* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BA 353: Operations Management
Inductive probability wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of statistics wikipedia , lookup
Bootstrapping (statistics) wikipedia , lookup
History of statistics wikipedia , lookup
Taylor's law wikipedia , lookup
Resampling (statistics) wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs sampling wikipedia , lookup
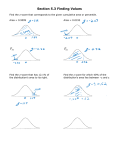
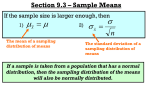
BA 253: Business Statistics Today More Normal More ICE 3 05/12/15 Weds Ch 7: Sampling Distributions Ch 8: Confidence Intervals/Sample Size Normal Distribution (Chapter 6) Review: Annual snowfall at DMR is normally distributed with mean 232 inches and standard deviation 58 inches. Let X = snowfall for this upcoming season. Estimate: a) P(X = 150) = 0% b) P(X ≤ 150) = 8% c) P(150 ≤ X ≤ 300) = 80% d) P(X ≥ 300) = 12% e) Middle 70%, 172 to 292 f) Top 15%. 292 Calculations: 1. 2. 3. 4. Draw picture. Calculate z-score Look up z-score in correct table (may have to subtract from 100% or 50%) Verify answer seems OK z-score Calculations P(1.00 ≤ z ≤ 2.00) Which z-score has 65% to the right of it? Example 1: What is the probability that Apple goes out of business? Example 2: Historically, demand for a product is normally distributed with mean 550 and standard deviation 82. Calculate: a) P(D ≤ 550) and P(D ≥ 550) b) Demand under 450 is considered “low.” What is the probability of low demand? c) Demand between 450 and 600 is “typical.” What is this probability? d) Demand between 600 and 700 is “high.” What is this probability? e) The supplier only has 700 units on hand. If demand is greater than 700, the supplier will have a shortage, which of course, is bad for business. What is the probability that demand is greater than 700? f) In order to avoid shortages (as in part e)), how much inventory should the supplier keep on hand so that shortages only happen during the top 1% highest demand? In other words, to be 99% certain that all demand will be met? Example 3: According to Wikipedia, the GMAT has an average score of 546 with standard deviation 121, plus it follows a bell curve! a) Assume that to get into the MBA program at CU Boulder, you would need to score in the Top 10%. What score would you need to get? b) Assume that you need to be in Top 2% to get into the Michigan MBA program; what score would you need? c) And at Harvard, the Top 0.5%... ↑ Descriptive Statistics: Summarize Data ↑ ↓ Inferential Statistics: Estimate Population from Sample ↓ Chapter 7: Sampling and Sampling Distributions Ex: Collect n data, calculate sample mean = x = point estimate. Use simple random sample. Is x ≈ μ??? That is the question! The approximation gets better as the sample size, n, increases. How is x distributed? In other words, what is the probability distribution of the sample mean? Guess = _________________ Central Limit Theorem For large sample sizes (typically, n ≥ 30), the sample mean x is approximately normally distributed. CLT is true regardless of the original distribution of the data. As n↑, the standard deviation decreases. (That is, x gets closer to μ.) This is why the normal distribution is so common and so important. Show “CLT in Action” Sampling Distribution of x The sample mean, x , has mean μ, standard deviation and is n o Normally distributed if the underlying distribution is Normal. o Approximately Normally Distributed whatever the underlying distribution is if n ≥ 30. o As the sample size increases, n ↑, the sample mean gets closer and closer to the population mean, x ≈ μ. Ex: Normal with mean 100 and sd 20. Do on TI-83. Math, PRB, randNorm(100,20) – try it! 132, 104, 98, 137, 81, etc. How close is your result to 100? Is one data point enough? No. Get 5 numbers, then average. Closer. On Excel, get 30, 100, 1000 numbers and then average. As sample size increases, the approximation gets better.