* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 16.3 part 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
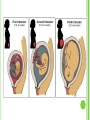
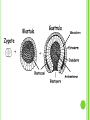
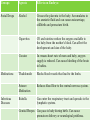
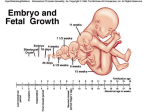
INCOMPATIBLE BLOOD http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/797150overview FASD PREMATURE BIRTH http://www.marchofdimes.com/baby/long-termhealth-effects-of-premature-birth.aspx# http://preemies.about.com/od/preemiehealthprobl ems/a/longtermimpact.htm CHAPTER 16 Section 16.3 -2 Embryonic and Fetal Development MORPHOGENESIS 1. 2. The development of an organism or part of an organism. Involves 2 process: Growth – increase in size. Differentiation – cell specialization. TRIMESTERS The nine months of pregnancy are divided into 3 trimesters. First Trimester – from conception until the end of the third month. Second Trimester – from the fourth month to the end of the sixth month. Third Trimester – from the seventh month until birth. FIRST TRIMESTER (1-12 WEEKS) Conception until the end of the third month. Fertilization occurs. Inner cells of the blastocyst have reorganized into a flattened disk made up or 2 layers. Later this 2 layer structure turns into a 3 three layered structure called a gastrula, this process is called gastrulation. Mesoderm The three layers of the gastrula are the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. Each of these layers will give rise to specific organs and structures. Ectoderm (outer layer) gives rise to: Skin, hair, finger nails, sweat glands Nervous system, brain Lens, retina, cornea Inner ear, cochlea, semicircular canals Mesoderm (middle layer) gives rise to: Muscles Blood vessels and blood Kidneys, reproductive structures Connective tissue, cartilage, bone Endoderm (inner layer) gives rise to: Liver, pancreas, thyroid, parathyroid Urinary bladder Lining of digestive system Lining of respiratory tract By the end of the first month, the embryo is about 1 cm long. Many of the important organs and systems are beginning to develop. The 4 chambered heart has formed, brain is visible and limb buds with tiny fingers and toes have developed. By the ninth week the embryo is known as a fetus. Arms and legs begin to move and a sucking reflex is evident. SECOND TRIMESTER (14 – 24 WEEKS) At the beginning the fetus is about 8 cm long. All organs have formed, but not quite fully developed. Organ development continues and fetus increases in size. Movement of fetus occurs. Soft hair covers the entire body. By the sixth month eyelids and eyelashed form. Bone cells replace cartilage that originally formed the skeleton. At the end the fetus is about 34 cm long. THIRD TRIMESTER (25 – 40 WEEKS) Baby grows rapidly. All organs are fully developed but must enlarge. Mass must increase. At the end before birth, the infant is approximately 51 cm long. HUMAN SEX DETERMINATION The sex of the baby is determined genetically. Females have two ‘X’ chromosomes. Males have an ‘X’ and a ‘Y’ chromosome. The gene for sex determination is found on the Y chromosome and is called the SRY (sex-determining-region of the Y chromosome). If the Y chromosome is present then the SRY gene is also present. All fetuses are identical until the sixth or seventh week. At this time if the SRY is present it will initiate the formation of testes in males which produce testosterone and cause the male characteristics to develop. If the SRY is absent female characteristics will develop. The balance of hormones in the bloodstream is extremely important during fetal development. Males and females produce both estrogen and testosterone. Males have more testosterone, and females have more estrogen but the other hormones are present as well. If there is an abundance of male sex hormones during fetal development the fetus may have the outward characteristics of a male but have female DNA or vice versa. (Hermaphrodites) TERATOGENS Teratogen - Any chemical, infectious disease, or environmental agent that might interfere with the normal development of a fetus or embryo. Ex. Social Drugs Medications Diseases Alcohol Cigarettes Cocaine Thalidomide Seizure medication Rubella Herpes Groups Agents Effects on Embryo Social Drugs Alcohol Crosses the placenta to the baby. Accumulates in the amniotic fluid and can causes miscarriage, stillbirth and premature birth. Cigarettes CO and nicotine reduce the oxygen available to the baby from the mother’s blood. Can affect the development and size of the baby. Cocaine In creases heart rate of mom and baby, oxygen supply is reduced. Can cause bleeding of the brain in babies. Thalidomide Blocks blood vessels that lead to the limbs. Seizure Medication Reduces blood flow to the central nervous system. Rubella Can enter the respiratory tract and spreads to the lymphatic system. Medications Infectious Diseases Genital Herpes Can pass to baby during birth. Can cause premature delivery or neurological problems. WHAT’S NEXT? Do: Study booklet 16.3 part 1& 2 Monday 16.3 part 2 Tuesday o Quiz on 16.3 part 1& 2 & 16.3 part 3 Wednesday o Health unit demos & concept map Thursday Review… jeopardy? Friday Unit B Exam: Reproduction & Development