* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GENETICS NOTES PART II – OTHER TYPES OF INHERITANCE
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
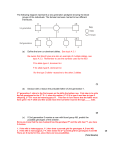
GENETICS NOTES PART II – OTHER TYPES OF INHERITANCE Some patterns of inheritance do not follow Mendel’s laws, and are more complex. Below are some examples of these other types of inheritance. Multiple Alleles = _______________________________________________________________ o For Human blood, there are ______ alleles for blood type _____, _____, and _____ Codominance = _________________________________________________________________ o Example #1: For Human blood, ______ is codominant to the ______ allele, and both ______ and ______ alleles are dominant to the ______ allele The result of the above is the possibility of 4 phenotypes: Phenotypes o Genotypes Example #2: Cattle hair color When both the red allele and white allele are present – both red and white hairs will be seen. Phenotype Red Roan White Genotype Incomplete Dominance = _________________________________________________________ o Example: Snap Dragons (flowers) o Red flower x White flower = all pink flowers!!!!! RR = RW = WW = Practice Problem #1: A type AB person is crossed with a type O person. What are the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of this cross? Type of Inheritance Pattern: _____________________________________________ Parent Genotypes: ___________ X __________ Square: Genotypic Ratio: Phenotypic Ratio: Practice Problem #2: What two genotypes will produce all four phenotypes of blood? Type of Inheritance Pattern: _____________________________________________ Parent Genotypes: ____________ X ______________ Square: Genotypic Ratio: Phenotypic Ratio: Practice Problem #3: A white cow is crossed with a roan cow. What are the possible genotypic and phenotypic ratios? Type of Inheritance Pattern: _____________________________________________ Parent Genotypes: ___________ X __________ Square: Genotypic Ratio: Phenotypic Ratio: Practice Problem #4: If roan cow is crossed with a roan cow, what are the possible genotypic and phenotypic ratios? Type of Inheritance Pattern: _____________________________________________ Parent Genotypes: ___________ X __________ Square: Genotypic Ratio: Phenotypic Ratio: Practice Problem #5: A pink flower is crossed with a pink flower. What are the possible genotypic and phenotypic ratios? Type of Inheritance Pattern: _____________________________________________ Parent Genotypes: ___________ X __________ Square: Genotypic Ratio: Phenotypic Ratio: Practice Problem #6: If pink is crossed with a white flower, what are the possible genotypic and phenotypic ratios? Type of Inheritance Pattern: _____________________________________________ Parent Genotypes: ___________ X __________ Square: Genotypic Ratio: Phenotypic Ratio: II. SEX-LINKED GENES: ________________________________________________________ In humans, the 23rd pair of chromosomes are called the ________________________________ Females are ___________ and males are __________ for this pair. If we cross a male and a female: Genotypic Ratio Phenotypic Ratio Therefore, the _________ determines the sex of the child. Some _________ are carried on the _______ chromosome. When writing genotypes they are written as ___________________. Two examples of genes carried on the X chromosome are ______________ & _______________ Because they are carried on the X chromosome, they are called ____________________ traits. Hemophilia: A disorder when a persons _________________________________________ The X chromosome can carry a ___________allele, written as ________, which codes for __________ blood clotting or a ___________ allele, written as _________ which codes for __________ blood clotting (the hemophilia gene) Female Genotypes Female Phenotypes Male Genotypes Male Phenotypes Color Blindness: A disorder where a person ______________________________________ Female Genotypes Female Phenotypes Male Genotypes Male Phenotypes o As you can see from the above phenotypes and genotypes, in order for ___________ to have hemophilia or color blindness, they only need ________ recessive allele. (b/c they only have _____ ______ chromosome) o Females need ______ recessive alleles to show these traits (b/c they have ____ ____ chromosomes). Therefore, more _________ tend to show sex-linked traits. o Practice Problem #7: Cross a woman that is a carrier (heterozygous) for hemophilia with a male hemophiliac. Parental Genotypes: Mom : _________ Dad: _________ Cross: Genotypic Ratio Phenotypic Ratio Practice Problem #8: Cross a woman that is color blind with a man with normal vision. Parental Genotypes: Mom : ________ Dad: _________ Cross: Genotypic Ratio Phenotypic Ratio