* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Liver Functions Part II
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
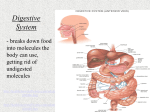
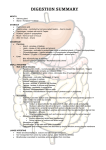
Liver Functions Part II 3E1 From where we left off… In the small intestines • Complete digestion occurs in the small intestines • End products (glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, glycerol) diffuse into the blood vessels lining the small intestines. • This process is called Absorption. Some animal samples • Guess what is the organ shown! • From which animal? Adaptation of the small intestine for absorption Structure of small intestine What do you see in the intestinal walls? How do the folds and villi help in absorption? • The presence of folds and villi in the intestinal wall increase surface area More adaptations from the small intestine • the epithelial cell of the intestinal wall • One-celled thick epithelial wall and microvilli further increases surface area The small intestines • What makes the small intestines suitable for Absorption? 2) Villi and microvilli 1) Elongated ileum, Inner surface of the ileum is folded These features provide large surface area:vol for absorption The small intestines • What makes the small intestines suitable for Absorption? 3) Many blood vessels lining the small intestines Absorption • Absorption occurs by: – Diffusion – Active transport • After absorption, Glucose and amino acids enter the blood capilliaries Glycerol and fatty acids enter the lacteals How does absorption takes place in the intestines Absorption of fatty acids and glycerol • Glycerol and fatty acids diffuse into the epithelium where they combined to form minute fat globules and enters the lacteals • Fat globules mix with lymph in the lacteals to form chyle • Liver is not involved * Assimilation and function of the liver Overview Role of Digestion Large Intestine & Others Mouth & Oesophagus Gall Bladder &Pancreas Stomach Small Intestine Overview – 4 Stages Ingestion Assimilation Digestion Absorption Lesson objectives: • • Describe the fate of glucose, amino acids and fats in the blood that leaves the intestines, after a meal. Describe the 5 major roles that the liver plays in the human body – – – – – Regulation of blood glucose concentration Deamination of amino acids Production of bile Detoxication Iron storage Fate of glucose and amino acids Transport and utilization of absorbed foods In the Liver! Types of absorbed food products Glucose Amino acids Fats From the small intestines to the liver! How?? Connected by a vein called Hepatic Portal Vein! Guess which part the vein connects to the intestine? B C D A Carbohydrate metabolism Hepatic portal vein transports sugars like glucose from the intestines to the liver Question! Requires only 3 glucose molecules for breathing Receives 5 glucose molecules from the intestines how many molecules of glucose do you think the liver would transport to the lungs? Requires only 3 glucose molecules for breathing Receives 5 glucose molecules from the intestines Liver in Glucose metabolism Hepatic portal vein Carbohydrate metabolism In the liver…. 1. Some glucose carried in the blood to be distributed to the rest of the body - Tissue respiration Insulin and glucagon In the liver…. -Glucose (excess) Glycogen (stored) Hormone : Insulin - If the glucose level is too low in the blood Glycogen (stored) Glucose Hormone: Glucagon What about the amino acids absorbed by the small intestines? Similar route as sugars: Intestines hepatic portal vein liver general blood circulation Liver in Protein metabolism Hepatic portal vein Amino acid metabolism Fate of amino acids •Converted into protoplasm •Used for growth & repair of wornout parts •Formation of enzymes & hormones •Excess amino acids cannot be stored : Deamination Deamination H O H | || —N— —C— C—OH | H R Amino group Carbon residue Ammonia (toxic) glucose Urea (non-toxic) glycogen Fat metabolism (Liver not involved) Intestines lacteal lymphatic vessels blood rest of the body Fate of Fats • maintenance of cell membranes •Production of hormones • Excess fats stored in adipose tissues When glucose supply is low, fats will be oxidised in the liver to provide energy Summary: 5 major roles that the liver plays – Regulation of blood glucose concentration – Deamination of amino acids – Iron storage – Production of bile – Detoxication True/False • Liver is part of the alimentary canal True/False • Carbohydrates are digested in the liver True/False • Excess amino acids are deaminated True/False • Fats are absorbed in the liver and transport to other parts of the body for usage.