* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Standard solar model wikipedia , lookup
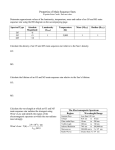
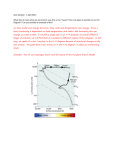
Name ______________________________________Date________________________Hr_____________ Study Guide You should be able to: Define and label the parts of the sun including: core (4), corona (7), solar wind (6), chromosphere (2), photosphere (1), solar flare(8), prominence (5), and sunspot (3). Explain the H-R diagram and the where each type of star lies on it. Classifies stars according to their absolute magnitude, temperature, and luminosity State what part of its lifecycle our sun is in. Main sequence State magnitudes of stars from the H-R diagram. White dwarfs, main sequence, giants, supergiants (be able to use the H-R diagram to label and classify) List the spectral classes for stars in order. O,B,A,F,G,K,M State the name and shape of our galaxy. The Milky Way – it is spiral shaped Describe the nuclear fusion reaction that takes place in the sun and where it takes place. Takes place in the core – hydrogen is fused into helium, reactions generate energy in the form of heat and light Describe the rotation of the sun. Sun turns on its axis from west to east like the Earth Rotation is fastest at the equator (about 25 days) Rotation is slowest at the poles (about 35 days) Uneven rotation may account for violent solar activity Describe the lifecycle of an average star. See notes Describe the lifecycle of a massive star. See notes Describe each stage of a star’s life cycle. Nebula - the cloud of gas and dust from which a star forms Giant - helium is being fused into carbon and the star is now brighter but cooler Supernova - violent explosion of a massive star when the core collapses causing the outer layers to blow away main sequence star - as soon as fusion starts, the star is in this stage fusing hydrogen into helium Protostar – cloud of gas and dust that is now spinning Supergiant – similar to a giant but does not stop with carbon fusion it continues fusion to the dead end element Black hole - spinning causes the core to collapse allowing nothing to escape Neutron star - the left over core of a supernova that begins to rotate very fast Explain the Doppler shift in terms of color and direction. If an object is moving away from us, the color spectra will shift toward red Red shift and blue shift are referred to as Doppler shifts and are named after Christian Doppler Explain sunspot cycles. They last 11 years Sunpot max = most active outbursts for about 4 years Min = least active with minimal spots There may be as many as 300 at one time or none at all List and describe each layer of the sun. Core Chromosphere Photosphere Radiation zone Corona Convection zone List and describe surface features of the sun. Granulation – bright spots that are the tops of hot gas currents from the convection zone Sunspots – dark, cool spots on the photosphere; magnetic storms about the size of Earth Prominences – fiery arch – occur when charged particles flow between 2 sunspots Solar flare – sudden explosive outburst of light that occurs when 2 sunspots come together and the charged particles flowing between them explode outward Describe the electromagnetic spectrum and which wavelengths are visible to the human eye. Series of color bands broken up and arranged in the order of wavelengths From longest to shortest: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet Identify the relationship between wavelength and energy content (traveling direction). Longer wavelength = less energy Shorter wavelength = greater energy Complete the following diagram Complete the following diagram Top arrow: wavelength increasing Bottom: Frequency increasing (high frequency/energy = short wavelength; low frequency/energy = long wavelength)