plates. 7. Boundaries occur mainly on the sea floor, a few on land. 8. Geologists can use the theory to understand the geologic history of Earth. Rocks reveal how the Appalacian Mountains and U. S. Northeast coast formed. Geologists can also use the theory to predict major geologic events along plate boundaries.