* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Option A - IBperiod5
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
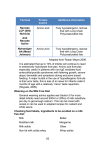
Option A.3 A.3.1 Distinguish between the composition of human milk and artificial milk used for bottlefeeding babies. [ Include lactose versus glucose, human milk proteins, differences in fatty acid composition, and lack of antibodies in artificial milk. Aim 8: There is an ethical issue involved here, as profit-making companies produce artifical milk. There are concerns that restrictions on the advertising of artificial milk in the developled world have led to greater marketing of it in developing countries, with health consequences for these babies.] Human Milk Artificial Milk Carbohydrate Lactose Lactose or glucose polymers Protein Source 65% whey proteins, 35% casein 18% Bovine whey and 82% bovine casein; or soya proteins Fatty Acids Human butterfat Palm, coconut, soy or safflower oils Antibodies Antibodies present in the first milk (colostrum) No antibodies for fighting human diseases present A3.2 Discuss the benefits of breastfeeding Aim 8: The bonding between a mother and child, and social attitudes to breastfeeding in public could be discussed. TOK: This is an example of the need for research findings to be passed on effectively from the scientific community to mothers worldwide. Advantages: Promotes mother baby bonding Provides immunological protection for the baby against many infections and diseases Acts as natural birth-control method reducing chance of conception while mother is lactating and therefore allows more time between birth of one child and the next Helps mother lose weight after pregnancy, promotes contractions in the uterus and controls postpartum bleeding. Avoids allergies to proteins in cows’ milk or soy that can develop when babies consume artificial milk It is also less expensive than formula and very convenient… always fresh. A3.3 Outline the causes and symptoms of type II diabetes ( this is sometimes called non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus) . [ Include differences in susceptibility between ethnic groups. TOK: The nature of risk factors and the difficulties of making decisions about the relative influence of nature and nurture could be discussed. There are clear differences in susceptibility to type II diabetes, with some populations of Native Australians (Aboriginal Australians) and Maoris having higher rates of incidence. This could lead to a wider consideration and appreciation of the diversity in human societies combined with the need for parity of esteem.] Less than 2% of Chinese have Type II Diabetes 50% of Pima Indians have Type II Diabetes Type II Diabetes is a decreased responsiveness of body cells to insulin due to “burn-out” Causes: Diets rich in fat and low in fibre Obesity due to overeating and lack of exercise Genetic factors which affect fat metabolism Symptoms: Elevated levels of blood glucose Glucose in urine Dehydration and thirst resulting from excretion of large volumes of urine A 3.4. Explain the dietary advice that should be given to a patient who has developed type II diabetes. This includes the reduced intake of sugars and syrups. Carbohydrates should be complex, meaning that they still have fiber, proteins, and require more time for the body to digest. The point is to eat less processed food, and more whole food… in moderation A3.5.Discuss the ethical issues concerning the eating of animal products, including honey, eggs, milk, and meat. Some do not eat meant because they think that it is wrong for an animal to be slaughtered so that they can eat. People who do not eat meat are called vegetarians. Some vegetarians simply do not care for meat. There is also a stricter form of vegetarianism where they do not eat any meat or products from animals including milk, eggs, or even honey. These people are called vegans A3.6. Evaluate the benefits of reducing dietary cholesterol in lowering the risk of coronary heart disease. Low density lipoproteins ( LDL) are considered bad cholesterol, while high density lipoproteins are the good ones. LDL are more susceptible to forming plaques in the blood vessels, which is atherosclerosis. Exercise increases HDL levels, smoking increases LDL levels. There is a genetic portion of the problem as well as a dietary portion.. Cholesterol levels can be controlled by exercise, diet and statins ( which are drugs). A3.7. Discuss the concept of food miles and the reasons for consumers choosing foods to minimize food miles. [ Food miles are simply a measure of how far a food item has been transported from its site of production to its site of consumption. Transport of food causes air pollution, traffic congestion, and greenhouse gas emissions. Transport of food also allows continuity of supply and increased choice for consumers. Aim 7: Databases and spreadsheets could be used. Aim 8: A discussion of the conflicts between responsibility as global citizens and the right to exert personal freedoms might be appropriate. TOK: Some concepts or theories offer a new perspective, which can change our attitudes significantly. Here, food miles allow us to assess how much we, as individuals, are contributing to global warming by our selection of foods.] Food miles are important and raising awareness and lowering greenhouse gas emissions associated with food transport. The longer the food has to travel from production to consumption, they more green house gasses and natural resources are used (in most cases). Those who want to help the environment might choose to consume locally grown food therefore supporting the low food mile food industry.