* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory System summary
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
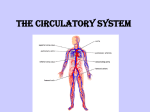
The Circulatory System The circulatory system serves as the transport system of the body. It moves needed nutrients like sugar, oxygen and amino acids to the body cells, while transporting waste materials like carbon dioxide, urea and heat so they can be removed from the body. The circulatory system also connects to each of the other body systems for chemical communication, by transporting hormones and other chemical signals to specific cells. The circulatory system includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The Heart. The heart is located near the center of the chest. The thick layer of muscle that forms the heart’s walls is called the myocardium. Contractions of the myocardium pump blood through the body. A contraction begins in a group of cells called the pacemaker. The impulse travels through the rest of the heart, causing it to contract. The heart is divided into right and left halves by the septum. The septum prevents the mixing of oxygen-poor and oxygen-rich blood. Each half of the heart has two chambers. The upper two chambers, or atria (singular: atrium), receive blood entering the heart. The lower two chambers, or ventricles, pump blood out of the heart. Flaps called valves lie between chambers. The valves keep blood from flowing backward in the heart. Pumping of the heart produces pressure. Blood pressure is the force of the blood on artery walls. Blood pressure moves blood through the body. The human body has a double-loop circulatory system. Blood moves through two basic pathways. Blood Vessels. As blood flows through the circulatory system, it moves through three types of vessels. • Arteries are large vessels that carry blood away from the heart. They have thick muscular walls to maintain blood pressure. Your pulse is felt in your arteries. • From arteries, blood flows into capillaries, the smallest vessels. In capillaries, materials such as carbon dioxide, oxygen and nutrients are exchanged between the blood and body tissues. Capillaries have the thinnest walls to allow diffusion in and out of the blood • From the capillaries, blood flows into veins. Veins carry blood to the heart. Large veins have valve, one way doors, that keep blood moving forward. Cardiovascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis and high blood pressure, are diseases of the circulatory system. Atherosclerosis is a condition in which fatty deposits build up in arteries. Both high blood pressure and atherosclerosis make the heart work harder. Both can lead to heart attack and stroke. You can prevent these diseases by exercising regularly, eating a low-fat diet, controlling your weight, and not smoking. 37–2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Blood is a type of connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. Blood regulates body • In pulmonary circulation, oxygen-poor blood flows from the heart to the lungs. In the temperature and pH. It protects the body from lungs, carbon dioxide is released from the blood and oxygen is absorbed. This oxygendisease. In addition, rich blood then returns back to the heart. blood can form clots to repair damaged blood vessels. • In systemic circulation, oxygen-rich blood is pumped throughout the body. In the Just over half of blood is a watery fluid called plasma. Proteins in plasma help to clot body, oxygen is delivered to body cells and carbon dioxide is picked up by the blood. blood and fight infections. The cellular portion of blood is made up of red blood cells, This oxygen-poor blood returns to the heart. white blood cells, and platelets. • Red blood cells carry oxygen. A protein called hemoglobin in red blood cells binds to oxygen and carries it throughout the body. • White blood cells guard against infection, fight parasites, and attack bacteria. There are many types of white blood cells. White blood cells called lymphocytes make antibodies. Antibodies are proteins that help fight infection. • Blood clotting is made possible by plasma proteins and platelets. Platelets are cell fragments. Platelets cluster around a wound and release proteins called clotting factors, leading to the formation of a clot. As blood circulates, some fluid called lymph leaks from the blood into surrounding tissues. The lymphatic system collects the fluid that is lost by the blood and returns it back to the circulatory system. The lymphatic system is a network of lymph vessels, lymph nodes, and organs. Lymph nodes act as filters and produce certain white blood cells that protect body cells. The lymphatic system also helps absorb nutrients and fight infection. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. What is the main purpose of the circulatory system? What are the three parts of the circulatory system? What is the septum and what does it do? What are the two upper chambers (rooms) of the heart called? What are the two lower chambers of the heart? Where are the vales found and what do they do? What is happening during the pulmonary circulation? What is happening during systemic circulation? Where does blood flow in the arteries? Where are gasses and nutrients moved into or out of the blood? What takes blood back to the heart? What causes arteriosclerosis? How can arteriosclerosis be prevented? What are two different jobs of the blood? What is the watery part of blood called? What do red blood cells do? What does the oxygen stick to in the red blood cells? What do white blood cells do? How does the blood clot? How does the lymphatic system and the circulatory system work together? 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. Match the following terms to the phrase. Some may have more than one answer. Answers may be used more than once. Artery Vein, Capillary Takes materials to the heart Which is the smallest blood vessel Where gas exchange occurs Has blood circulating through it. Takes materials away from the heart Which one is always in the middle of the other two Can have a buildup of fatty deposits 28. Compare and contrast Red blood cells and White blood cells Red White 29. Below are the parts of the heart. Put them in order of how the blood flows, starting at the right atrium: Right atrium left atrium lungs body Pulmonary artery Left ventricle Pulmonary vein Right ventricle Aorta Organs and muscles A Right Atrium B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. Determine if the following statements are true or false. If true, write true. If false, write a new sentence to make it true. 30. Hemoglobin is found in white blood cells, to carry oxygen. 31. The septum separates the atrium from the ventricles 32. Food leaves the blood and enters cells through the capillaries 33. Veins take blood away from the heart. 34. Exercise and a good diet can help to prevent Atherosclerosis. 35. The pulmonary circulation takes blood to the brain. 36. Oxygen rich blood travels to the lungs in the pulmonary artery 37. Valves keep the blood flowing in one direction. 38. The watery fluid in the blood is called platelets 39. Draw a diagram that shows what the circulatory system does. 1. In the diagram below, a. Color the Arteries – Red, Capillaries – Green, Veins – Blue b. Draw arrows to show how the blood moves through the heart and blood vessels. Each blood vessel should have an arrow. c. Label the Right Atrium (RA), Left Atrium (LA), Right Ventricle (RV), Left Ventricle ( LV)