* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DATA WAREHOUSES
Full employment wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Modern Monetary Theory wikipedia , lookup
Nominal rigidity wikipedia , lookup
Exchange rate wikipedia , lookup
Phillips curve wikipedia , lookup
Long Depression wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Early 1980s recession wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative easing wikipedia , lookup
Real bills doctrine wikipedia , lookup
Helicopter money wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
Interest rate wikipedia , lookup
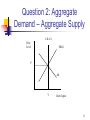
Banking with Trust Student Coaching 1 What is the Case About? Review Federal Reserve Stabilization Policy Play with Some Economic Numbers Apply Statistical Regression Incorporate Findings in Report Intended for Your Peers at the bank 2 Basics of Stabilization Policy (Standard Fed Version) Economy Fluctuates Around a Trend Rate of Growth Too Fast Growth is Bad as it Leads to Inflation Too Slow Growth is Bad as it Causes Unemployment Stabilization Policy Forecast Inflation and Output Growth in the Near Future “Lean Against the Wind” 3 Question 1: Looking at the Data on the Spreadsheet Percent Change = (New Value – Old Value) Old Value E. g. Percent Change = (101 – 100)/100 = .01 or 1% Inflation is Calculated as the Percent Change in the GDP Price Deflator GDP Deflator = 100*(Nominal GDP)/(Real GDP) E.g. Deflator = 100*(4000)/(5000) = 80.0 4 Question 2: Aggregate Demand – Aggregate Supply Aggregate Demand (AD) – Quantity of Goods and Services that Households, Firms, and the Government Want to Buy at Each Price Level Long Run Aggregate Supply (LRAS) – Production of Goods, Services (Real Output) Depends on Supply of Labor, Capital, Natural Resources, Technology – Price Level Does Not Affect Short Run Aggregate Supply (SRAS) – Quantity of Real Output Supply at Each Price Level 5 Question 2: Aggregate Demand – Aggregate Supply LR A S Price Level SRAS P AD Y Real Output 6 Question 3: Money Supply and Interest Rates Interest Rate (Price of Money) - Determined in a Market for Loanable Funds Money Demand Curve Shows Relationship between Money Demand and Interest Rates Money Supply – Quantity of Money Fixed by the Federal Reserve 7 Question 3: Money Supply and Interest Rates Interest Rate MS R MD Money 8 Question 5: Scatter Plot Click Insert/Chart/XY (Scatter) then click Next. Be Sure Cursor is on Data Range Window, Highlight Two Data Columns, then Click Next. Add Titles to Chart & Click Next. Check New Sheet and Click Finish. Click a Datum Point on Chart with Right Mouse Key, Add Trendline, & Click Linear. 9 Question 5: Regression Analysis Click Data/Data Analysis on right /Regression & Click OK. On New Window Check Labels Box and Put Cursor on X Range. Highlight X Data Including Label. Put Cursor on Y Range & Highlight Y Data (Including Label), Then Click OK. Click Format/Column/AutoFit to Widen Columns. 10 Question 5: Regression Analysis R Square – Coefficient of Determination – Percent Variation in Rate of Inflation (Y) Accounted for by Variation in Growth Rate of Money (X). X Coefficient Measures Slope of Trend Line. (Positive Sign - Positive Relationship, Negative Sign – Negative Relationship) P-Value Measures Observed Level of Significance. (Probability of Error) 11