* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download chapter 33 (18)
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Balance of trade wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Real bills doctrine wikipedia , lookup
Currency War of 2009–11 wikipedia , lookup
Money supply wikipedia , lookup
Modern Monetary Theory wikipedia , lookup
Interest rate wikipedia , lookup
Currency war wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
Global financial system wikipedia , lookup
Foreign-exchange reserves wikipedia , lookup
International monetary systems wikipedia , lookup
Balance of payments wikipedia , lookup
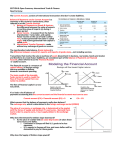
CHAPTER 33 (18) Questions for Thought and Review 2. When someone sends 100 British pounds to a friend in the United States, the transaction will show up in the component of the current account called net transfers, which include foreign aid, gifts, and other payments to individuals not exchanged for goods or services. It will also appear on the capital account as a receipt of foreign currency just like the purchase of a British stock or bond. 4. A capital and financial account deficit means that financial outflows are more than financial inflows. The excess supply of dollars is balanced by a current account surplus, which means Americans are producing more than they are consuming. In the long run, capital account deficits are nice because you are building up holdings of foreign assets, which will provide a future stream of income. 6. In the early 1980s the U.S. government was pursuing tight monetary policy and expansionary fiscal policy. The high interest rate resulted in a strong dollar. Expansionary fiscal policy failed to stimulate domestic demand as export demand fell sharply due to the high dollar. This, accompanied by the high interest rate that had cut investment, drove the economy into a recession with twin deficits, but a strong dollar. 8. It was likely increasing because imports are positively correlated with national income. 10. If Japan ran an expansionary monetary policy, it would increase Japanese imports of U.S. goods and make American goods comparatively more competitive, and thereby decrease the U.S. trade deficit. The U.S. dollar would rise relative to the Japanese yen. 12. Since the effect of monetary policy is to push the exchange rate down in all effects, this will not change the effect presented in the chapter, other than to eliminate the effect through income and replace it with the effect through prices. 14. We would use a combination of purchasing power parity, current exchange rates, and estimates of foreign exchange traders to determine the long-run exchange rate of the Neverback. This combination approach can be justified only by the “that’s all we have to go on” defense. Since no one really knows what the long-run equilibrium exchange rate is, and since that exchange rate can be significantly influenced by other countries’ policies, the result we arrive at could well be wrong. 16. Both fixed and flexible exchange rate systems have advantages and disadvantages. While fixed exchange rates provide international monetary stability and force governments to make adjustments to meet their international problems, they have some disadvantages as well: they can become unfixed, creating enormous instability; and their effect of forcing governments to make adjustments to meet their international problems can be a disadvantage as well as an advantage. Flexible rates provide for orderly incremental adjustment of exchange rates and allow governments to be flexible in conducting domestic monetary and fiscal policies, but also allow speculation to cause large jumps in exchange rates (and, as before, the government flexibility may be a disadvantage too). Given the pluses and minuses of both systems, most policymakers have opted for a policy in between-partially flexible exchange rates. 18. They will sell that currency, which will force the government to use reserves to protect the currency. Once the government runs out of reserves, it may be forced to devalue the currency, making the speculator’s predictions self-fulfilling. 20. He was advocating significant trade restrictions. These trade restrictions would have likely provoked retaliation by our trading partners, hurting international cooperation, and hurting the world economy. 22. The U.S. would want to hold up the value of the dollar to help prevent the surge in import prices that would result from the fall in exchange rates, and to keep foreigners from buying our assets cheaply. Other countries would want a higher value of the dollar in order to keep their goods competitive with U.S. goods. 24. Two disadvantages is loss of independent monetary policy for those countries that adopt the euro and loss of national identity because the country must give up its own currency. Problems and Exercises 2. The graph below shows the fundamental analysis of the supply and demand for British pounds sterling in terms of dollars, and the effect of the following changes: Price of pounds in dollars per pound S0 S1 P1 P0 D1 P2 D0 Q0 Q1 Q2 Quantity of pounds a. b. c. d. A rise in the UK price level causes foreign goods to become cheaper. British demand for foreign currencies will tend to increase, and foreign demand for pounds will tend to decrease. Thus supply of pounds shifts outward from S0 to S1 and the demand for the pound shifts inward from D1 to D0. The exchange rate value of the pound falls from P1 to P2. A reduction in U.S. tariffs would tend to shift the demand for pounds to the right from D0 to D1 as Americans buy more imports from the UK. If supply is at S1, the exchange rate value of the pound rises from P2 to P0. A boom in the UK economy means an increase in its income, causing an increased demand for imports and an increase in the demand for the foreign currency to buy those imports, thus resulting in an increase in the supply of pounds. (This may also set off an expectations effect.) Thus, the supply of pounds shifts outward from S0 to S1. If demand is at D0, the exchange rate value of the pound falls from P0 to P2. If interest rates in the UK rise, there will be an increased demand for its assets, so the demand for pounds will increase from D0 to D1 and the supply of pounds will decrease from S1 to S0 as fewer British investors sell their pounds to buy foreign assets. The exchange rate value of the pound rises from P2 to P1. 4. a. Supplier; b. Supplier; c. Supplier; d. Demander; e. Demander; f. Demander. 6. a. b. c. d. e. Current account Current account Current and capital and financial accounts Current account Capital and financial account 8. a. If foreigners start believing that there is an increased risk of default, they will require a higher premium to buy U.S. bonds. That is, they will offer a lower price to buy them (demand for U.S. bonds will shift to the left). As this happens, bond prices will fall and interest rates, which move in the opposite direction from their prices, will rise. The value of the dollar will fall as a result of the lower demand for bonds (foreigners will not be purchasing as many dollars). That is, the demand for dollars will also decline, lowering the value of the dollar. Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing. This hurts in the short run by reducing aggregate spending and crowding out private investment, a source of long-term growth for the U.S. economy. A lower value of the dollar may increase the competitiveness of U.S. goods in the global economy, but it also makes imports to the United States more expensive, which, in addition to hurting individuals, may hurt businesses who use imports as intermediate goods in their production processes. b. Web Questions 2. The answer to this question depends on the country chosen. We chose Brazil. a. The Brazilian currency is the real. b. The currency remained virtually unchanged from 2004 to 2005. c. Brazil has gotten inflation under control. Unemployment is expected to decline as the economy continues to grow. Fiscal spending is under control. The economy appears to be in good health, which may be contributing to a stable currency.