* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam 3 Review - Iowa State University
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
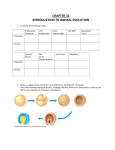
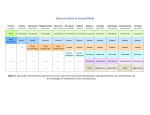
Worksheet: Exam Review 3 Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Kelly Course: Biol 211 (1) Instructor: Roe Date: 02/24/14 1.) What is the correct sequence of events during an animal's early development 1. gastrulation 2.metamorphosis 3. fertilization 4. cleavage A) 4-3-2-1 B) 4-3-1-2 C) 3-2-4-1 D) 3-4-2-1 E) 3-4-1-2 2.) The fate of the blastopore distinguishes between Protostomes in which it becomes the___________, and Deuterostomes in which it becomes the___________. A) mouth, coelom B) anus, mouth C) coelom, archenteron D) mouth, anus E) none of the above 3.) Many of the Phyla existing today first appear in the fossil record over 500 mya during the . A) Ediacarian Period B) Cretaceous Period C) Permian Period D) Carbiniferous Period E) Cambrian Period 4.) Cephalization is most closely associated with which of the following? A) a sessile existence B) concentration of sensory structures at the anterior end C) a vertebral column D) a predatory lifestyle E) a sedentary lifestyle 5.) Which cells in a sponge are primarily responsible for trapping food particles? A) choanocytes B) pore cells C) spicules D) amebocytes E) epidermal cells 6.) Sponges differ from all other animals in that they: A) lack cells B) are sessile C) display radial symmetry D) are hermaphrodites E) lack true tissues 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 [email protected] http://www.si.iastate.edu 7.) Acoelomates are characterized by: A) the absence of a brain B) the absence of mesoderm C) a coelom not completely lined with mesoderm D) a solid body without a cavity surrounding the internal organs E) dueterostome pattern of development 8.) Generally, parasitic flatworms belong to which class(es) A) Cestoda. B) Trematoda. C) Turbellaria. D) Monongena. E) A, B, & D. 9.) Cnidarians are characterized by which of the following characters. 1. gatsrovascular cavity 2. cnidocytes 3. medusa stage 4. polyp stage 5. a pseudocoelom A) 1&4 B) 2&4 C) 1,2,3, & 4 D) 1, 3, & 4 E) All five 10.) The Class Anthozoa includes anemones and A) corals and hydrozoans B) jelly fish C) box jellies D) corals E) only anemones 11.) Blood flukes belong to which Class? A) Turbellaria B) Trematoda C) Monongena D) Cestoda E) Gastropoda 12.) Molluscs, being the coolest group of all organisms, includes all of the following except A) roundworms B) clams C) octopuses D) snails E) chitons 13.) The terminal (or final) host in the life cycle of a parasitic flatworm is at the stage when _______ occurs in the parasite. A) death B) metamorphosis C) sexual reproduction D) growth E) cyst formation 14.) Which group of Annelid have parapodia? A) Oligochaetea B) Polychaeta C) Hirudinea D) all of the above 15.) Humans usually acquire trichinosis by A) being bitten by a mosquito B) having unprotected sex with an infected partner C) not practicing good hygene D) eating undercooked pork 16.) Which of the following are characteristics of arthropods? 1. protostome development 2. bilateral symmetry 3. a pseudocoelom 4. three embryonic germ layers 5. a closed circulatory system A) 1 & 2. B) 1, 2, & 4 C) 2&3 D) 2, 3, and 5 E) 3, 4, & 5 17.) Among the invertebrates, Arthropoda is unique in that is has members that possess ___________. A) a cuticle B) a ventral nerve cord C) wings D) segmented bodies E) open circulatory system 18.) Nematodes can shed their exoskeleton. Therefore they belong to the Ecdysozoa along with which other group? A) Arthropoda B) Oligochaeta C) Dueterostomes D) Chitons 19.) The pharyngeal slits of chordates are thought to have been used for ___________first and ______________ in more derived chordates. A) jaw, part of the inner ear B) filter feeding, respiration C) Digestive system, reproduction D) locomotion, feeding 20.) Echinodermata includes all of the following except. A) Crinoidea B) Bryzoa C) Asteroidea D) Echinoidea E) Holothuroidea 21.) Which of the following descriptions is incorrect A) Echinodermata – bilateral symmetry as larvae, coelom present B) Nematoda – roundworms, pseudocoelomate C) Cnidaria – radial symmetry, polyp and medusa body forms D) Platyhelminthes – flatworms, gastrovascular cavity, acoelomate E) Calcarea – gastrovascular cavity, coelom present 22.) Which of the following is a shared characteristic of all chordates? A) scales B) jaws C) vertebrae D) dorsal hollow nerve cord E) a four chambered heart 23.) Lamprey differ from hagfishes in that they A) lack jaws B) have a cranium C) have pharyngeal slits D) have a notochord E) have a vertebral column 24.) According to one hypothesis, the jaws of vertebrates is derived from the A) scales B) skeletal rods that supported the pharyngeal slits C) vertebrae D) the cranium 25) The earliest mineralized structures in vertebrates is associated with A) reproduction B) locomotion C) feeding D) respiration E) defense 26.) Why is the amniotic egg considered such an important evolutionary breakthrough? A) Without amniotic eggs there would be no Dennys B) The shell allows incubation of eggs in a terrestrial environment C) It prolongs embryonic development D) It permits internal fertilization to be replaced by external fertilization 27.) To what structure are the scales of chondrichthyans most closely related? A) osteicthyan scales B) reptilan scales C) mammalian fur D) bird scales E) chondricthyan teeth EXTRA CREDIT 28.) The terms: egg-laying, pouched, and placental refer to which group? A) amphibians B) birds C) marsupials D) mammals E) reptiles 29.) Using the current hypotheses of chordate evolution. what is the sequence (from earliest to latest) in which the following structures arose? 1. amniotic egg 2. paired fins 3. jaws 4. swim bladder 5. four-chambered heart A) 2,3,4,1,5 B) 3,2,4,1,5 C) 3,2,1,4,5 D) 2,1,4,3,5 E) 2,4,3,1,5 Early Embryonic Deveopment for a triploblastic organism: Label the five steps What stage can you tell this is going to be a triploblast? Where is the blastopore? How many layers of tissue are present? Can you label them? What is the final host(s)? What are the intermediate hosts? Where does sexual reproduction occur? What is the body plan of a parasitic flatworm in comparison to a free living flatworm? Special Things? Classes Digestive Tract (GC, Complete, Other?) Circulatory System (Open or Closed?) Body Cavity (0, A, P, or C?) Blastopore Fate (P or D?) Tissue Layers (0,2, or 3?) Symmetry Commonly known as: Calcarea and Silacea Cnidaria Platyhelmint hes Rotifers Ectoprocts Brachipods Mollusca Annelida Nematodes Arthropds Echinoderms Chordates