* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Oceanside Middle School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
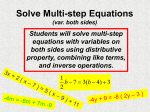
Name: ____________________________ Mr. Art Date: ________________ Period: _______________ Solving Linear Equations One-Step Equations (one operation) use inverse operations 1) 3x = 12 2) b – 9 = -14 3) a + 7 = 10 4) t 5 20 Two-Step Equations (two operations) Goal: Get the variable by itself First, work with the terms that do not have a variable (constant before coefficient) 1) 3y + 7 = 22 2) 3) 23 – 5y = 11 m 6 11.5 4 4) 52x – 213 = -57 Equations with parentheses – Distributive Property Use the distributive property to remove parentheses Then, use inverse operations to solve 1) 3(x + 2) = 21 2) 15 = -8(y + 4) 3) 4(3 – m) = -22 4) -2(3x – 2) = -10 Combining like terms Combine like terms that are on the same side of the equal sign Then, use inverse operations to solve 1) 3x + 4x = 28 2) 9x = 17 – 62 3) 8x – 2 + 3x + 7 = 27 4) 2y + 7 – 5y = 2.5 – 3 Variables on both sides of the equal sign Use inverse operations to get the variables all on one side of the equation (You cannot combine variables on different sides of the equal sign!) Then, use inverse operations 1) 2x + 17 = 3x 2) 5x = -10 + 3x 3) 12x = 10 – 8x 4) 8x – 10 = -30 + 3x Multi-Strategy Problems (more than one strategy) First, remove parentheses. Second, combine like terms Third, move all variables to one side of the equals sign Last, use inverse operations to isolate the variable. 1) 8 + 3(x + 7) = 4x 2) 2x – 3(x – 5) = 7x + 7