* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Orbits, Asteroids, and Comets
Scattered disc wikipedia , lookup
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
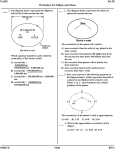
Orbits, Asteroids, and Comets The Geometry of Orbits • Planets revolve in an ellipse around the sun – An ellipse has two fixed points called foci that are on either side of the center of the axis – The sun lies at one focus and is not the center of Earth’s orbit The Geometry of Orbits • If the two foci are located near the ends of the axis, an ellipse is long and narrow • If the foci move closer together, the shape of the ellipse becomes circular Calculating Eccentricity (elongation) of an ellipse Eccentricity = distance between the foci length of the major axis e = d/L Gravity and the Planets • Gravity is the force that holds the planets and other objects in the solar system in their orbits • Any object that orbits another object in space is known as a satellite – Earth is a satellite of the sun – The moon is Earth’s satellite Gravity and the Planets • If a satellite has an elliptical orbit, gravity causes the speed to change – The satellite will move faster when it’s near its primary and slower when it’s farther away Gravity and the Planets • The closer a planet is to the sun, the faster it moves in its orbit – Mercury, the planet closest to the sun, travels about 1.6 times as fast as Earth and 10 times the speed of Pluto Eccentricity • Eccentricity is a number between 0 and 1 that tells you how round or elliptical orbit is. – An eccentricity of 0 means that the orbit is round • Planets have very round orbits – An eccentricity of 1 means that the orbit is elliptical • Comets have very elliptical orbits Kepler’s Planetary Laws of Motion • Used a lifetime of data kept by another astronomer (Brahe) to explain the motion of the planets • Two main ideas: – Objects orbiting the Sun move faster when they are near • a) Does the distance to the center of the Sun stay the same in any orbit? • b) Which orbit has the least variation in distance from the Sun throughout the orbit? Which has the most? • c) Earth’s orbit has an eccentricity of about 0.017. Compare this to the ellipse with the lowest eccentricity that you drew. Why does it make sense to describe Earth’s orbit as “nearly circular”? • d) The Hale-Bopp comet has an eccentricity of 0.9950. How would you describe this orbit? Why does it make sense that we only see this comet every 2,500 years?